Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of machine vision systems.
Continue reading to learn about:
- The fundamentals of machine vision systems
- Key components of machine vision systems
- Different types of machine vision systems
- Core functions of machine vision systems
- Practical applications of machine vision systems
- And much more...
Chapter 1: Understanding Machine Vision Systems
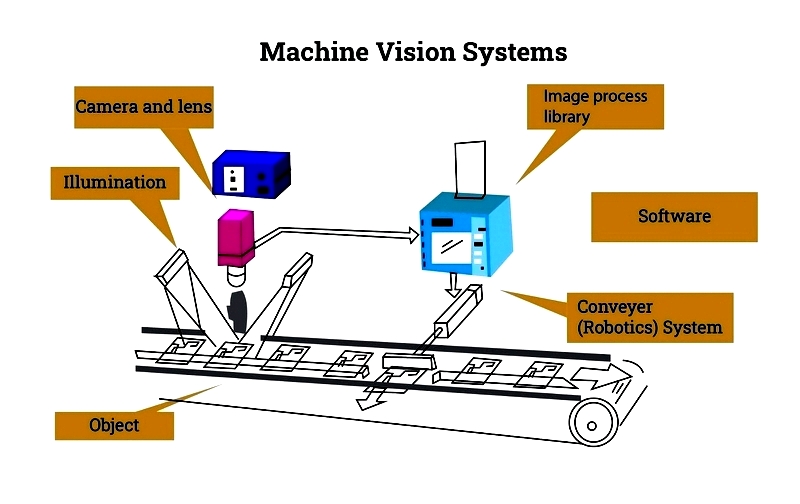
Machine vision systems integrate electronic components, computer hardware, and software algorithms to process and analyze environmental images. These systems provide operational guidance by automating processes, controlling equipment, and inspecting products through captured visual data.
Manufacturing industries widely implement machine vision systems to handle repetitive, labor-intensive tasks that challenge human workers. These systems dramatically improve productivity while reducing operational costs. For example, a production line vision system can inspect hundreds of parts per minute - a task that would be slower, more expensive, and prone to errors if performed manually. Human inspection also faces time constraints that may compromise comprehensive quality checks.
By delivering precise, consistent detection and measurement capabilities, machine vision systems enhance product quality and manufacturing yield. They enable early defect detection during production, preventing faulty components from reaching the market. Additionally, these systems improve traceability and ensure compliance with industrial regulations and specifications.
Chapter 2: Core Components of Machine Vision Systems
Machine vision systems represent specialized automated inspection solutions for manufacturing, quality control, robotics, and industrial automation. These intelligent systems typically incorporate five essential components that work together to achieve accurate visual analysis. Below we examine these critical elements and their role in building reliable vision systems. While some components may be familiar from other technologies, their integration enables the advanced functionality characteristic of modern computer vision and automated inspection platforms. Understanding these elements proves essential for selecting machine vision solutions for industrial applications.
Lighting in Machine Vision Systems
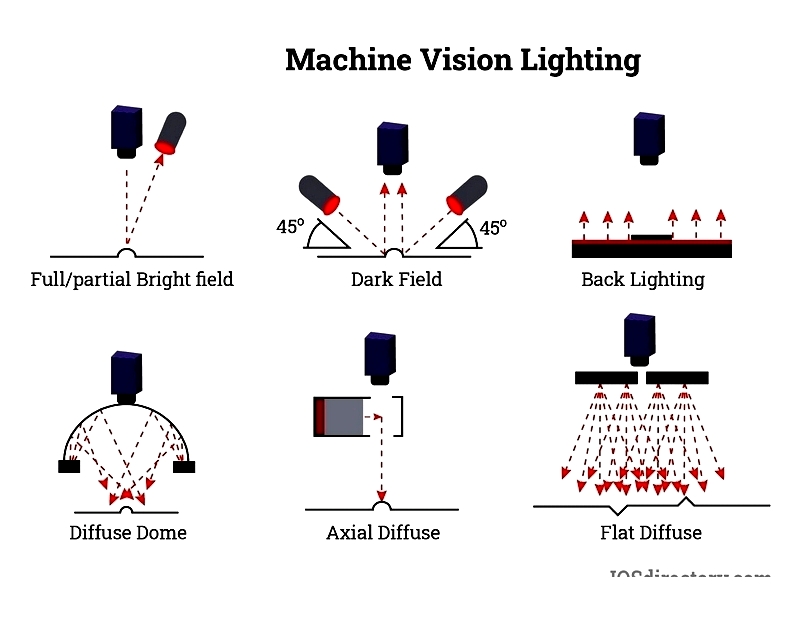
Proper lighting forms the foundation for accurate machine vision inspection. Optimal lighting creates high contrast and clear feature differentiation, enabling cameras to detect flaws and product characteristics precisely. Inadequate lighting produces poor image quality, leading to missed defects and unreliable measurements. Key lighting parameters - including source distance, illumination geometry, intensity, color temperature, and setup configuration - require careful optimization. Surface properties like reflectivity and material composition also significantly influence lighting choices. Well-configured lighting improves defect detection, alignment accuracy, and part recognition.
Machine vision applications employ various lighting technologies, including LED, quartz halogen, fluorescent, and xenon strobe lights, each offering distinct spectral and intensity characteristics. Lighting approaches can be directional or diffusive, affecting feature visibility. Effective lighting reduces errors, increases inspection speeds, and ensures image consistency - crucial for applications like OCR, barcode reading, and quality inspection.
Back Lighting
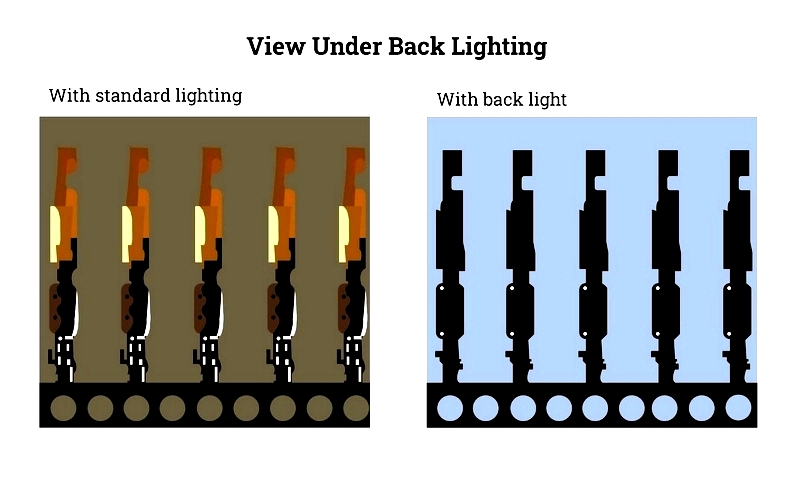
Backlighting positions the light source behind the target object, creating strong contrast with dark silhouettes against bright backgrounds. This technique effectively identifies holes, gaps, cracks, and other defects in transparent materials. Commonly used for dimensional measurement, sorting, and edge detection, backlighting often incorporates monochrome light and polarizers to minimize glare and enhance edge definition.
Diffuse Lighting
Diffuse lighting provides uniform, shadow-free illumination by scattering light in multiple directions. This approach benefits shiny, textured, or reflective surfaces by minimizing glare. Three primary diffuse lighting types serve machine vision applications:
- Dome Diffuse Lighting surrounds objects with light, reducing shadows and highlighting surface features - ideal for curved or glossy components.
- On-axis Lighting aligns with the camera's optical axis, enhancing visibility of surface variations like etchings.
- Flat Diffuse Lighting uses broad planar sources for even illumination, commonly applied in PCB and semiconductor inspection.
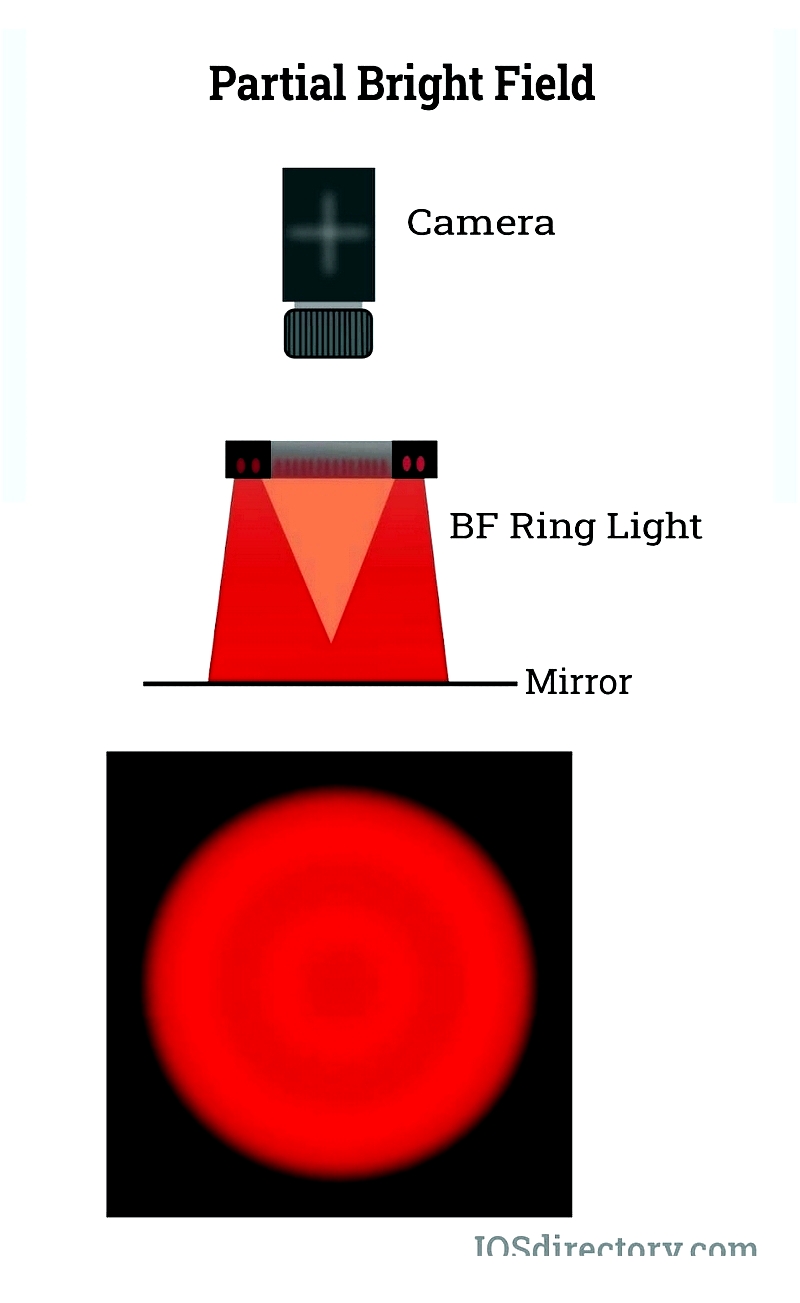
Partial Bright Field Lighting
Partial bright field lighting employs angled beams to accentuate surface textures and edges, providing excellent contrast for topographical features. While effective for flaw detection and printed circuit inspection, this method may create unwanted reflections on highly reflective materials.
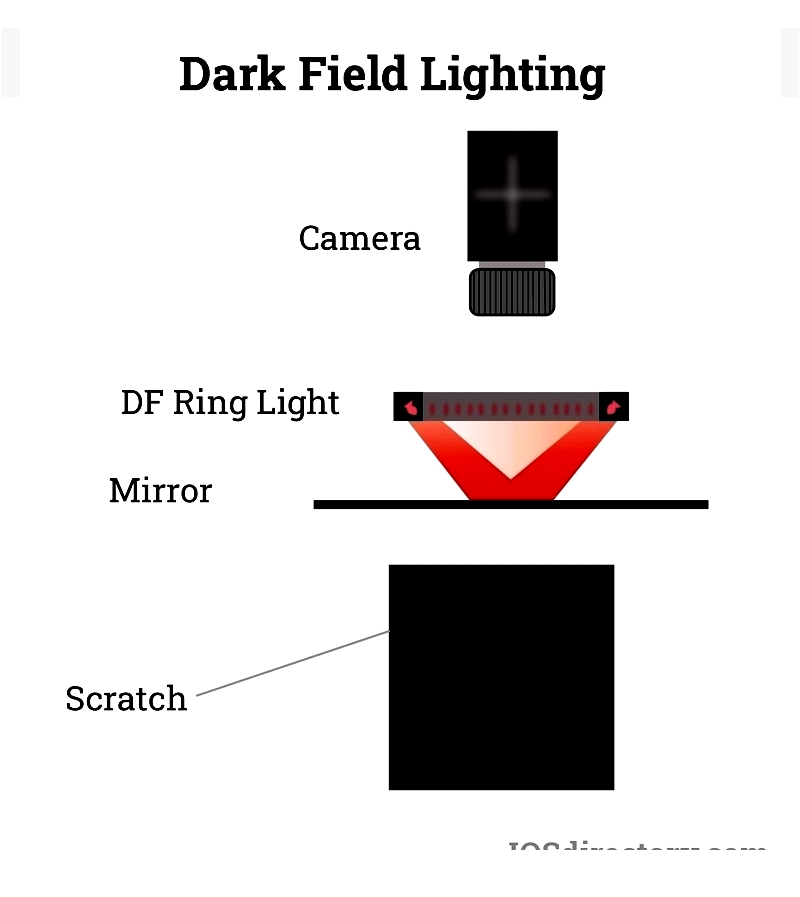
Dark Field Lighting
Dark field lighting uses low-angle illumination to reveal surface defects as bright features against dark backgrounds. This technique excels at detecting scratches, pits, and fine anomalies in glass, metal, and medical device manufacturing.
Specialty accessories like color filters and polarizers often enhance machine vision lighting systems. Filters adjust contrast or isolate wavelengths, while polarizers reduce reflections - both improving inspection accuracy in challenging environments.
Machine Vision Lenses
Lenses play a critical role in machine vision by focusing light onto image sensors. Lens selection significantly impacts image clarity, resolution, and feature detection. Machine vision lenses often feature chromatic aberration correction and come in various mounts for different applications. Proper lens selection is fundamental to industrial vision and quality control tasks.
- Field of view determines the inspection area - wider views suit large objects or multi-part inspection.
- Depth of field defines focus tolerance for moving objects, crucial for high-speed operations.
- Depth of focus indicates allowable sensor position variation while maintaining focus.
- Aperture controls light intake - smaller apertures increase depth of field but require brighter lighting.

Image Sensor
Image sensors convert optical images into digital signals for processing. Modern machine vision cameras use CCD or CMOS sensors, each offering distinct advantages. CCD sensors typically provide lower noise, while CMOS sensors offer faster frame rates. Both types serve high-precision automated inspection systems effectively.
Sensor performance depends primarily on resolution and sensitivity. Higher resolution enables detection of smaller features, while greater sensitivity ensures reliable performance in low-light conditions. Additional considerations include dynamic range, noise performance, and frame speed - all affecting throughput in industrial applications.
Vision Processing Unit
The vision processing unit executes image analysis algorithms, transforming raw images into actionable data. Using pattern recognition, defect analysis, and other advanced techniques, VPUs deliver high-speed automated inspections. Processing may occur in embedded cameras or external computers, depending on system requirements.
Common software functions include image enhancement, edge detection, measurement, and pass/fail decision-making. Modern systems often integrate with analytics and machine learning for comprehensive quality assurance and process insights.
Communication System
Communication systems enable data exchange between vision processors and automation environments. Reliable interfaces - including discrete I/O, Ethernet, and industrial protocols - ensure seamless integration with machinery and control systems. Fast communication supports immediate action based on inspection results, such as part rejection or robotic adjustment.
When selecting vision systems, compatibility with existing equipment, integration ease, and cybersecurity protections represent important considerations for communication components.




