Top 10 Machines for the Electronics Industry Manufacturers
Electronic manufacturing is a key driver of the global economy. It relies on precision, efficiency, and innovation. Manufacturers use specialized machines to produce everything from consumer gadgets to complex industrial systems. These machines are vital for ensuring quality, scalability, and cost-effectiveness. This article explores ten essential machines used in electronics manufacturing.
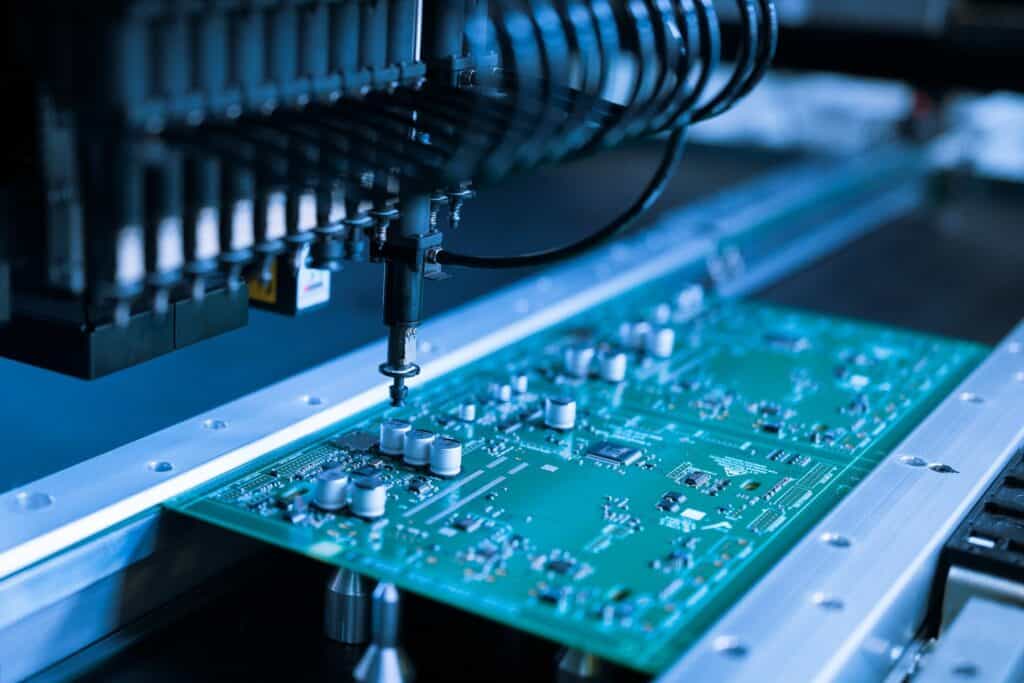
1. Surface Mount Technology (SMT) Pick-and-Place Machines
SMT pick-and-place machines are central to electronic assembly. They place surface mount devices (SMDs) onto printed circuit boards (PCBs) with high precision. These machines use vacuum nozzles to pick components from feeders. Advanced vision systems calibrate each part's position for placement accuracy. High-speed models place over 100,000 components per hour. They handle various sizes, from tiny 0201 packages to large connectors. Dual-lane systems process multiple PCBs at once to maximize output.
2. Reflow Soldering Ovens
Reflow ovens create permanent solder joints on PCBs. They melt solder paste to attach SMD components. The process has four stages: preheat, soak, reflow, and cooling. The preheat stage raises the temperature gradually. The soak stage ensures the PCB heats evenly. The reflow stage melts the solder. The cooling stage solidifies the joints. Many ovens use a nitrogen atmosphere to reduce oxidation. Multiple heating zones allow precise temperature control.
3. Automated Optical Inspection (AOI) Systems
AOI systems automatically inspect PCBs for defects. They use high-resolution cameras and smart algorithms. These systems check solder joints, component placement, polarity, and markings. They compare captured images to a pre-programmed standard. They find defects like solder bridges, missing parts, and misalignments. 3D AOI systems also measure solder volume. They integrate into production lines for real-time feedback. This reduces the need for manual inspection and improves consistency.
4. Selective Soldering Systems
Selective soldering systems solder through-hole components. They apply molten solder to specific areas on a PCB. A programmed nozzle targets individual components. Local preheating prevents thermal shock. Nitrogen coverage is common to reduce oxidation. These systems work well for mixed-technology boards with both SMD and through-hole parts. They offer more consistency than manual soldering.
5. Printed Circuit Board (PCB) Manufacturing Equipment
PCB manufacturing uses several machines to produce bare boards. Photoplotters transfer circuit patterns onto copper-clad laminates. Etching machines use chemicals to remove excess copper. Drilling machines create holes and vias. Plating equipment deposits copper to form conductive pathways. Lamination presses bond multilayer boards under heat and pressure. AOI systems check for shorts, opens, and misalignments. This equipment ensures PCBs meet design specifications.
6. Injection Molding Machines
Injection molding machines produce plastic parts. They make electronic enclosures, connectors, and components. These machines inject molten plastic into a mold cavity. They use materials like ABS, PC, and nylon. Precise control of temperature and pressure ensures part quality. Robots often remove finished parts from the mold. This process is ideal for high-volume production with tight tolerances.
7. Wire Harness Assembly Machines
Wire harness machines automate cable production. They cut, strip, and crimp wires. They handle various wire gauges and types. Crimping units attach terminals to wire ends. Testing systems check for continuity and insulation resistance. These machines assemble complex harnesses for cars, planes, and industrial electronics. Software allows quick changeovers between designs. Automation reduces errors and increases output.
8. X-Ray Inspection Systems
X-ray systems provide non-destructive internal inspection. They find hidden defects in solder joints and packages. They inspect BGAs, CSPs, and QFNs under the component. Computed tomography (CT) creates 3D models for detailed analysis. Software automatically flags defects based on set criteria. X-ray is critical for medical, aerospace, and automotive electronics. It ensures solder joint integrity.
9. Semiconductor Fabrication Equipment
Semiconductor equipment makes integrated circuits (ICs). Photolithography machines transfer circuit patterns onto silicon wafers. Etchers remove material to form transistors. Chemical Mechanical Polishing (CMP) machines flatten wafer surfaces. Ion implantation changes the electrical properties of silicon. Deposition systems add thin layers of material. These machines operate in cleanrooms to prevent contamination. They are essential for producing microprocessors and memory chips.
10. 3D Printing and Rapid Prototyping Machines
3D printers build parts layer by layer from digital models. Technologies like SLA and FDM create parts with complex geometries. They produce prototypes, jigs, and fixtures. Some materials are conductive for printing simple circuits. This allows for fast prototyping and lowers development costs. 3D printing supports small-batch production without traditional tooling.




