Introduction
This article provides comprehensive information about metal Stamping.
Continue reading to explore topics including:
- What is metal stamping?
- Types of metal stamping operations
- Capabilities of metal stampers
- Parts and types of metal stamping dies
- metals used in metal stamping
- Advantages and disadvantages of metal stamping
- And more...

Chapter 1: What is metal Stamping?
metal stamping is a cold-forming process that converts metal sheets or coils into specific shapes. This method uses specialized tooling where a punch applies force to reshape the metal sheet. With sufficient pressure, the process can cut or form the sheet into precise, pre-designed configurations.
The process begins with tooling creation using CAD and CAM technologies. The tooling is meticulously designed to ensure each punch, bend, or cut achieves the required precision. CAD models often feature intricate details, with complex tooling composed of multiple components. once prepared, various methods can produce the final part.
metal stamping techniques typically fall into three categories: progressive, fourslide, and deep draw stamping. Progressive die stamping uses multiple stations, each performing a distinct operation. Fourslide stamping employs four simultaneous tools to shape the workpiece. Deep draw stamping pulls the workpiece into a punch for forming. Each method offers unique advantages for specific industrial applications.
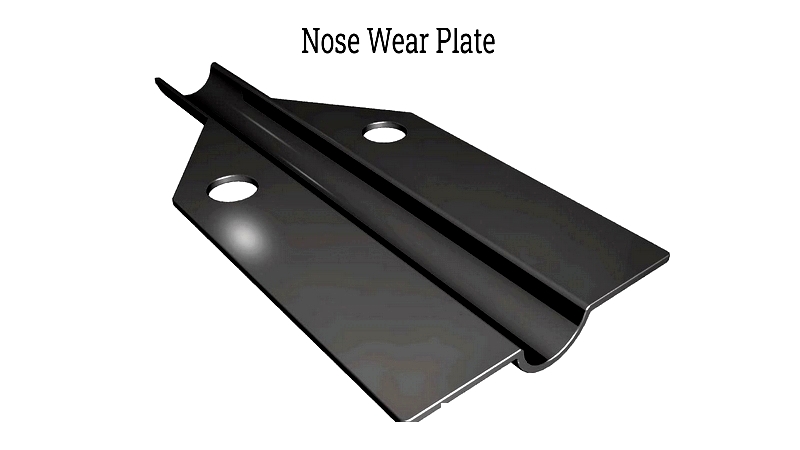

metal stampers are versatile machines capable of performing various cutting and forming operations. They can integrate multiple steps into a single tooling method, often completing these in one stroke. Additionally, they can process multiple parts simultaneously. Their automation and control features benefit fabricators by increasing production speed, reducing labor costs, and improving part quality and consistency. With precise tooling, stampers can produce components with complex designs.
These machines manufacture diverse products, from simple items like washers and springs to sophisticated components for engines and automotive parts. Stamped metal products serve numerous industries and end users.

Chapter 2: What are the Different Types of metal Stamping Machines?
Various metal stamping machines cater to specific manufacturing needs and applications. Selecting the right equipment depends on production volume, material type, required tolerances, and component complexity. Understanding each machine's capabilities is crucial for achieving optimal efficiency, quality, and cost-effectiveness. Below are the most common metal stamping presses:
Mechanical Presses
Commonly used for blanking, punching, and forming, mechanical presses employ a crankshaft and flywheel system to generate consistent force. Known for high-speed performance and precision, they're ideal for mass-producing sheet metal and automotive components.
Hydraulic Presses
Using hydraulic cylinders, these presses deliver adjustable force suitable for thick materials, deep drawing, and complex dies. Their versatility makes them popular in aerospace and heavy machinery manufacturing.
Servo Presses
Equipped with servo motors, these advanced presses offer precise control over speed and position. Their programmable features make them suitable for precision stamping in electronics and automotive industries.
Progressive Die Stamping Presses
Designed for high-volume production, these presses use multi-station dies to perform sequential operations. They maximize material utilization and reduce cycle times for small to medium parts.
Transfer Presses
These handle complex operations requiring multiple forming steps. An automated transfer mechanism moves workpieces between stations, making them ideal for large structural components.
Fine Blanking Presses
Specialized for precision parts with tight tolerances, these presses minimize secondary finishing. They're commonly used for automotive safety components and medical devices.
Stamping Punch Presses
Versatile machines for blanking, piercing, and embossing. Available in mechanical and hydraulic versions, they suit both prototyping and volume production.
Turret Punch Presses
Featuring rotary turrets with multiple tools, these CNC presses excel at sheet metal fabrication. They're ideal for producing enclosures and brackets in electronics manufacturing.
Hot Stamping Machines
Using heat and pressure, these machines apply foil or pigment for decorative effects. They're valued for durable finishes in automotive trim and appliance accents.
Coining Presses
Generating immense pressure, these produce crisp, detailed designs for coins and precision components. They're essential for minting and decorative applications.
Choosing the Right Machine: Consider production needs, material properties, and precision requirements. Consult manufacturers for tailored solutions. For more information, explore our stamping services or contact our technical team.
Chapter 3: What are the types of metal stamping operations?
metal stamping operations involve shaping, cutting, or forming metal using stamping machines and dies. These processes are fundamental for producing components across industries. Key steps include design, tooling development, material feeding, stamping, quality control, and post-processing. Understanding these operations helps optimize efficiency and quality.
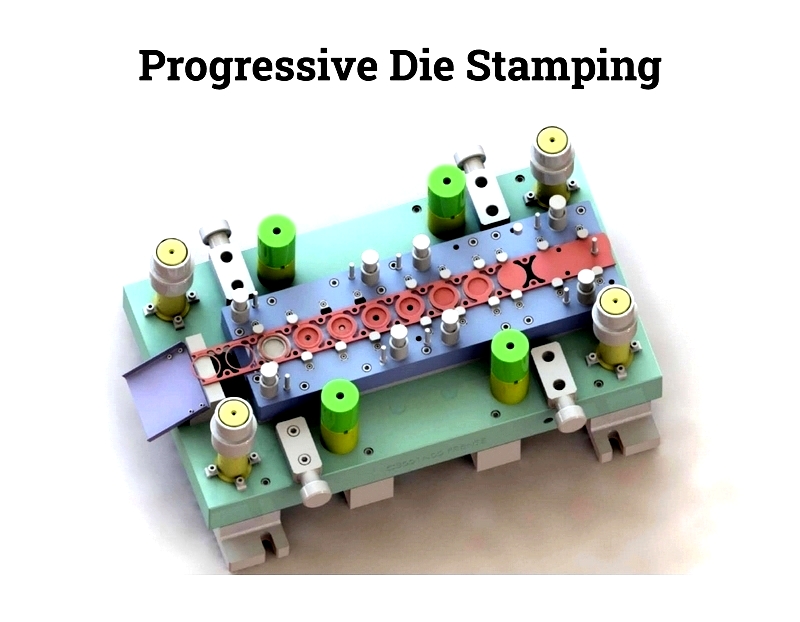
Progressive Die Stamping
This high-volume process feeds continuous metal strips through multi-station dies. Each station performs specific operations like blanking or bending. The finished part separates at the final stage, ensuring high productivity with minimal waste.
Advantages: Fast production of complex parts, consistent repeatability, and reduced costs. Best for shallow forms rather than deep draws.
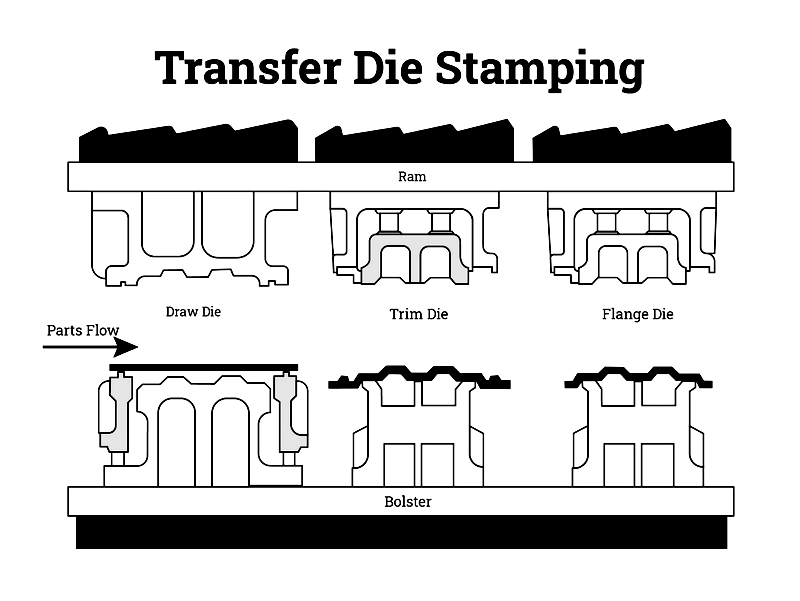
Transfer Die Stamping
This method blanks workpieces before transferring them between stations. Ideal for deep drawing and large components like automotive panels, it enables multiple forming steps without distortion.
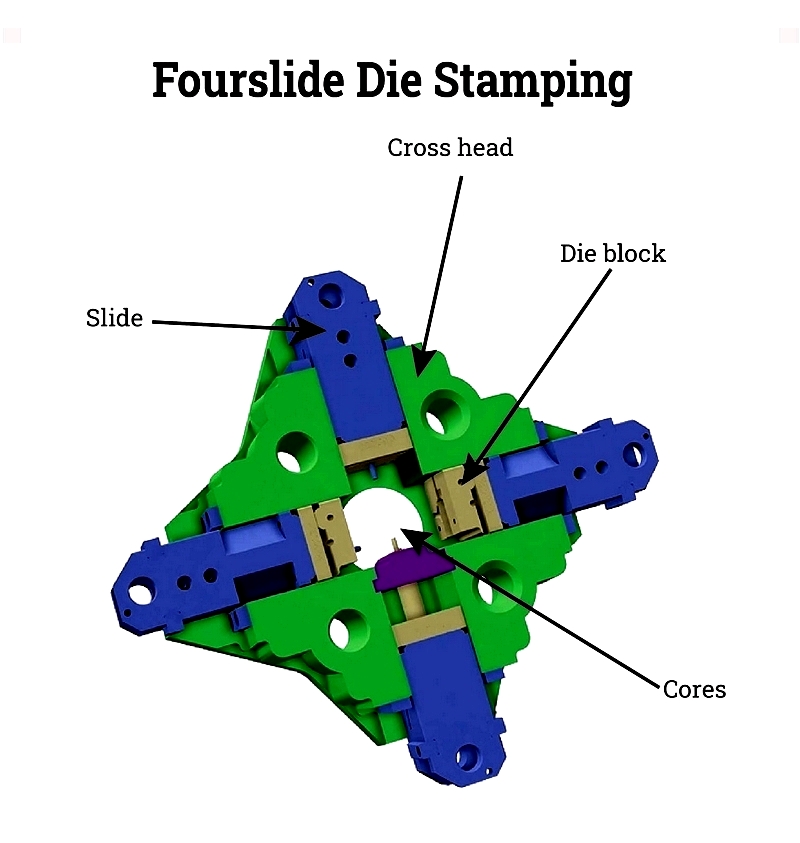
Fourslide Stamping
Using horizontally moving dies, this process creates complex geometries with multiple bends. It's efficient for cylindrical shapes and wire forms, offering rapid cycle times and reduced scrap.
Compound Stamping
This high-efficiency method performs multiple operations in one stroke. Ideal for flat parts like washers, it increases speed while minimizing secondary processes.

Hot metal Stamping
This advanced process heats metal to increase workability before stamping. It produces high-strength components, particularly for automotive applications. While slower than cold stamping, it offers superior strength-to-weight ratios.
Chapter 4: What are the leading metal stamping machinery options?
In North America, various metal stamping machines support diverse industries. These machines enable efficient mass production while driving technological advancement. Below are some prominent options:
Komatsu E2W Series Presses
Manufacturer: Komatsu
Known for precision and energy efficiency, these servo-driven presses offer accurate control and reduced operating costs.




