Introduction
This article provides information about 55-gallon plastic drums and their applications.
You will learn about:
- What a 55-gallon plastic drum is
- How 55-gallon plastic drums are manufactured
- The types of plastic used in 55-gallon plastic drums
- The different varieties of 55-gallon plastic drums
- And more...

We can assist with your research by connecting you with industry experts.
Chapter One – What is a 55 Gallon Plastic Drum?
A 55-gallon plastic drum is a durable container designed for storage and transportation, constructed from industrial-grade high-density polymer. These drums feature thick walls that provide excellent durability, strength, and longevity, making them suitable for safely storing various substances. Their seamless design makes them particularly effective for containing hazardous solids and liquids.

Known for their strength and durability, 55-gallon plastic drums are essential in industries like distribution, shipping, and storage. Their robust construction makes them valuable for chemical handling, food processing, and manufacturing applications.
Chapter 2 – How 55 Gallon Plastic Drums are Made
The production of 55-gallon plastic drums begins with selecting high-density polymers, typically HDPE or LLDPE for specialized applications. These materials are chosen for their impact resistance, chemical stability, and suitability for storing industrial liquids, food products, hazardous materials, and pharmaceuticals. Raw materials start as resin pellets or granules, which may come from recycled plastics or virgin resin, meeting strict quality standards.
While resin materials may look similar, their molecular structure, strength, and density vary significantly. These viscous substances become rigid polymers through polymerization. Modern drum manufacturing favors synthetic resins like HDPE for their mechanical properties, durability, and chemical resistance. Food-grade resins comply with FDA and USDA requirements, making them suitable for hygienic packaging.
Manufacturing Processes
The three main processes for producing 55-gallon plastic drums are rotational molding, injection molding, and injection blow molding. Injection blow molding is the most common and efficient method, creating seamless, durable drums. In blow and injection molding, melted resin pellets are injected into a drum-shaped mold to form leak-proof vessels. Rotational molding, ideal for custom designs, uses resin powder in a rotating heated mold for uniform wall distribution. These methods allow for UN/DOT compliance, stackability, and tamper-evident features.
Resin Pellets
Resin pellets, the base material for drum production, are typically clear or white but can be colored. Standard colors like blue, white, yellow, and black are readily available, while custom colors can be produced for branding. During molding, these pellets are melted to form a parison, the precursor to the final drum shape.
To enhance durability, manufacturers add UV stabilizers to resin pellets. These additives protect against sunlight damage, with black plastic offering the best UV resistance. Lighter colors are better suited for indoor use. This customization ensures buyers can select drums appropriate for their storage needs.

Blow Molding Drums
Blow molding is the primary method for manufacturing 55-gallon plastic drums, ensuring consistent wall thickness and structural integrity. The process involves inflating a parison with pressurized air inside a mold. There are three main blow molding techniques:
- Extrusion Blow Molding: Molten resin is extruded vertically to form a parison, which is then inflated in a mold.
- Injection Blow Molding: Resin is injected into a preform mold, then transferred to a drum mold for final shaping.
- Injection-Stretch Blow Molding: The parison is stretched and blown for enhanced strength, used for high-performance drums.
Each method offers advantages in production speed, precision, and cost, making blow-molded drums ideal for bulk liquid transport and hazardous materials.
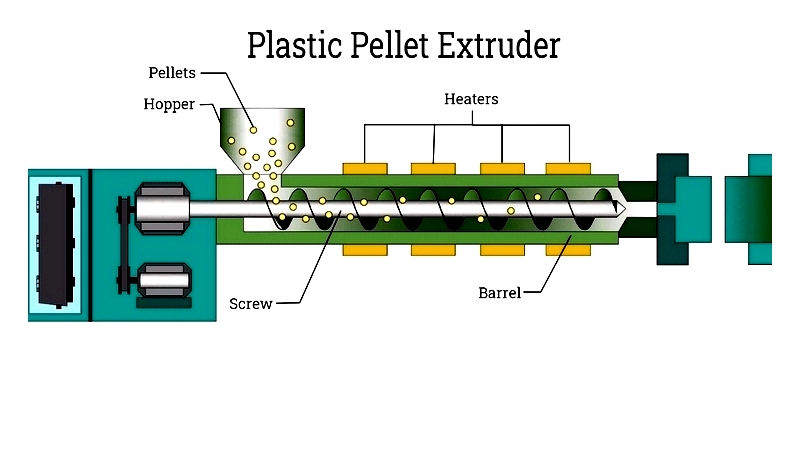
Feeding Plastic Pellets
The process starts with resin pellets being fed into a hopper, either manually or via automated systems. The pellets are then conveyed into an extruder, where they are heated and mixed. Precise temperature control ensures uniform melting, creating a defect-free parison.
Maintaining proper temperature and feed rate is crucial for preserving material properties and preventing defects. The feeder and extruder's capacity and automation level influence both cost and quality, important factors when comparing suppliers.
Inserted into the Mold
The melted parison is placed into an open drum mold, designed for precise capacity and geometry. Mold features like venting and cooling channels ensure uniform wall thickness and structural integrity, critical for industries ranging from food processing to chemical containment.
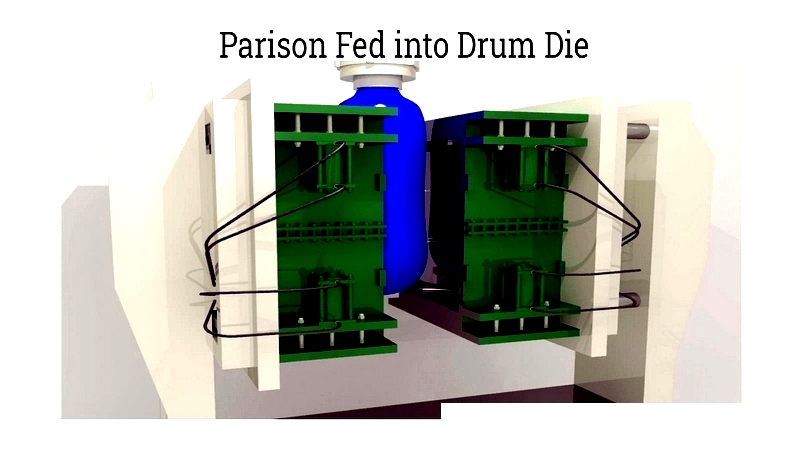
Closing the Die
The die sections are pressed together using pneumatic or hydraulic systems, sealing the parison ends. A top opening allows for pressurized air injection, ensuring the drum meets performance standards for pressure and leak resistance, particularly important for DOT/UN-rated containers.

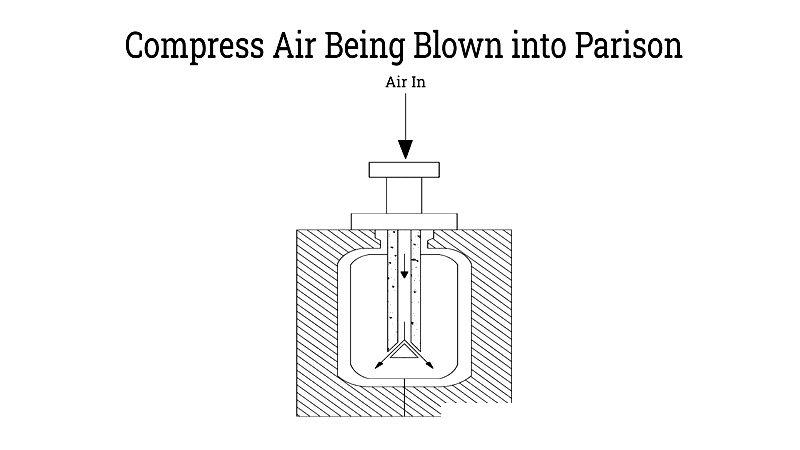
Air Being Forced into Parison
Compressed air is injected into the parison at high pressure, expanding it against the mold's interior. This step ensures even wall distribution and eliminates weak spots, crucial for safely storing liquids and hazardous materials.
Removal of Solidified Drum
After cooling, the mold opens, and the finished drum is ejected. Secondary operations may include trimming excess material, adding bung holes, or printing information. This efficient process ensures consistent quality and compliance with international standards.

Rotational Molding Drums
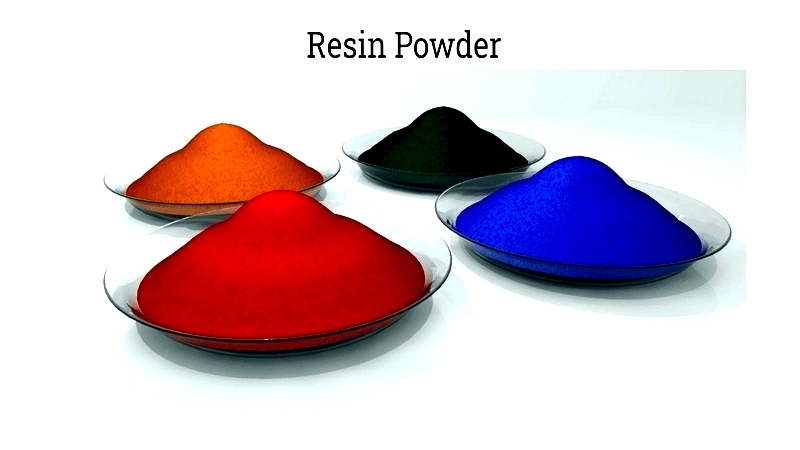
Resin Powder
Rotational molding uses resin powder, typically polyethylene or specialty plastics, for custom shapes or smaller production runs. The powder remains solid until heated in the mold, allowing precise control over wall thickness and properties.

Rotational Mold
Rotational molds are made




