Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of warehouse automation.
It covers key topics including:
- Principles of Warehouse Automation
- Levels and Drivers of Warehouse Automation
- Types of Warehouse Automation
- Why and How to Automate a Warehouse
- Contemporary Warehouse Automation and Robotics
- Applications and Benefits of Warehouse Automation
- And Much More…
Chapter 1: Understanding Warehouse Automation Principles
This section examines the fundamentals of warehouse automation and its operational mechanisms.
Defining Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation replaces labor-intensive, repetitive tasks with automated systems, allowing workers to focus on critical activities like quality control.

Material handling automation utilizes software to perform basic tasks with minimal human intervention. Equipment can convey, load, unload, weigh, process, and feed bulk solids, functioning similarly to manufacturing robots to improve materials handling efficiency.
Exploring Digital Automation
Digital automation employs robotics, data, and software to reduce manual operations. Benefits include seamless ERP integration, enhanced safety, improved security, and better data management. By minimizing human error and manual tasks, it increases efficiency, improves customer service, boosts employee morale, and reduces error-related costs. Technologies like mobile barcode scanning and RFID further enhance these benefits.
Implementing digital automation requires initial investments in deployment, training, hardware, software, and maintenance. Potential risks include data loss, equipment damage, and cybersecurity threats.
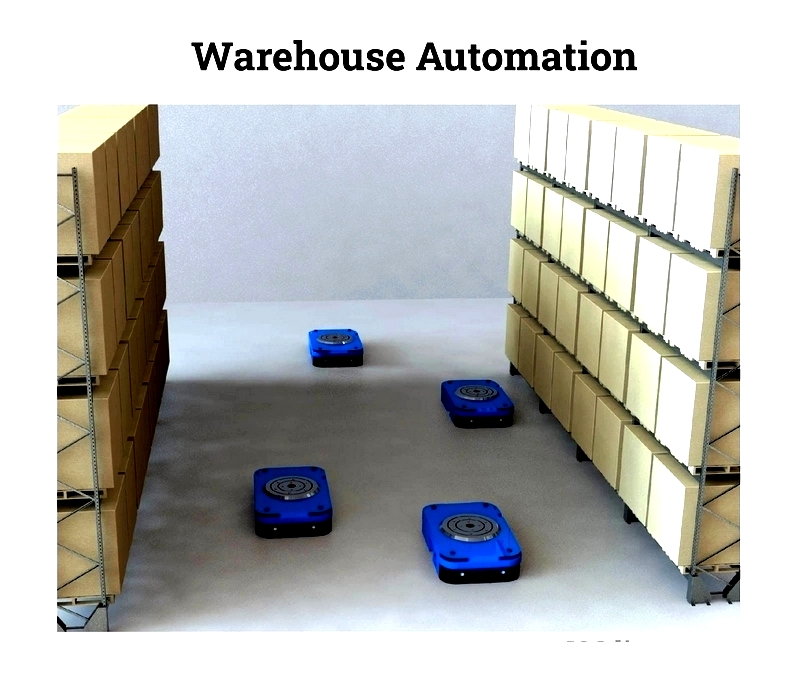
Understanding Warehouse Physical Automation
Physical automation reduces employee movement time, optimizing workflows. Robotics enhance warehouse capacity, efficiency, service reliability, and scalability. However, challenges include high upfront costs, operator skill shortages, and expensive maintenance for specialized equipment.
Effective use of automated warehouse systems requires careful planning, particularly in high-volume facilities that can accommodate specialized automation equipment.
Mechanics of Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation falls into physical and digital categories. Digital automation uses electronics and software to reduce manual work and streamline vendor and customer management, including warehouse management systems and AIDC technologies.
Digital automation enhances security, reduces operational risks, and improves ERP efficiency. While it decreases human error and manual labor, implementation requires significant initial investments in training, support contracts, and system setup.
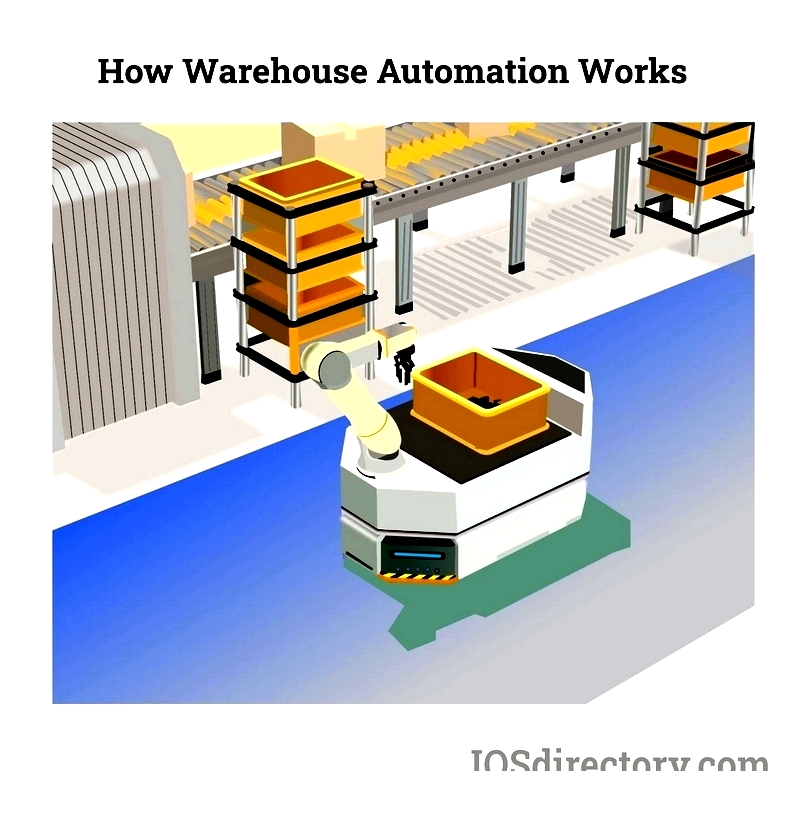
Physical automation reduces labor demands through advanced equipment like AGVs and robotic systems, improving efficiency and storage capacity. It offers scalability and reliability but faces challenges like skilled labor shortages, high initial costs, and maintenance expenses.
Chapter 2: Levels and Drivers of Warehouse Automation
This chapter examines different automation levels and the key factors driving adoption in modern supply chains.
Levels of Warehouse Automation
Warehouse automation evolves through distinct levels, each defined by technological integration.
Low Automation
Low-automation warehouses rely heavily on manual processes. Workers handle inventory movement, data collection, and equipment operation. While basic tools like barcode scanners may exist, these facilities often face productivity inconsistencies, high error rates, limited hours, labor costs, turnover, defects, and unexpected stoppages. Limited automation makes supply chain optimization difficult, prompting many companies to explore advanced solutions.
Automation with Robotics Warehouse Management Systems
Combining WMS with robotics transforms operations. WMS software manages logistics flows, optimizing inventory tracking and storage. Integrated robotics like AGVs and AMRs improve goods movement, picking accuracy, and replenishment. This automation benefits e-commerce fulfillment centers and manufacturers seeking scalable solutions through enhanced efficiency, space utilization, and real-time data access.
Advanced Automation
Advanced automation uses industrial robots, cobots, AS/RS, and conveyors for complex operations. Machine learning and AI-driven systems handle picking, sorting, packaging, and shipping, delivering higher throughput, faster processing, better inventory accuracy, improved safety, and cost reductions. This level suits high-volume distribution centers and just-in-time logistics operations.
Drivers of Warehouse Automation
Business demands, rising labor costs, consumer expectations, and efficiency needs drive automation adoption. AS/RS and advanced inventory management boost productivity, reduce costs, enhance safety, and support resilient supply chains.
Key technologies and trends include:
Picking Automation
Automated picking systems like GTP solutions and robotic shuttles reduce travel time, improve accuracy, and accelerate order assembly. These systems help warehouses meet e-commerce demands for rapid fulfillment, especially in high-SKU environments.
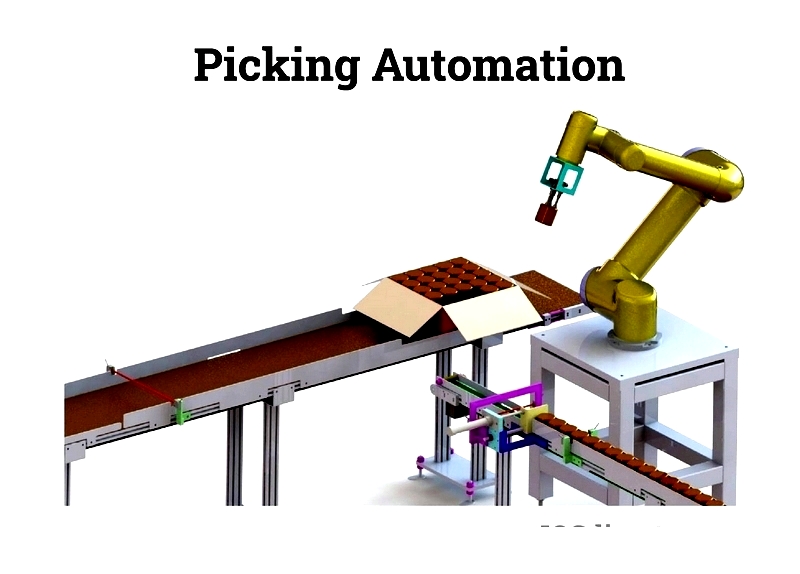
Automated material handling systems, including conveyors and robotic arms, move products efficiently while providing real-time inventory monitoring and quality control.
Intelligent Internal Transportation
AGVs, AMRs, and conveyor systems reduce manual handling and improve workflow. These solutions allow worker reassignment to higher-value tasks and optimize material flow in warehouses.
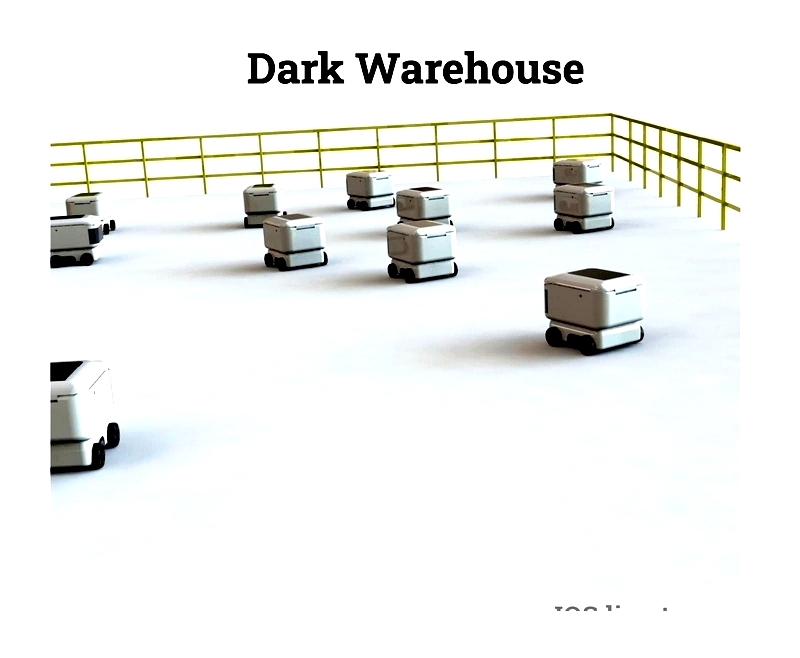
Dark Warehouses
Fully automated dark warehouses operate without human intervention or lighting, using robotics and AS/RS for 24/7 operation. Benefits include lower energy use, reduced labor needs, and improved security, supporting sustainable supply chain initiatives.

Automated Truck Loading/Unloading Systems
Robotic palletizers and dock equipment streamline freight operations, reducing cycle times, manual handling, and damage while improving safety and efficiency.
SaaS Warehouse Management
Cloud-based WMS offers scalable, real-time inventory control with reduced IT overhead. These systems support automation integration and data-driven decision-making for growing businesses.
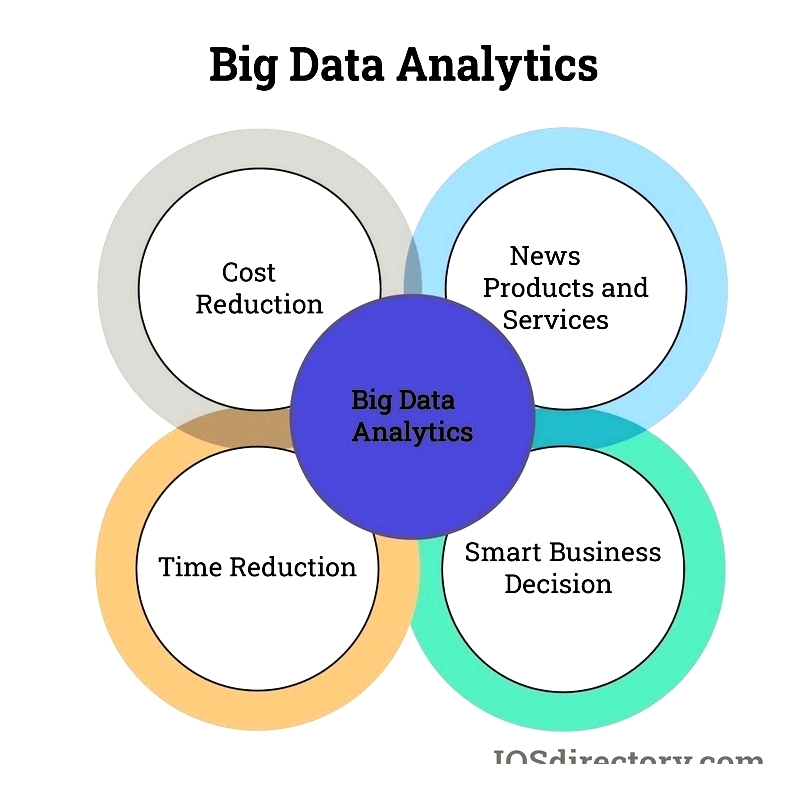
Big Data Analytics
Automation generates data for predictive analytics, demand forecasting, and process optimization. IoT sensors and AI enhance AS/RS performance, route optimization, and KPI monitoring in modern warehouses.