Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of roller conveyors.
You'll learn detailed information on various topics including:
- What is a Roller Conveyor?
- Construction of Roller Conveyors
- Types of Roller Conveyors
- Applications for Roller Conveyors
- Benefits of Roller Conveyors
- And Much More...
Chapter 1: What is a Roller Conveyor?
Roller conveyors serve as essential components in material handling systems. They employ a series of evenly spaced cylindrical rollers to efficiently transport boxes, materials, objects, and parts across open spaces or between different elevations. Designed at convenient heights, these conveyor frames facilitate easy manual loading and unloading. For optimal performance, items transported via roller conveyors should have firm, flat surfaces to ensure smooth movement across the rollers.
These conveyors offer remarkable versatility, being utilized in various applications such as accumulation, inertia reduction, and rapid product sorting. Powered roller conveyors feature rollers connected to motors through mechanisms like chains, shafts, or belts, enabling precise control over movement speed. These systems can operate bidirectionally, allowing for reversible movement and transportation of products between different levels, with motors capable of changing item direction as needed.
Chapter 2: How is a Roller Conveyor Constructed?
Roller conveyors are vital elements in material handling systems and warehouse automation, renowned for efficiently transporting goods, boxes, and pallets throughout production lines and distribution centers. Modern roller conveyors are precision-engineered with specific features to meet diverse industrial needs across manufacturing, logistics, packaging, and food processing sectors. While designs may vary in structure, drive mechanisms, and manufacturer-specific features, all share fundamental characteristics. Understanding their construction helps facility managers and engineers select optimal conveyor solutions for specific application requirements.
Powered roller conveyors, also known as live roller conveyors, utilize small belts, poly-v belts, or plastic spools to deliver consistent roller traction. Friction belts or durable roller chains positioned beneath the conveyor bed engage with heavy-duty rollers for smooth product movement. These drive systems connect to a central shaft running the conveyor length, linked to energy-efficient electric motors that power rollers and ensure reliable motion control.
Rollers
Conveyor rollers are cylindrical metal components fitted into frames with high-precision bearings at each end. Various roller types accommodate different load capacities, operational speeds, and environmental conditions. Rubber and plastic rollers enhance friction for gentle handling, while steel and aluminum rollers offer low rolling resistance and durability for heavy industrial applications. Selection considerations include load type, maintenance needs, and wear resistance to ensure seamless material flow and product integrity.
Plastic Rollers
Plastic conveyor rollers provide lightweight, cost-effective solutions for light-duty applications. Easy to install with minimal maintenance, they comply with OSHA noise standards, reducing sound levels in busy production areas. Their corrosion, rust, and moisture resistance makes them ideal for harsh or washdown environments, while easy-clean properties suit packaged goods, pharmaceuticals, and food products in the food and beverage industry. They also meet sanitary conveyor system standards for hygienic applications.
Nylon Rollers
Nylon rollers deliver superior durability and strength for medium to heavy-duty loads. Manufactured from synthetic polymers, they offer excellent abrasion resistance, chemical stability, and operational reliability in high-traffic logistics centers. Like plastic variants, nylon rollers are lightweight, easy to install, and contribute to operator safety through minimal vibration and noise. These characteristics make them popular in e-commerce fulfillment, packaging, and parcel delivery sectors where quiet, efficient operation is valued.

Rubber Coated Rollers
Rubber-coated rollers feature protective natural or synthetic rubber layers bonded to steel, stainless steel, or plastic cores. This coating enhances grip, cushions fragile products, and provides durable protection for both rollers and transported goods. Rubber composition and hardness are selected based on specific industry needs, such as anti-static, abrasion-resistant, or chemical-resistant properties. Widely used in automotive, packaging, printing, textile, and metal fabrication industries, these rollers are valued for durability, slip prevention, and secure movement across inclined or fast conveyor lines.
Customizable to various load requirements, rubber-coated rollers increase surface friction to prevent product slippage and improve throughput in automated systems.
Steel and Stainless Steel Rollers
Steel and stainless steel rollers represent the premium standard for heavy-duty industrial use. These metal rollers offer unmatched longevity, strength, and wear resistance, ideal for pallets, bulk containers, and heavy materials. Stainless steel adds corrosion resistance for cleanrooms, food production, and chemical processing environments. Both types can be customized with different diameters and wall thicknesses for maximum structural integrity.
In complex systems, steel roller cores are often overmolded with plastic, nylon, or rubber for targeted performance benefits. Compatible with various conveyor types, stainless steel rollers support precision bearings, adjustable shafts, and custom solutions for modern automated warehouses.
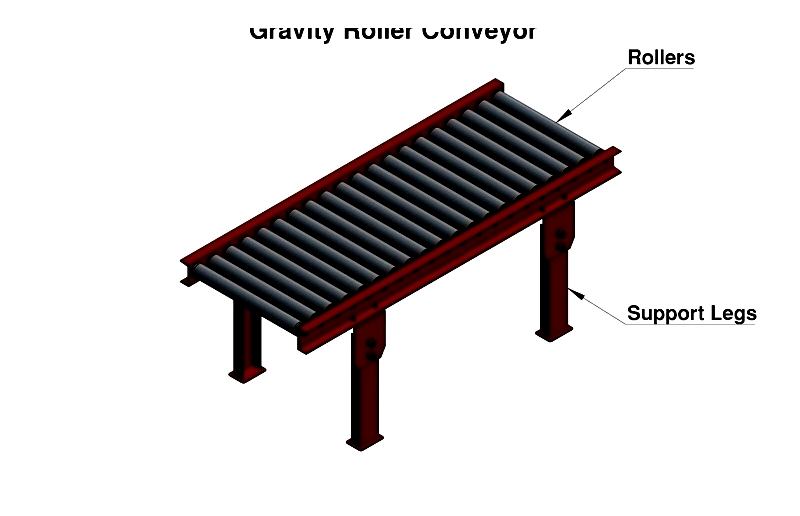
Structure of a Roller Conveyor
Roller conveyor frames provide essential structural support and alignment for efficient material transfer. frames can be permanently installed or configured as portable units adaptable to dynamic layouts. Typically constructed from steel, stainless steel, or lightweight aluminum, each material offers distinct advantages: aluminum resists rust and facilitates relocation, while steel and stainless steel provide robust durability for continuous heavy-duty use.
Support legs come in various sizes, materials, and configurations to accommodate different load capacities, conveyor lengths, and installation conditions. Common designs include tripod or "H" configurations, with "H" types subdivided into light, medium, and heavy-duty constructions. Made from sturdy channel material, support legs can be customized with leveling feet, casters for mobility, or shock-absorbing mounts for vibration isolation.

Roller Conveyor Motor
Powered roller conveyors rely on motorized drive systems, typically featuring 24-volt DC motors for energy efficiency, low noise, and safer operation. Advanced motorized roller conveyor systems (MDR) divide conveyors into independently controlled zones, each powered by its own motor-driven roller. This zoned approach enables accumulation, product sorting, and merge/diverge functions crucial for order fulfillment and warehouse automation. Operators can precisely control speed, direction, and sequencing to optimize flow in batch or continuous processing environments.
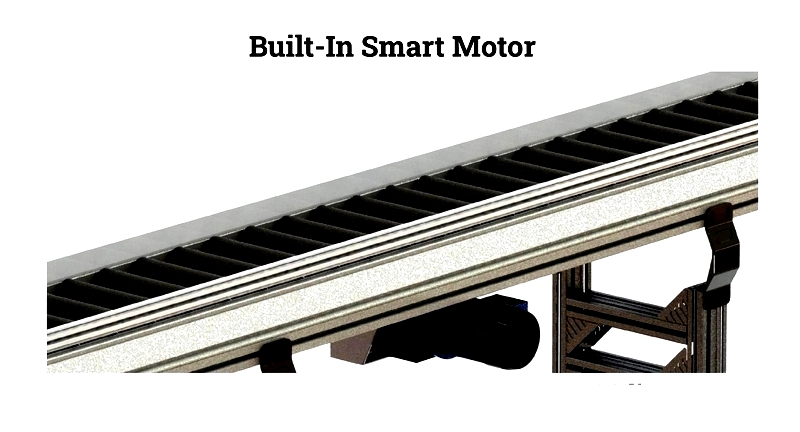

Modular MDR systems offer scalability, energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance downtime, making them increasingly popular for smart factory and Industry 4.0 applications.
Non Precision Bearings
Non-precision bearings like sleeve bearings and bushings provide economical solutions for conveyor rollers operating at lower speeds under light-to-moderate loads. Featuring looser tolerances than precision bearings, they accommodate small misalignments and reduce production costs. Primary applications include package handling, assembly lines, and sortation conveyors where precise positioning is less critical than in high-speed automated systems.
Angular Contact Ball Bearings
Angular contact ball bearings support combined radial and axial loads through stable contact at specific angles relative to bearing axes. Close raceway spacing enables these bearings to withstand high dynamic forces in fast-moving or heavily loaded conveyor lines. Configurations include single row, double row, and four-point contact designs, each optimized for different operational needs and installation footprints.





