Introduction
This article covers everything you need to know about Swiss screw machining and its applications.
You will learn about:
- Swiss Screw Machining fundamentals
- The Swiss Screw Machining process
- Different types of Swiss Screw Machining
- Industrial applications
- And more...
Chapter 1: What is Swiss Screw Machining?
Swiss screw machining is a specialized method for mass-producing precision components using automated lathes that precisely control each cutting operation. Unlike conventional screw machining, it synchronizes workpiece and cutting tool movements to achieve tight tolerances and produce complex parts efficiently.
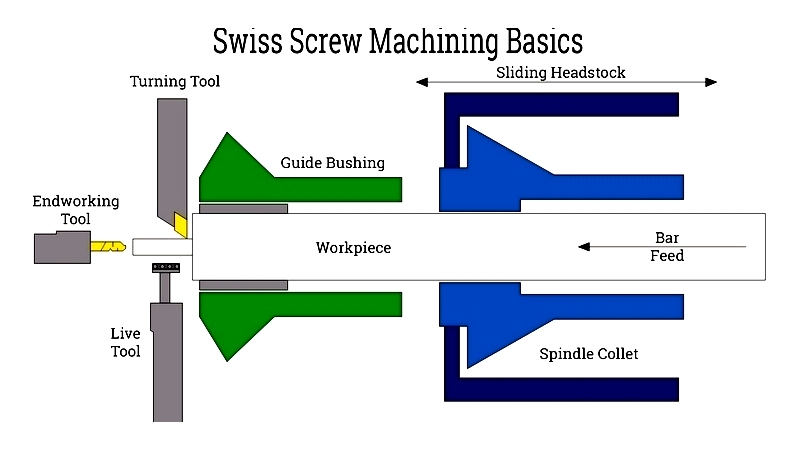
This subtractive manufacturing process removes material from the workpiece through Z-axis motion. A guide bushing supports the bar in front of turning tools, allowing operators to work on extended lengths with high accuracy.
Developed during Switzerland's industrialization, Swiss screw machining originally helped watchmakers produce horology components. Before its invention, lathe operations were labor-intensive and time-consuming, requiring manual handle adjustments for precision metalworking.
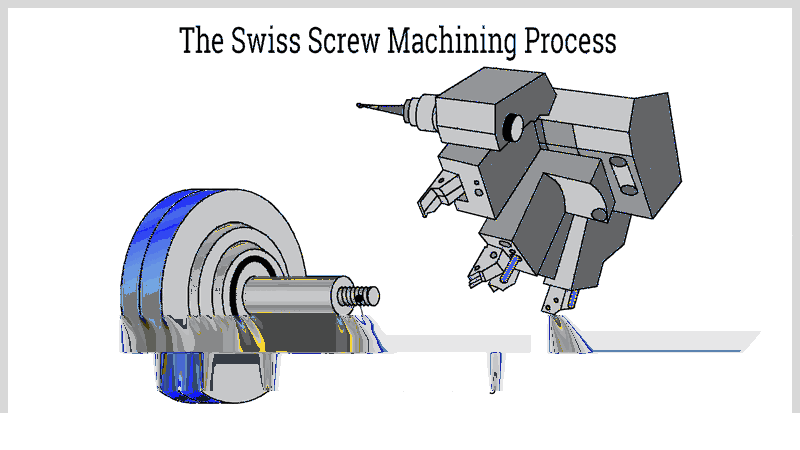
Chapter 2: The Swiss Screw Machining Process
Also called Swiss-type turning, this precision CNC machining process uses specialized lathes with multiple tool holders around the spindle and a coaxial tailstock. It excels at producing small, high-precision components with tight tolerances and minimal defects for industries like medical devices, aerospace, electronics, and automotive.
While variations exist—including CNC and automatic Swiss machines—all follow fundamental turning principles for efficiency. The key is securely holding the workpiece while coordinating tool and workpiece movements for precise material removal.
Despite producing complex parts, the core process remains straightforward and repeatable. Like all advanced machining, it requires careful engineering, programming, and preparation to maintain quality standards.
Holding the Workpiece
Secure workpiece holding is crucial for achieving precise tolerances. Instability can cause vibrations, leading to tool wear and compromised accuracy—especially problematic in high-volume production.
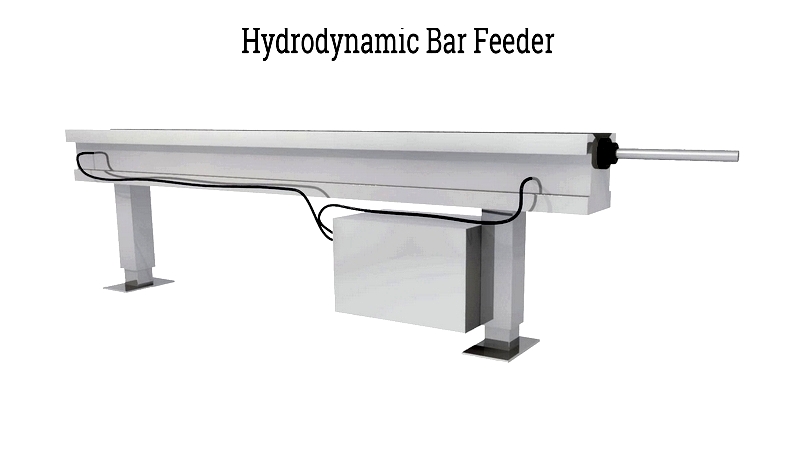
Modern Swiss lathes use two main automatic bar feeders:
- Hydrodynamic Bar Feed System – Uses pressurized oil in a tube to support and feed workpieces. Reduces noise and vibration, ideal for small-to-medium production and prototyping.
- Hydrostatic Bar Feed System – Features guide channels with hydraulic fluid support, handling longer bars (4-24 ft) for large-batch production.
These automated systems represent significant improvements over manual feeding methods.

Chucking Collet
This mechanical gripping mechanism uses a three-jaw power chuck, hydraulic cylinder, and drawtube to clamp and center workpieces during rotation. Precise jaw pressure regulation prevents deformation of delicate components.

Guide Bushing
A defining feature of Swiss machining, guide bushings support workpieces near the cutting zone to minimize deflection. This enables production of slender parts with tight tolerances (as precise as 0.0002 inches).
Types include:
- Rotary Guide Bushing – For larger diameters, rotates with the part
- Fixed Guide Bushings – Stationary, for small diameters
- High Precision Guide Bushings – For medical implants and electronics
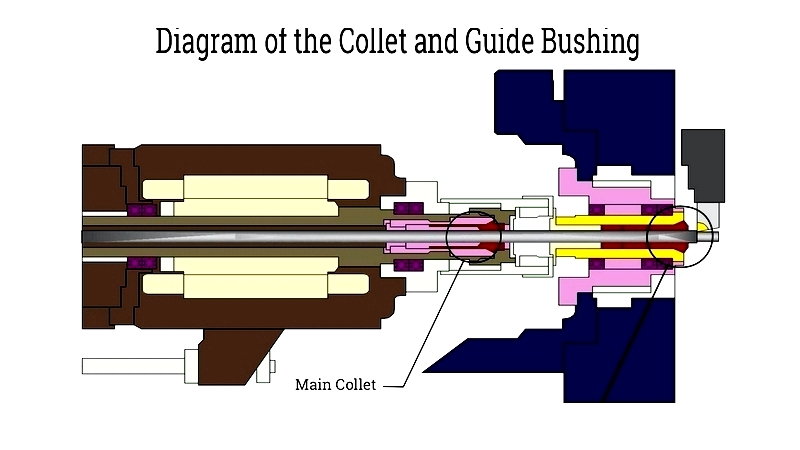
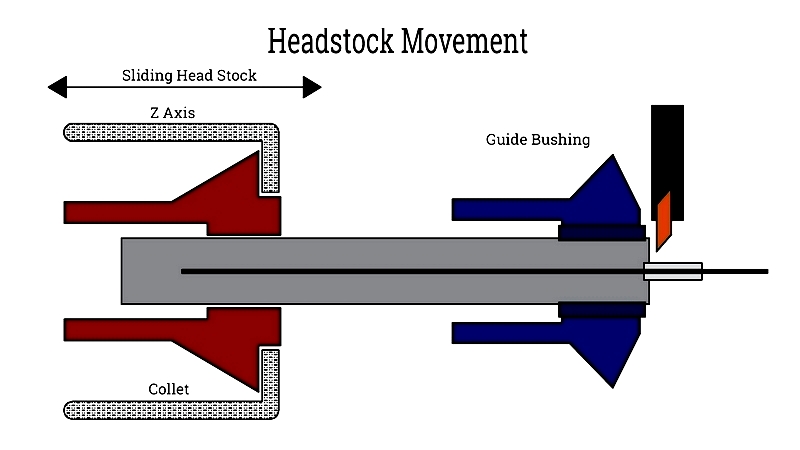
Headstock Movement
Swiss machines feature movable headstocks that slide along the Z-axis, positioning workpieces dynamically. This design allows cutting tools to operate extremely close (1-3mm) to the workpiece, enhancing stability and accuracy for complex parts.
Spindle
Swiss machines often use multiple spindles (main and auxiliary) for diverse operations like turning, drilling, milling, and threading. Spindle types include:
- Belt Driven – Up to 8000 rpm, adjustable speeds
- Direct Drive – Up to 12000 rpm, smoother operation
- Integrated – Built-in motor for micro-manufacturing
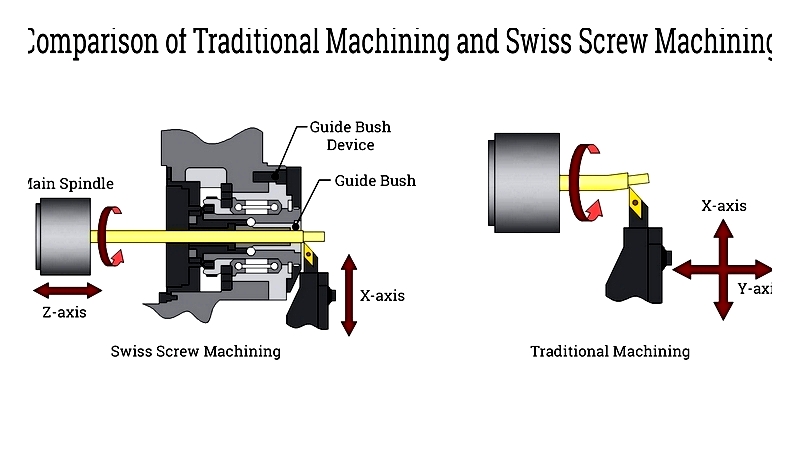
Traditional CNC vs. Swiss Machining
Key differences include:
- Swiss machines feature movable headstocks for slender parts
- Multi-axis capabilities (up to 6+ axes) for complex geometries
- Ability to complete multiple operations in one cycle
Ideal for medical devices, aerospace components, and electronics requiring tight tolerances.
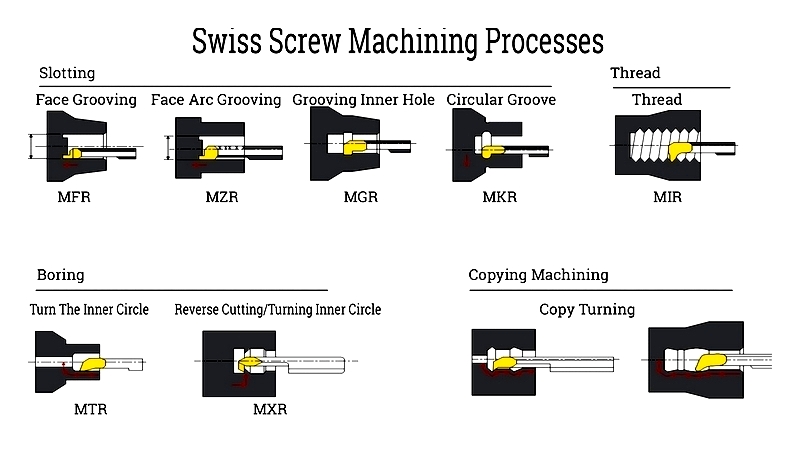
Chapter 3: Types of Swiss Screw Machining
Originally developed for watch screws, Swiss machining now produces precision components across industries. Two main types exist:
Automatic Swiss Screw Machining
Uses cam-driven lathes for high-volume production of simple-to-moderate complexity parts. Compatible with various metals and plastics.
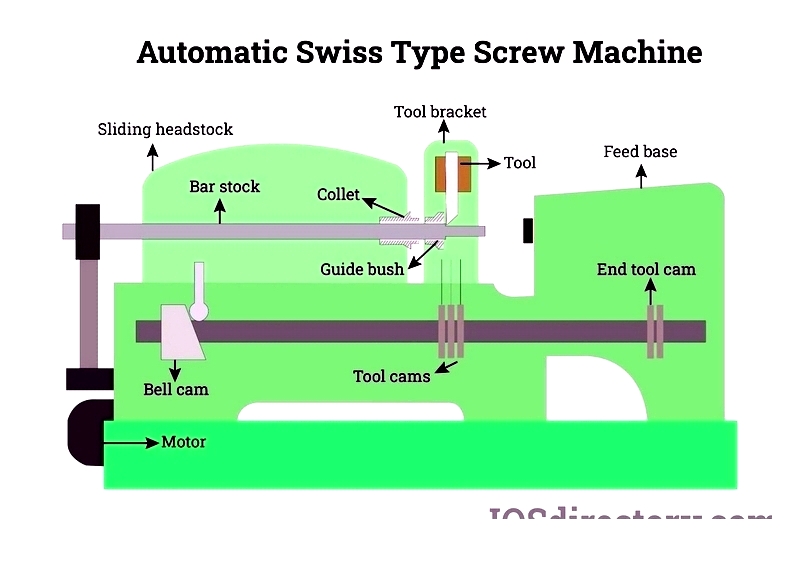
Advantages:
- Cost-effective for large runs
- Consistent accuracy
- Minimal secondary finishing
CNC Swiss Screw Machining
Digital controls enable complex geometries and tight tolerances for medical and aerospace applications.
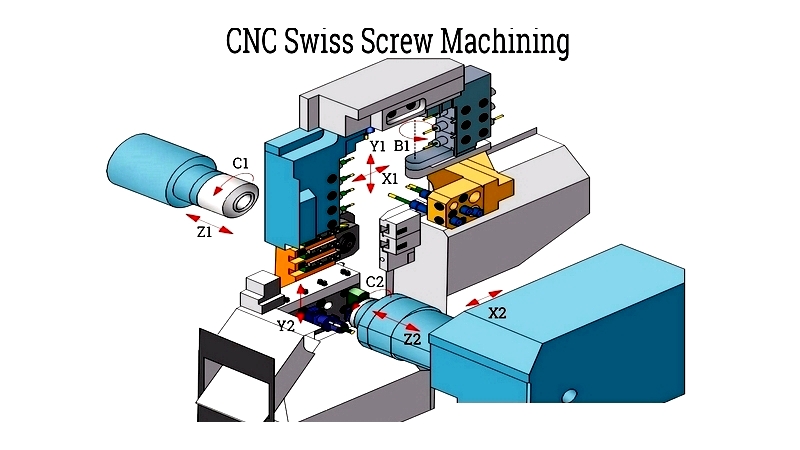
Advantages:
- Superior precision
- Quick design changes
- Digital quality control
- Wide material compatibility
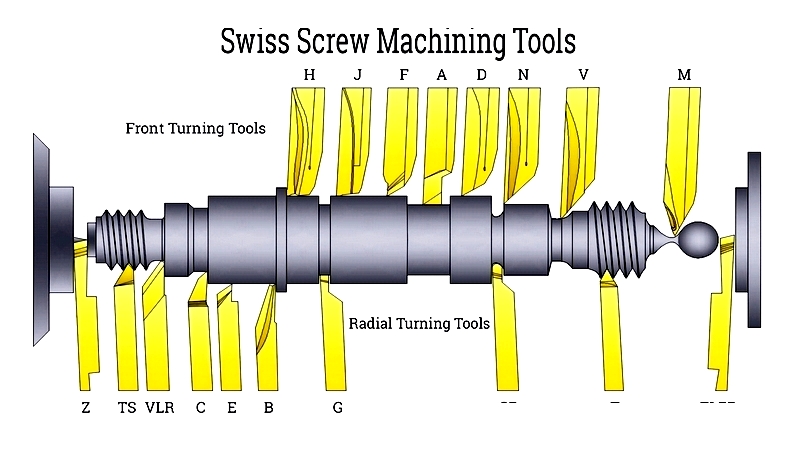
Chapter 4: Swiss Screw Machining Tools
Specialized tools enable precise material removal for high-tolerance parts.