Introduction
This article offers detailed insights into sandblast cabinets, covering their construction materials, applications, advantages, and limitations.
You'll find answers to key questions such as:
- How do sandblast cabinets function?
- What makes sandblast cabinets preferable to other cleaning and surface preparation equipment?
- What capabilities do sandblast cabinets offer for optimizing manufacturing operations?
- What materials are used in constructing sandblasters?
- How should I specify a sandblast cabinet when ordering or submitting an RFQ?
- Which types of abrasives and blast media are commonly used?
- Can used abrasives and blast media be disposed of, reused, or recycled?
- Does blast media cause wear on cabinet components?
- And more...
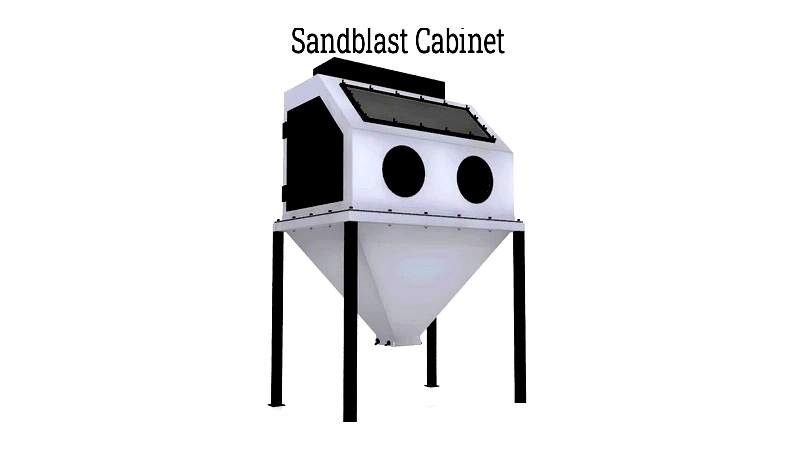

What is a Sandblast Cabinet?
A sandblast cabinet is a specialized apparatus designed to propel abrasive materials onto part surfaces for cleaning, surface modification, or creating abrasions. These systems use various media like sand or metal shot, propelled by compressed air, pressurized water, or blast wheels.
Also known as abrasive blast cabinets, they may be called dry blast cabinets, wet blasting cabinets, micro-abrasive blast cabinets, or shot peening cabinets depending on their specific design and application.
Sandblast Cabinet Types and Technologies
Sandblast Cabinet Technology
Understanding sandblaster operation requires knowledge of the underlying technology. The abrasive media's composition, particle size, shape, and hardness, along with delivery method, significantly impact efficiency, finish quality, and performance in applications like rust removal or paint stripping.
The propulsion technology defines cabinet construction and classification. Key technologies include:
Air Blast or Dry Blast Cabinets – These use compressed air to propel media, ideal for precision cleaning and surface preparation. They come in two types: suction (siphon feed) and direct pressure.
Suction or Siphon Blast Cabinet – These utilize the venturi effect to draw abrasive into an air or water stream. Known for simplicity and low maintenance, they're cost-effective but require higher air pressure for consistent media flow.
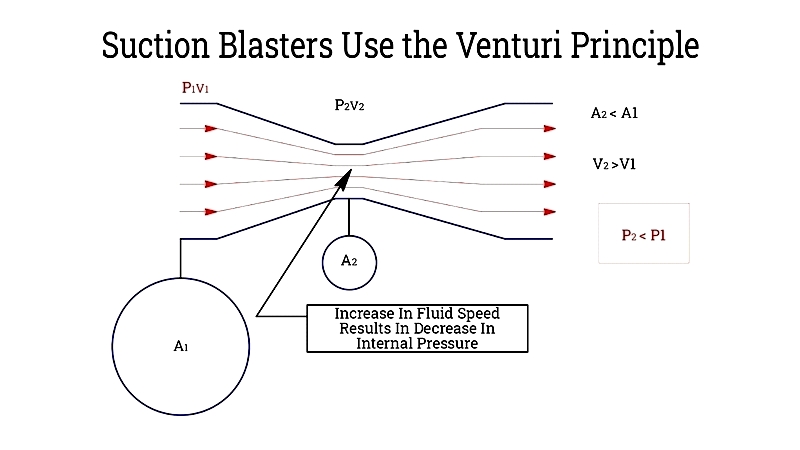
Venturi devices create vacuums for moving abrasives efficiently. While economical, suction blasters are less aggressive, making them suitable for delicate work but requiring longer cleaning times.
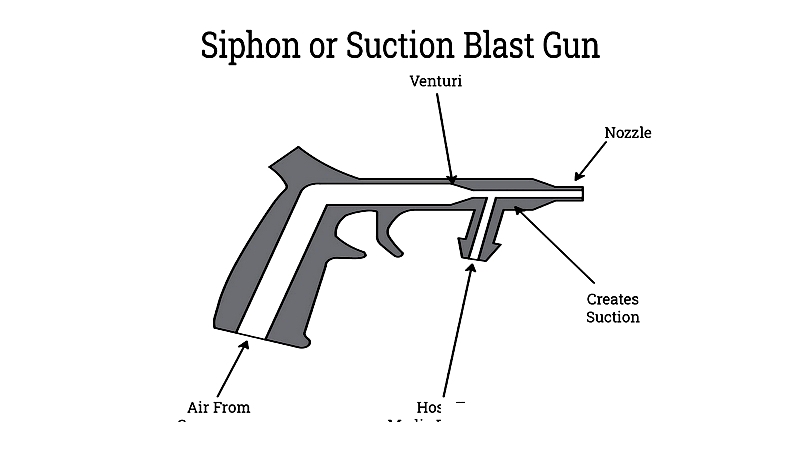
Gravity-fed systems are a suction blaster variant, with media fed from above the gun via gravity.
Direct Pressure or Pressure Blast Cabinets – These high-performance systems use pressure vessels to forcefully propel media, offering faster cleaning (up to 4x speed) and better control than suction systems. They handle heavier abrasives effectively but require more compressed air and rigorous maintenance.
Pressure systems excel in high-volume production and can precisely control surface roughness (Ra). Their kinetic energy formula (K = ½ mv2) shows how velocity exponentially increases cleaning power.
Wet Abrasive Blast Cabinets – Using water instead of air, these reduce dust by over 90%, making them ideal for hazardous materials. They keep workpieces cooler and can recycle media, though no system eliminates all dust completely.
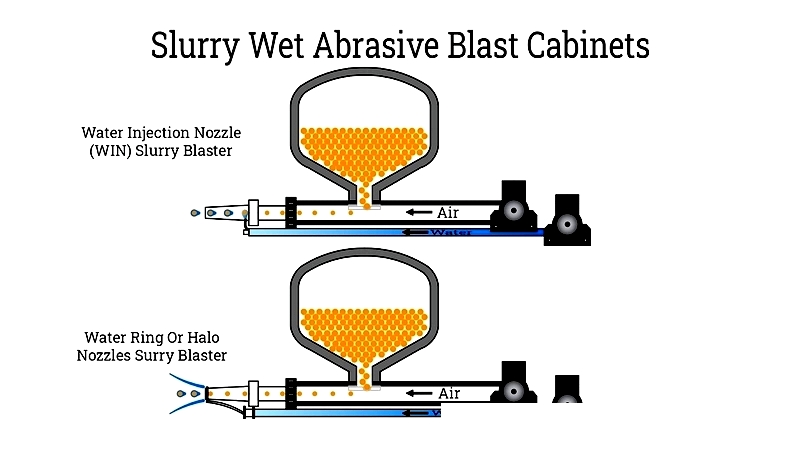
Slurry Sandblast Cabinets – These hybrid systems combine dry blasting with water injection, reducing dust by 50-85%. They offer flexibility but produce muddy residue that requires management.
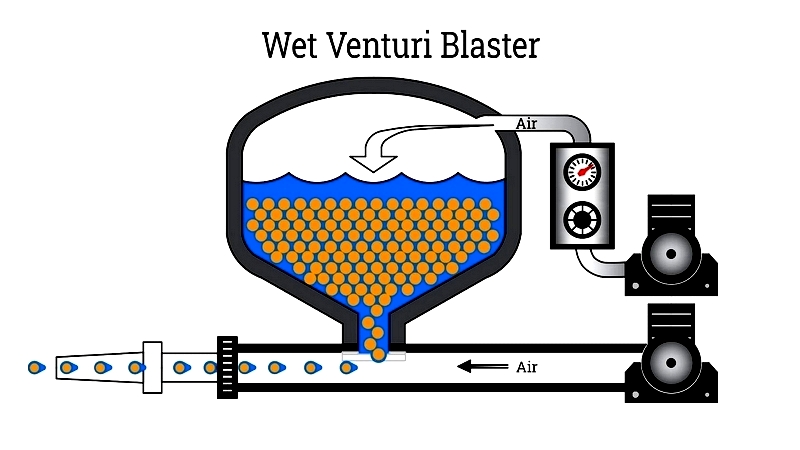
Wet Venturi Sandblast Cabinets – Similar to dry suction systems but using water-abrasive slurries. They achieve excellent dust reduction but require high pressures and offer less flow control.
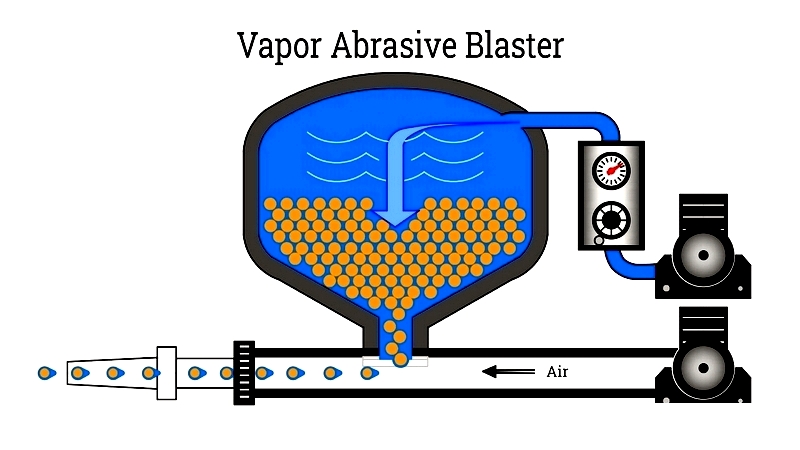
Vapor Abrasive Sandblast Cabinets – Advanced systems premixing abrasive and water under pressure, achieving 95% dust suppression. They're versatile, using less media and water than other wet systems.

Ice Blast Cabinets – Specialized systems using dry ice or water ice for delicate cleaning. They leave no residue and are ideal for sensitive applications like food processing or electronics.
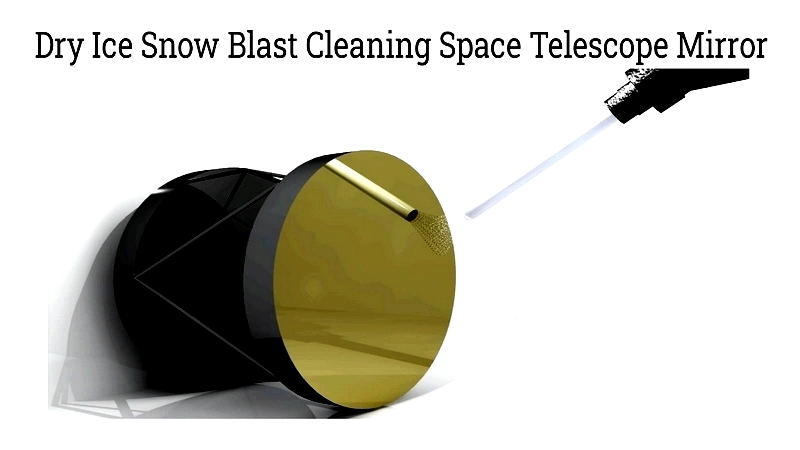
Dry ice sublimates harmlessly, while water ice evaporates, making both environmentally friendly options for contaminant-free cleaning.




