Introduction
This article provides a detailed discussion about metal shims.
After reading, you should understand the following:
- What metal shims are
- How metal shims are made
- Types of metals used for shims and their benefits
- Industrial and domestic applications of metal shims
- Advantages of different metal shims
- Factors to consider when selecting metal shims
And more...
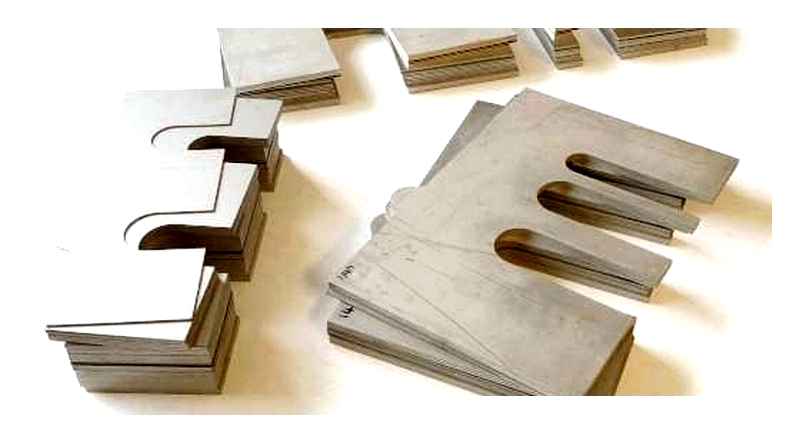

Chapter One: Understanding metal Shims
Definition of a Shim: A shim is a versatile material used to fill gaps or spaces, especially in construction and mechanical applications. They can range from simple materials for balancing tables to durable metals for heavy machinery. Shims ensure proper alignment and performance in assemblies where precision is crucial.
Shims often act as compensators, filling small gaps between machine components. Typically made of metal, these precise components prevent contact between loose-fitting parts, avoiding potential damage. By filling these gaps, shims reduce manufacturing costs and time while enhancing equipment durability and efficiency.
Chapter Two: How metal Shims Are Made
metal shims are precision components used across various industries. Their manufacturing processes depend on required tolerances, material type, and application needs. Below are common metal shim fabrication methods, each selected to balance quality, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness.
Stamping/Pressing
The first step in shim manufacturing often involves creating specialized tools based on precise shim specifications. Die-cast steel rules cut thin sheet metal like stainless steel or brass. A sharp steel rule die ensures the finished component meets exact thickness and dimensional requirements.
For each new order, steel rule dies are custom-made to ensure consistency. Economical materials minimize tooling costs, allowing repeat orders without additional fees. After cutting, shims undergo deburring for smooth edges and are inspected before packaging.
The stamping process involves four main steps:
- Selecting the appropriate shim material and ordering tooling
- Cutting the material with a stamp press to optimize yield
- Inspecting shims for tolerances and edge quality
- Packaging shims to prevent damage during delivery
Note that thick metal shims or hard alloys are typically not cut using stamping, as it may damage the die. For high-volume production, stamping remains cost-effective.
CNC Laser Cutting
CNC laser cutting is ideal for prototyping or producing intricate shapes. A high-powered laser follows computer-programmed paths to create detailed geometries. Unlike stamping, laser cutting doesn't require custom tools, streamlining production. This method works well with stainless steel, aluminum, titanium, and specialty alloys.

Laser cutting reduces setup times and offers excellent repeatability for both small and large batches. It's favored for its efficiency, minimal waste, and ability to maintain tight tolerances.
Water Jet Cutting
Water jet cutting uses high-pressure water with abrasive powder to cut materials without heat. This method suits temperature-sensitive materials like certain alloys and composites. It's commonly used for high-strength steel, rubber, plastic, and ceramic shims.
EDM Wire Cutting
Wire-cut EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) precisely cuts conductive materials using electrical charges. This method is ideal for high-precision, thin-gauge shims with complex shapes, making it essential for tooling and microfabrication.
Turning
Turning is a subtractive process where a lathe rotates the workpiece while cutting tools shape it. This method is primarily used for round metal shims or custom washers in automotive and industrial applications.
Punching and Nibbling
Punching uses mechanical or hydraulic presses to create shapes or holes in metal sheets. Nibbling involves incremental punches for complex geometries, useful in electronics and aerospace industries.
Choosing the Best metal Shim Manufacturing Process
Consider factors like production volume, tolerances, material type, and budget when selecting a manufacturing method. Consult with metal shim suppliers for services like surface finishing and rapid prototyping.
Chapter Three: Leading Types of metal Shim Machinery
Various advanced machines are available for precise metal shim manufacturing. These machines produce custom shims with tight tolerances for industries like aerospace, automotive, and electronics.
Trumpf TruLaser Series - Laser Cutting Machines
Manufacturer: Trumpf Inc.
The Trumpf TruLaser series offers high-speed, accurate cutting for various metals. Its fiber laser technology ensures excellent cut quality, while automation features streamline production.
Omax 80X Series - Waterjet Cutting Machines
Manufacturer: Omax Corporation
The Omax 80X series uses high-pressure waterjets for precise cutting without heat distortion. It's ideal for complex shapes in hardened steel and exotic alloys.
Amada AE Series - Turret Punch Presses
Manufacturer: Amada America, Inc.
The Amada AE series provides rapid punching and forming for metal shims. Its CNC controls and automated tool changes ensure efficiency and repeatability.
Haas VF Series - CNC Machining Centers
Manufacturer: Haas Automation, Inc.
The Haas VF series offers flexibility and precision for complex shims. Its multi-axis control and wide tooling selection suit high-mix, low-volume orders.
Komatsu H1F Series - Stamping Presses
Manufacturer: Komatsu America Industries LLC
The Komatsu H1F series is designed for high-volume shim production. Its hydraulic presses deliver consistent quality at high cycle rates.
When selecting metal shim production machinery, consider material compatibility, tolerances, production volume, and automation needs. Stay updated on industry trends and consult experts for the best results.
Remember that technology evolves quickly. For the latest information, conduct thorough research and consult industry specialists.




