Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of gate latches.
Key topics covered include:
- Principles of Gate Latches
- Types of Gate Latches
- Selection Considerations and Installation Recommendations
- Applications and Benefits of Gate Latches
- And More...
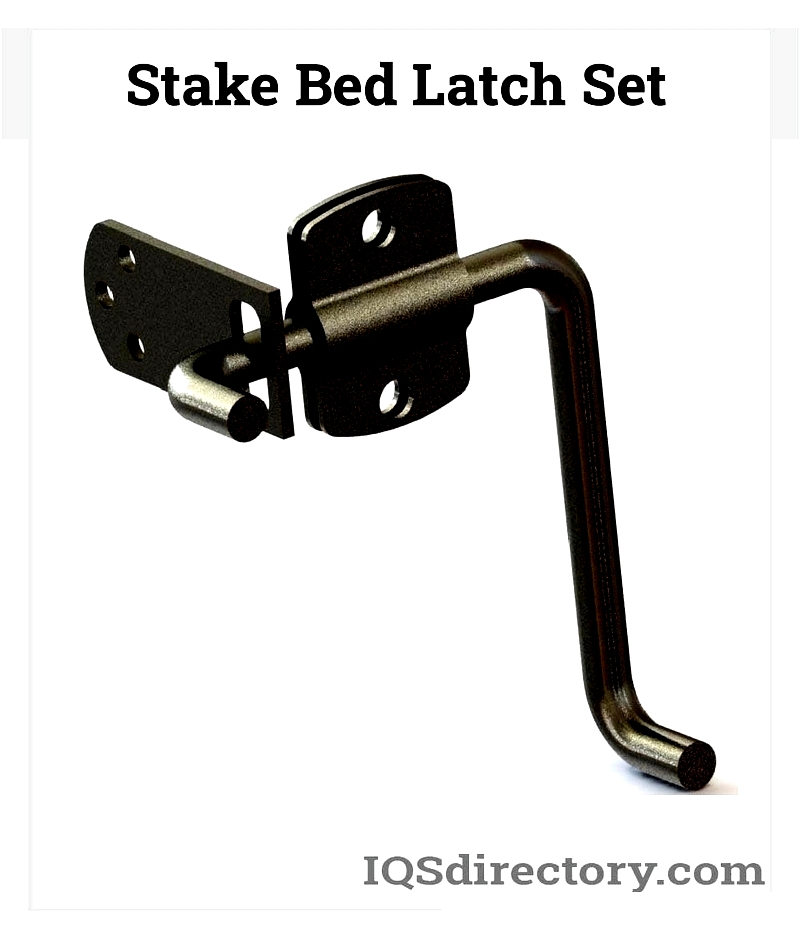
Chapter 1: Understanding Gate Latch Basics
This chapter examines the fundamental concepts of gate latches and their construction materials.
Defining Gate Latches
A gate latch is a securing mechanism for gates on fences or truck beds. It typically consists of a metal lever and bar system where lifting the lever releases the latch while lowering it engages the lock. While lacking integrated locks, these latches can be paired with padlocks for enhanced security.
Manufactured from durable materials like steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, gate latches come in various designs for right or left-handed use. The three main categories are gravity latches, spring-loaded latches, and bolt-secured latches.

Available in single or double-sided configurations, proper latch performance depends on matching with suitable hinges and well-built fences. Operational designs fall into three primary types: spring-loaded, bolt-secured, and gravity latches.
Materials for Gate Latches
Gate latches are manufactured in diverse materials, each offering distinct advantages. Material durability significantly impacts selection. For example, while cast iron enhances home aesthetics, it may rust quickly without maintenance. Environmental assessment is therefore crucial for determining material suitability.
Typically crafted from weather-resistant materials, gate latches require periodic maintenance for extended lifespan. Material choice affects both visual appeal and functional performance through variations in style, color, and finish.
Stainless Steel
Stronger than aluminum, stainless steel resists warping and bending under stress or temperature changes. Though more expensive, its corrosion resistance and sleek appearance make it ideal for durable applications. Available in raw silver or powder-coated finishes for harsh environments.
Monthly lubrication minimizes squeaking and environmental damage. Regular cleaning with mild soap maintains appearance.
Maintenance: Wash with mild dish soap and warm water, then dry thoroughly.
Bronze
Premium-priced bronze offers exceptional durability and aesthetic appeal, developing an attractive patina over time. Its natural strength eliminates need for powder coating.
Annual wax application prevents green patina formation and extends lifespan.
Maintenance: Apply protective wax annually.
Aluminum
Lightweight and corrosion-resistant, aluminum suits high-wear environments. Its brittleness necessitates quality gate stops to prevent arm strain. Available in silver or powder-coated finishes across various styles.
Most economical option with functional and decorative versatility.
Brass
Ideal for classic designs, brass offers substantial feel but requires regular polishing to prevent tarnishing.

Specialized cleaners and UV-resistant coatings preserve shine and integrity.
Maintenance: Regular polishing maintains luster.
Iron
Common in traditional designs, iron latches often feature black powder coating for protection. Less suitable for coastal areas due to saltwater corrosion.
Durable in optimal conditions with good value proposition.

Maintenance: Remove rust with steel wool and apply protective spray or paint.
Chapter 2: Gate Latch Varieties
Essential for residential, commercial, and industrial fencing, gate latches impact security and convenience. The market offers numerous types tailored to specific needs, materials, and security levels. Proper selection ensures reliable performance, protection, and ease of use. Below are common latch types with their features, benefits, and applications.
Bolt Latches
Classic one-sided design with sliding metal rod mechanism. Ideal for backyard gates and privacy fencing. Simple installation and low maintenance with padlock compatibility.
Available in galvanized steel, stainless steel, and brass for rust resistance. Sizes range from decorative to heavy-duty industrial.
Gravity Latches
Self-latching design using gravity for automatic closure. Popular for garden gates and pet enclosures.

Often two-sided with optional locking features. Pair with self-closing hinges for pool safety compliance.
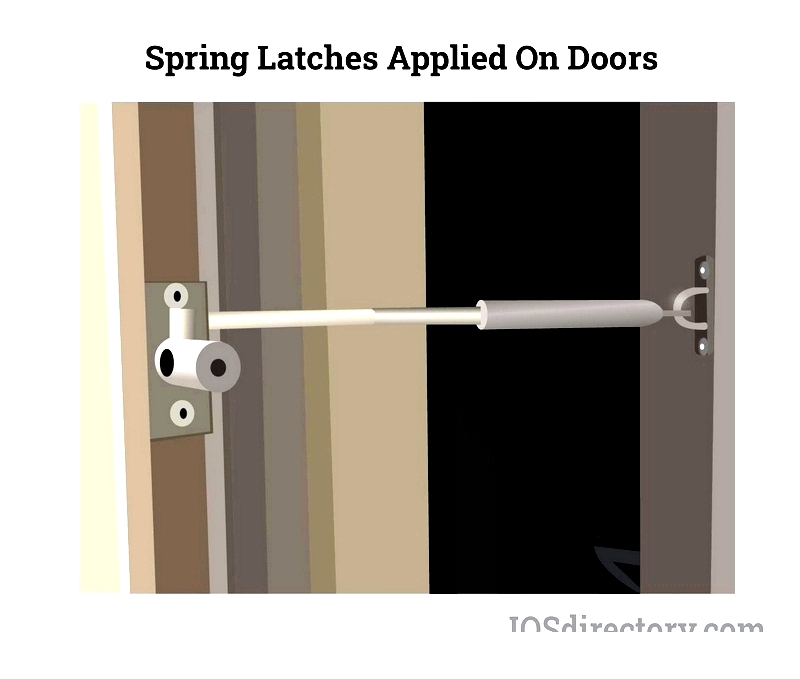
Spring-Loaded Latches
Automatic spring mechanism ensures positive closure. Suitable for high-use environments.
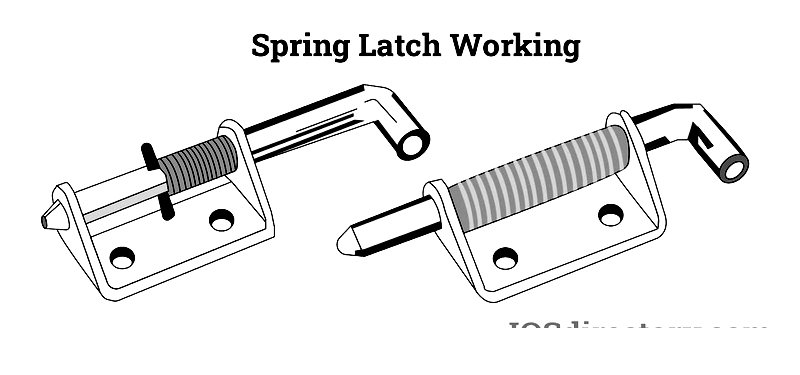
Durable option for residential to industrial gates with various locking configurations.
Thumb Latches
Decorative two-sided design for wooden gates. Features thumb depressor for operation.

Ideal for garden gates with optional locking features.
Ring Latches
Dual-sided operation with interlocking rings. Suitable for various gate materials.

Available in gravity or spring-loaded versions with locking options.
Lever Latches
User-friendly lever handles for easy operation. Suitable for entry gates and enclosures.
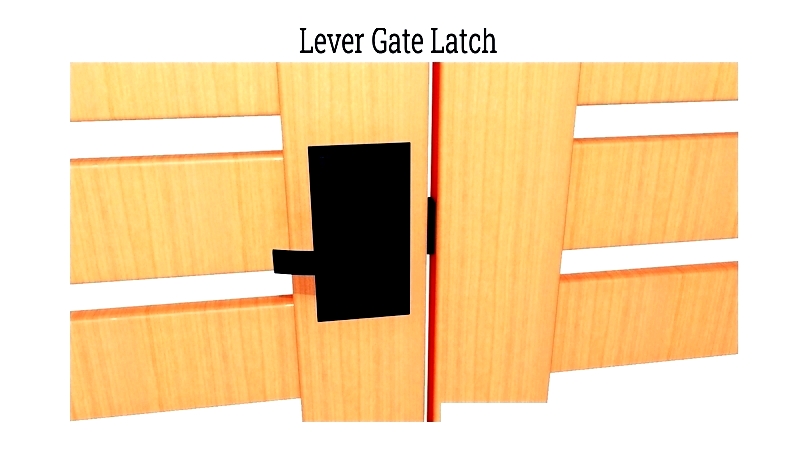
Gravity or spring-assisted models with optional locking.
Side-Pull Latches
Safety-focused design for pool gates and




