Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of magnetic door latches.
Key topics covered include:
- Principles of Magnetic Door Latches
- Design, Installation and Materials of Magnetic Door Latches
- Types of Magnetic Door Latches
- Applications and Benefits of Magnetic Door Latches
- And More...

Chapter 1: Understanding the Principles of Magnetic Door Latches
This chapter examines the functionality and operation of magnetic door latches.
Defining Magnetic Door Latches
A magnetic door latch consists of a magnetic component and striking pad designed to keep doors securely closed. Also known as magnetic door stops or catches, these devices are commonly used in cabinets and lightweight doors.

These latches feature a magnetized catching body paired with a ferromagnetic strike plate, making them effective for automatic door securing. Some models use dual magnets—one on the door and another on the frame—ideal for light-duty applications.
The latch casing is typically made from non-ferromagnetic metal or plastic, housing a bar magnet. Steel plates at the magnet's top and bottom concentrate magnetic flux. These plates contact the striker plate when engaged. Latches can be surface-mounted or concealed, with the strike plate on the door edge. The magnetic connection forms when the door closes.
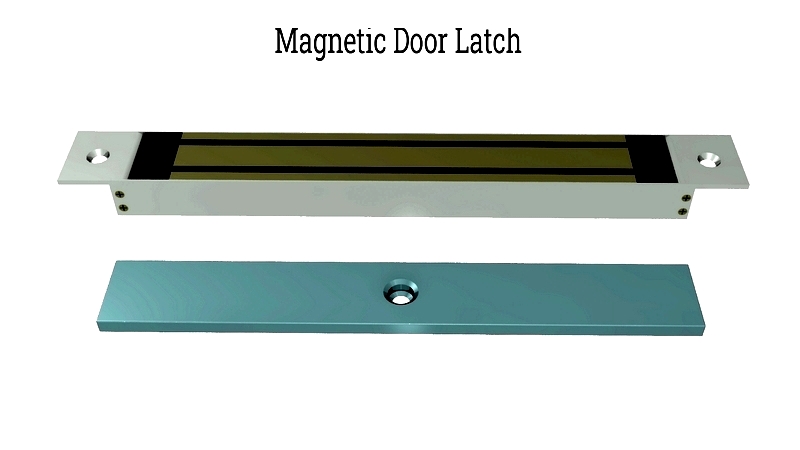
A standard magnetic catch includes an armature plate and magnet. The magnet is installed on one surface, the plate on another, creating a magnetic bond when aligned. Separation requires breaking this bond.
Electromagnetic locks, powered by electricity, often integrate with access control systems. These may connect to motion sensors, exit switches, or credential readers. Some models feature signal switches for lock management.
Magnetic latches are fail-safe, unlocking during power outages. Continuous power maintains the locked state. They operate on AC or DC current, providing strong holding force. Fire-rated magnetic locks must connect to alarm systems for emergency release.
Locks with 500-1,000 lbs. holding force suit interior wood/aluminum doors. Higher security applications require 1,000-3,000 lbs. capacity for hollow metal doors.
Available in various shapes (round, square, rectangular), larger models offer greater holding force. Some include battery backups for power outage protection.
The Functionality of Magnetic Door Latches
Electromagnetic locks use electromagnetism to secure doors when energized. Proper alignment between lock and armature plate is essential. These devices create strong magnetic fields through coiled wire solenoids.

Magnetic flux increases significantly when solenoids surround ferromagnetic cores like iron, enhancing latch effectiveness.
Chapter 2: Design, Installation, and Materials of Magnetic Door Latches
This chapter covers magnetic latch design, installation, and material selection for various applications.
Magnetic Door Latch Design
Modern latches combine precision metal plates with strong permanent or electromagnets. Typically housed in durable plastic casings with mounting flanges, they offer reliable operation for diverse applications.
The magnetic force holds doors securely while allowing easy manual or automated release. Simple door closure reactivates the catch, making these latches popular for access control systems.

Available in various designs, material selection affects both performance and aesthetics. Key considerations include:
Material: High-quality latches use durable metals like carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum alloys. Polycarbonate and rubber components reduce noise in high-traffic areas.

Finishing: Electroplating, powder coating, and painting enhance corrosion resistance and appearance.
Polishing: Mechanical and electrochemical processes ensure smooth, burr-free surfaces.

Strength: Categorized as light, medium, or heavy-duty based on component thickness and composition.
Mounting: Options include flush, mortise, or surface mounting for different architectural needs.
Handedness: Available in left/right configurations, with many designs being reversible.
Installation Process
Suitable for various door types, installation requires proper bracket selection for alignment. Filler plates assist with limited-space installations.
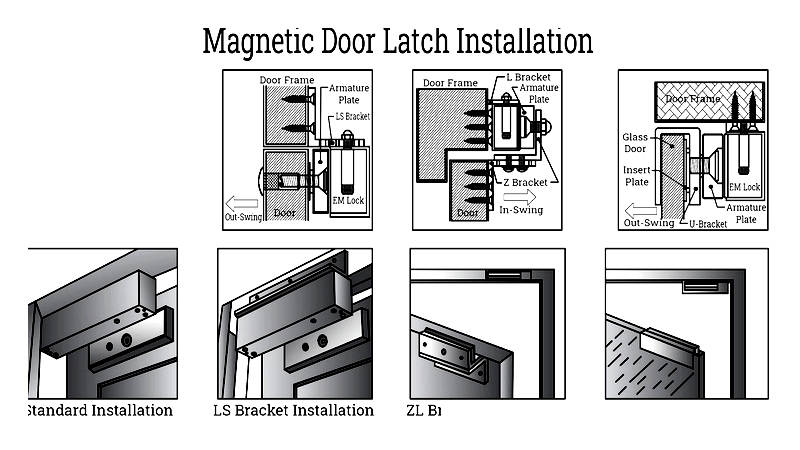
Inward-swinging doors: Mount electromagnet on frame header, armature plate on door.
Outward-swinging doors: Install electromagnet on side header with Z-bracket armature.
Shear locks allow bidirectional operation, while fire-rated installations require emergency release integration.
Materials Overview
Manufactured through precision metal stamping and welding, magnetic latches offer durability for various applications.

Aluminum: Lightweight and rust-resistant, ideal for light-medium duty.

Brass: Decorative choice requiring regular polishing.
Bronze: Durable with distinctive patina, suited for architectural applications.

Chrome: Glossy finish best for low-traffic areas.

Iron: Rugged option needing regular maintenance.

Stainless Steel: Premium corrosion resistance for demanding environments.




