Introduction
This article provides a comprehensive overview of investment casting.
You'll explore key topics including:
- What is Investment Casting?
- The Investment Casting Process
- Types of Investment Casting
- metals Used in Investment Casting
- And Much More...
Chapter One - What is Investment Casting?
Investment casting is a metalworking process that involves creating a ceramic shell around a wax pattern to produce components with exceptionally smooth surfaces. The wax pattern is typically made using an aluminum die. After casting, the final products show minimal parting lines or mold marks, which are removed during finishing to achieve the desired smoothness.

This method produces parts while minimizing waste and energy consumption. Its key advantage lies in the high precision and tight tolerances of the final products.
Chapter Two - The Investment Casting Process
Also known as lost wax casting, this ancient technique originated in China and was rediscovered by modern industry in the 20th century. Today, it's essential for manufacturing complex, high-precision components with excellent surface quality, making it popular in aerospace, automotive, medical, and energy applications.
During World War II, investment casting gained prominence for producing precision parts unattainable through traditional methods. Post-war, it became the preferred choice for industrial applications requiring intricate designs like turbine blades and medical implants where accuracy and surface finish are critical.
The Investment Casting Process
This precision casting method involves multiple meticulous steps to ensure quality and consistency. Using engineered patterns, shell coatings, and controlled heating cycles, it produces near-net-shape parts that minimize machining requirements. Below we outline each step and key considerations for optimizing quality, cost, and material selection.
Investment Casting Tooling
Tooling focuses on wax injection dies that create patterns for the lost wax process. Precision tooling ensures dimensional accuracy and surface finish. The required tooling depends on part geometry, tolerances, production volume, and alloy material, all determined during engineering planning.
Advanced Product Quality Planning (APQP) examines each production stage to prevent errors and minimize waste. This comprehensive approach ensures tooling - including dies, patterns, and cores - is designed for defect prevention and efficient workflow, especially for complex geometries.
Investment Casting Die
The wax injection die results from APQP and forms the basis for wax patterns. Typically made from high-grade aluminum for its thermal conductivity and formability, these dies support efficient production. Steel may be used when superior durability or tighter tolerances are needed.

Waxes Used in Investment Casting
Various wax types are selected based on flow properties, melting temperature, and application needs. The choice significantly impacts process yield, speed, and final quality. Common types include:
- Filled pattern wax
- Non-filled pattern wax
- Runner wax
- Water-soluble wax
- Sticky wax
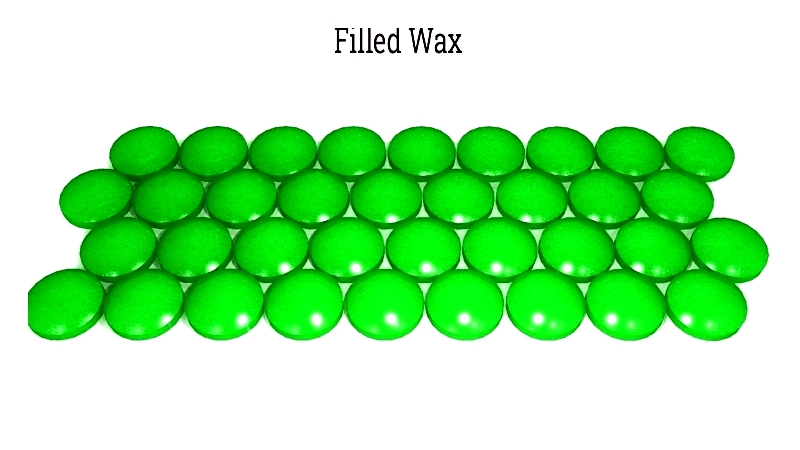
Filled Pattern Wax
Contains additives for dimensional stability and reduced shrinkage. Ideal for large or intricate parts requiring precise tolerances in aerospace and industrial applications.
Non-Filled Pattern Wax
Contains minimal filler while maintaining mechanical properties. Preferred for complex geometries and smooth patterns in medical device manufacturing.

Runner Wax
Engineered for strength with low viscosity. Its low melting point enables efficient dewaxing and minimizes shell cracking.
Water Soluble Wax
Enables complex internal geometries by dissolving to leave cavities. Used for aerospace components and medical implants. Removal involves water baths with mild acids for residue-free cavities.
Sticky Wax
Bonds wax patterns securely during assembly. Ensures alignment during handling and coating, critical for production runs.

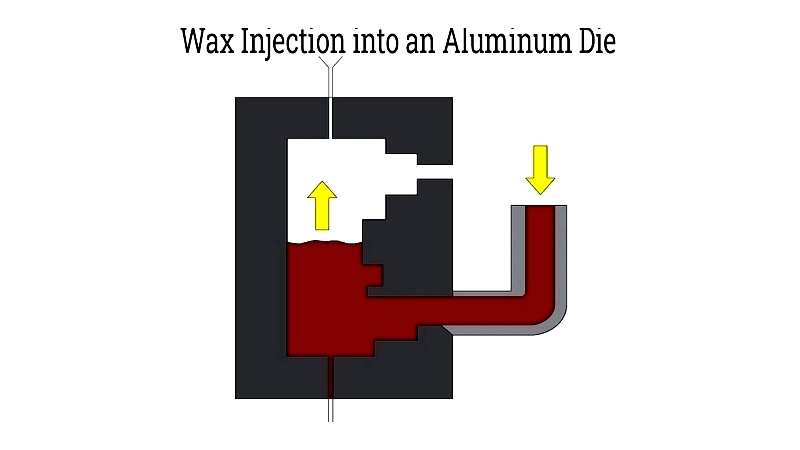
Investment Casting Wax Injection
Wax is injected into dies at controlled temperature and pressure to form patterns slightly oversized to account for shrinkage. The process begins with melting wax pellets in a holding tank, then injecting through a heated hose into the die cavity to replicate fine details.
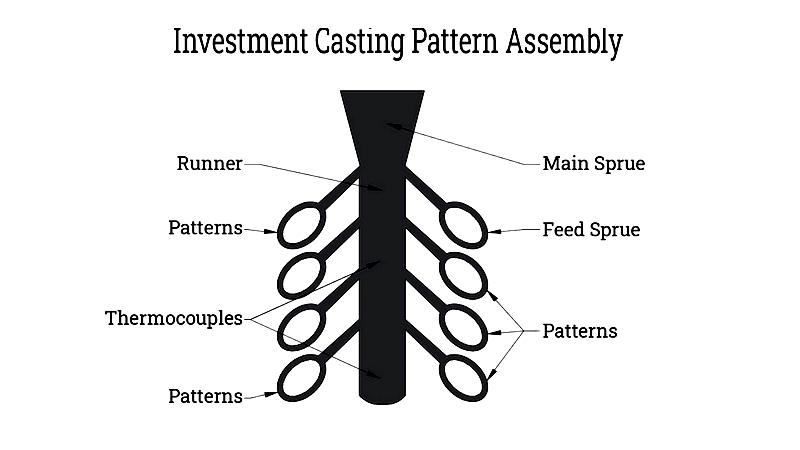
Pattern Assembly
Multiple wax patterns are assembled onto a central runner system for batch processing. The runner distributes molten metal during casting. Patterns are attached using melted wax or adhesives, with connections smoothed for structural integrity.
Shell Coating
The wax assembly is dipped in a slurry mixture to build a ceramic shell. Multiple layers are applied with drying between each to achieve required thickness and strength. This process impacts final surface quality and part integrity.

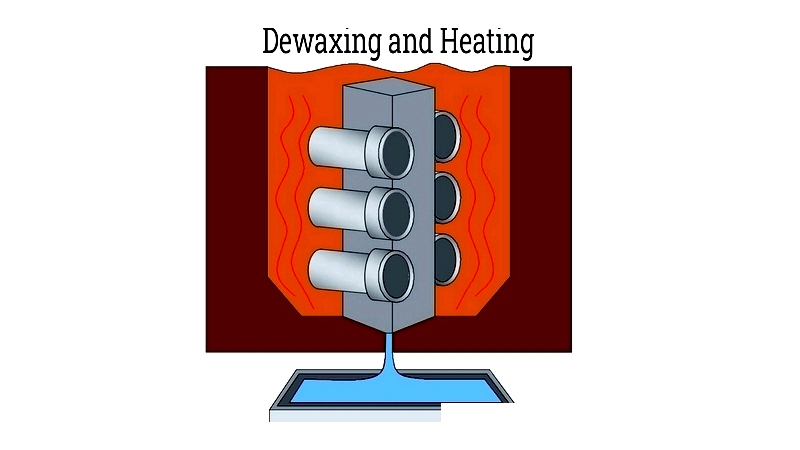
Dewaxing and Heating
Wax is removed using steam in an autoclave, followed by furnace heating to strengthen the shell. Temperature control is critical for process consistency and defect prevention.
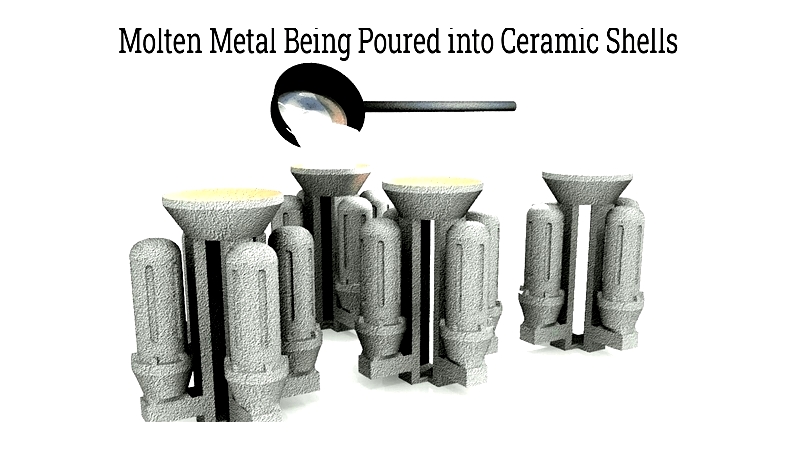
Molten metal Casting
metal is poured into preheated shells with precise temperature control. Vibration may be used to ensure complete filling. Proper cooling rates are essential for dense, high-quality castings.

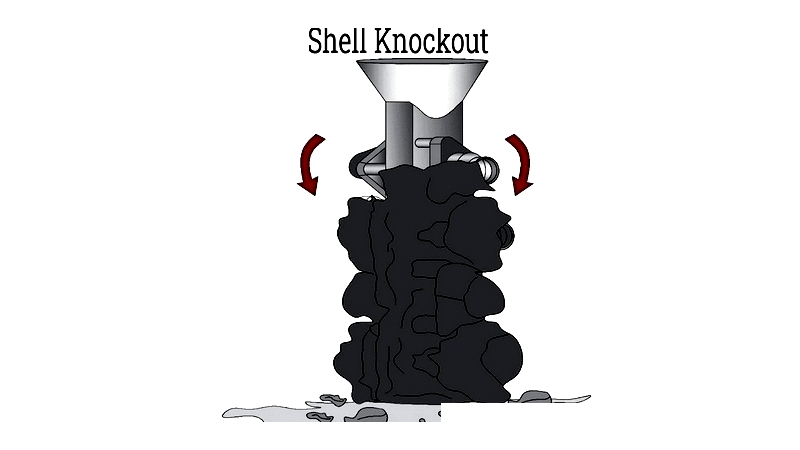
Shell Knockout or Removal
After cooling, the ceramic shell is removed using mechanical, hydraulic, or chemical methods. Care is taken to preserve delicate features while completely eliminating the shell.
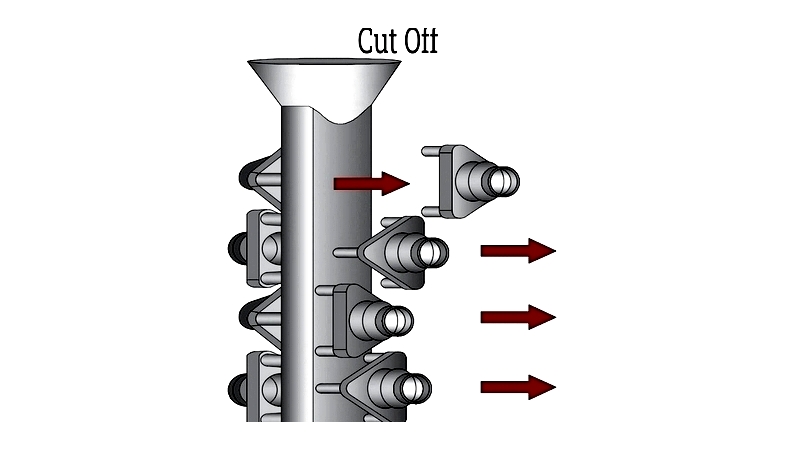
Cut Off
Parts are separated from runners using saws, torches, or lasers. Remaining material is ground away to meet dimensional requirements.