Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of metal grating.
You'll discover information on:
- What metal Grating Is
- metal Grating Types
- metals Used in metal Grating
- metal Grating Manufacturing Process
- And more...

Chapter One – What is metal Grating?
metal grating consists of metallic sheets arranged in a grid or lattice pattern, achieved through perforation or assembly. Widely used across industries, it serves as stairs, platforms, scaffolding, and shields. Manufacturing methods include expansion, perforation, shaping, and welding.
Originally developed to improve underground air circulation and prevent heat buildup, metal grating gained recognition during World War II for rapid runway and emergency path construction, earning the nickname "magic carpets."
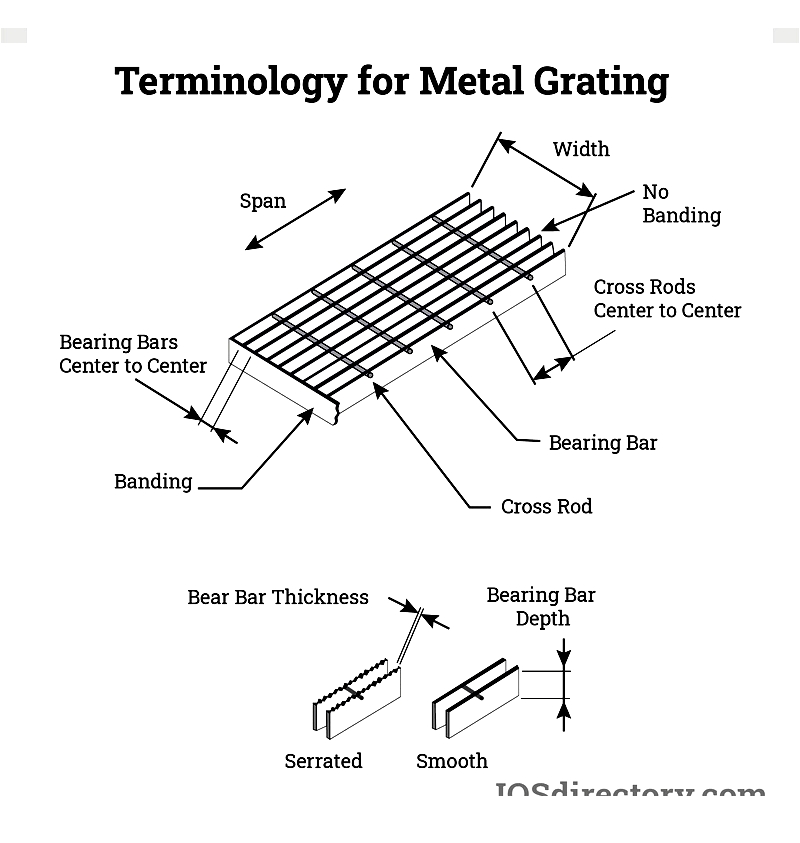
Key design considerations include thickness, bar sizes, pattern openings, load capacity, and installation environment. Available in standard or custom sizes, metal gratings adapt to specific application needs, with customized options frequently addressing unique installation requirements.
Common metals for grating include iron, carbon steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, typically used for non-slip applications requiring secure platforms.
metal gratings come in various patterns and designs, including steel grating-plate combinations. Production methods like welding, press-locking, or metal plate integration ensure durability in demanding environments.
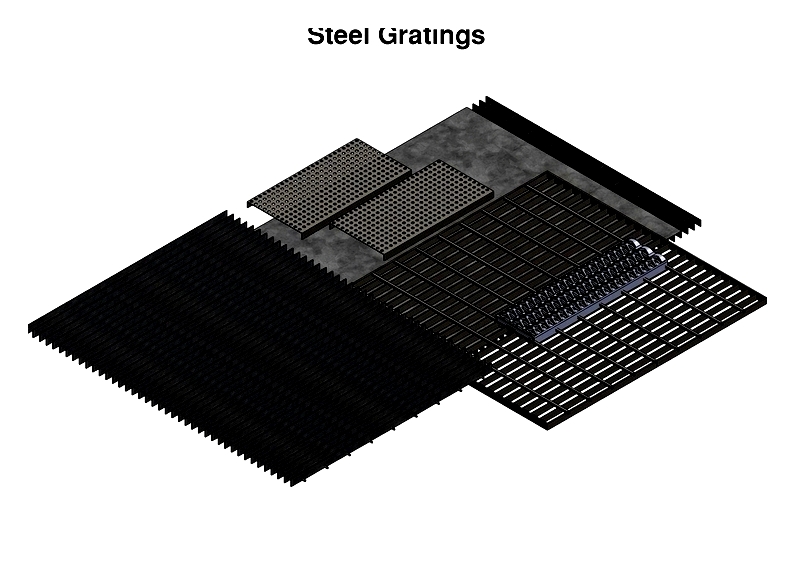
Chapter Two – Types of metal Gratings
Engineers and designers create functional metal grating solutions tailored to load-bearing, safety, and environmental needs. Key specification factors include thickness, surface area, load capacity, span, bar dimensions, panel size, and opening patterns (oval, square, diamond) that impact industrial and architectural performance.
Additional design considerations include light transmission, ventilation, drainage, acoustics, aesthetics, and slip resistance. Heavy-duty applications often use welded steel or pressure-locked bar grating for strength in manufacturing plants and chemical facilities.
Expanded metal Gratings
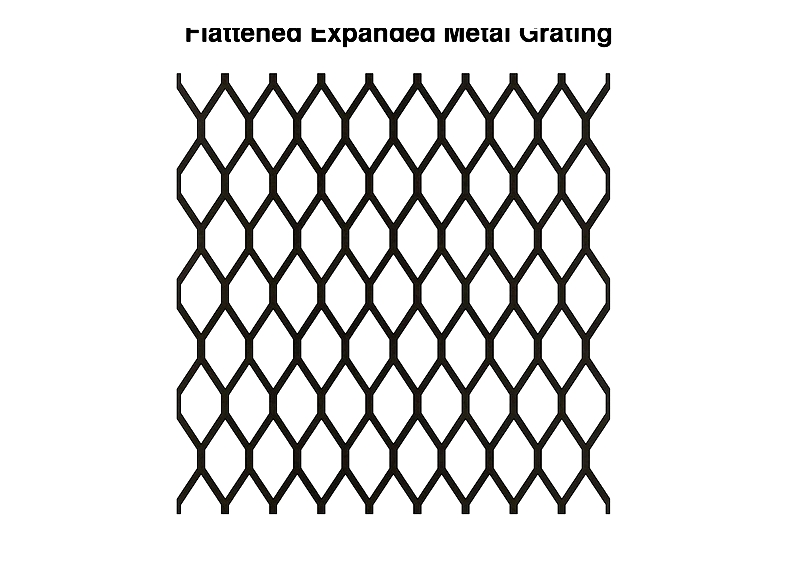
Expanded metal grating features a diamond-shaped mesh created by slitting and stretching metal sheets, offering rigidity without welding. Made from carbon steel, stainless steel, or aluminum, it suits indoor/outdoor and corrosive environments.
Standard versions provide slip resistance for walkways and platforms. Flattened types offer smooth surfaces for foot traffic, while raised versions enhance traction for safety-critical areas.
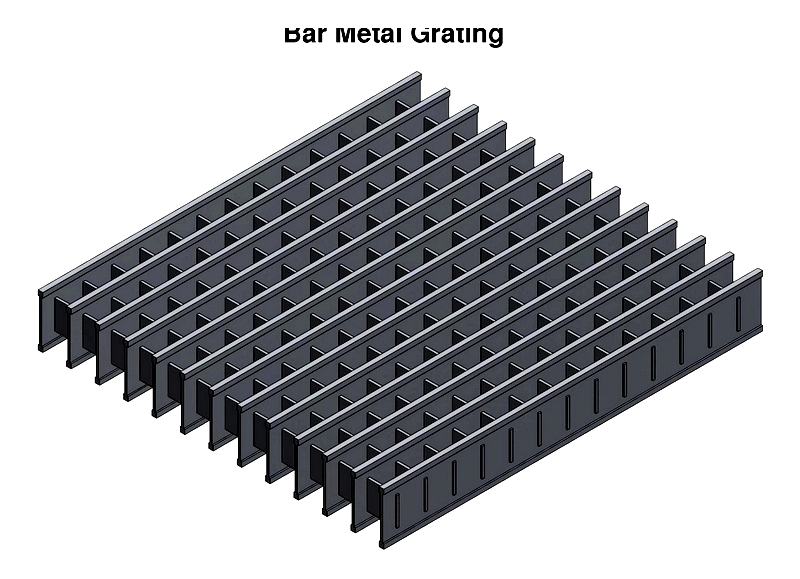
Bar metal Grating
Industrial bar grating consists of parallel load-bearing bars connected by cross bars via welding, press-locking, riveting, or swaging. Welded versions provide maximum rigidity for industrial flooring and catwalks.
Material selection (galvanized steel, stainless steel, aluminum) depends on load, environment, and corrosion needs. Its strength-to-weight ratio and open design make it ideal for trench covers, stair treads, and bridges.
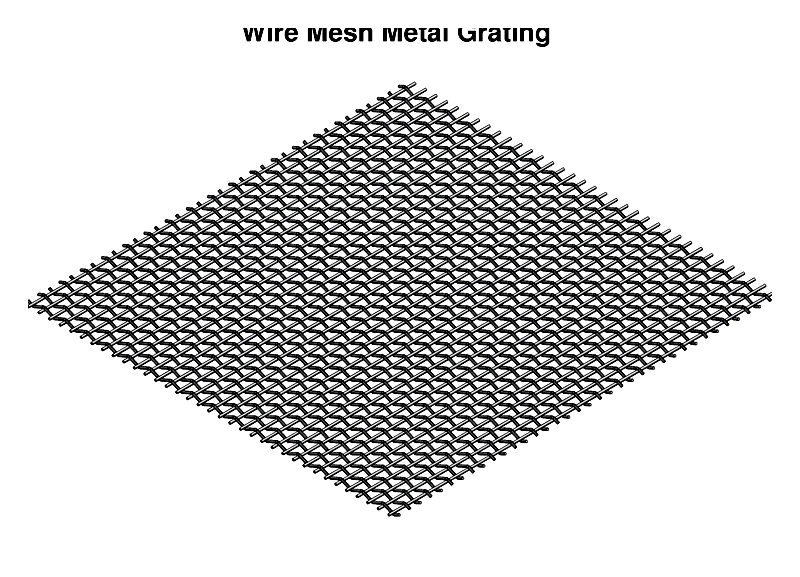
Wire Mesh metal Grating
Wire mesh grating features intersecting wires in grid patterns, valued for adaptability and strength. Welded versions offer structural integrity, while woven types provide flexibility.
Used for machine guarding, fencing, and filtration, stainless steel versions resist harsh environments.
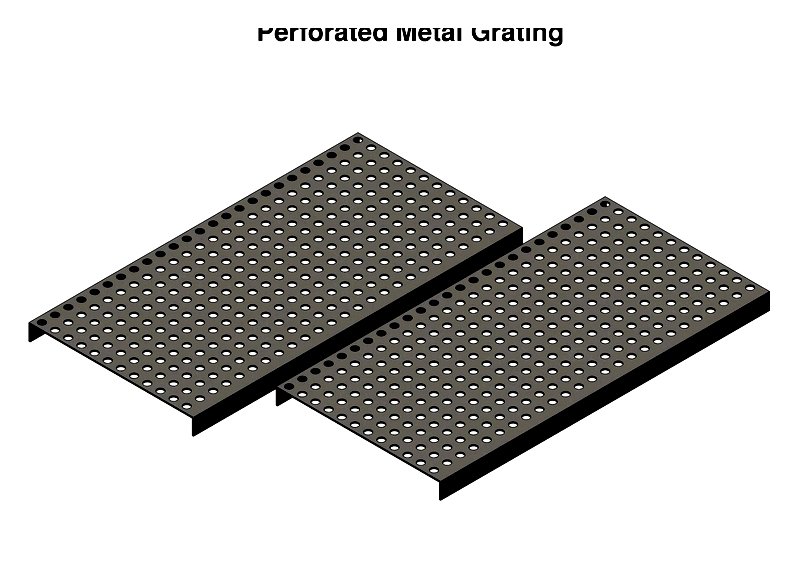
Perforated metal Grating
Perforated grating contains precision-cut holes in metal sheets, offering strength and slip resistance. Applications include industrial flooring, architectural facades, and filtration systems.
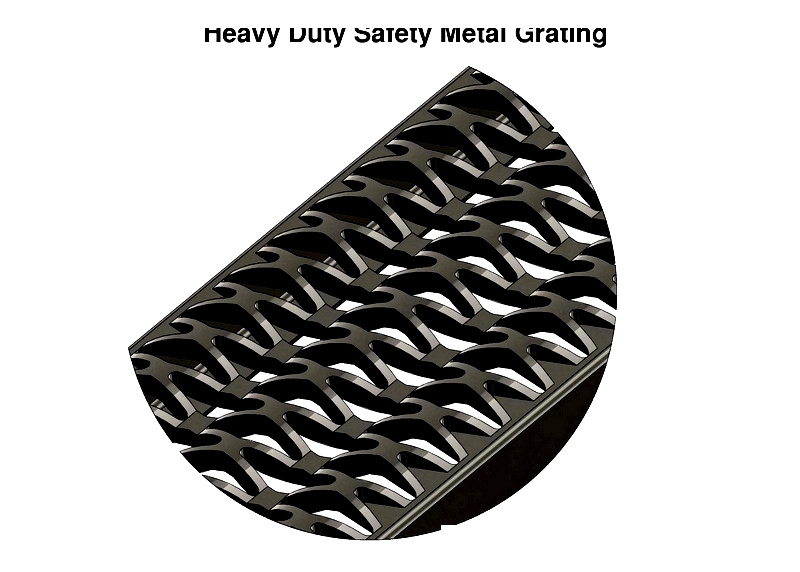
Safety Grating
Safety grating features diamond/serrated patterns for slip resistance in industrial settings. Designs allow drainage and airflow, meeting OSHA standards with galvanized or stainless steel construction.

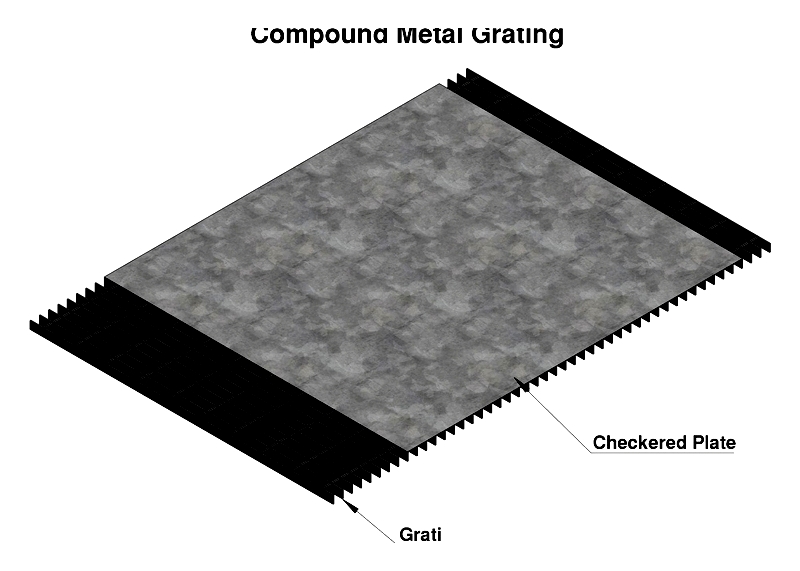
Compound metal Grating
Combining bar grating with checkered plates, compound grating increases traction and load distribution. Ideal for industrial platforms and bridge decks.
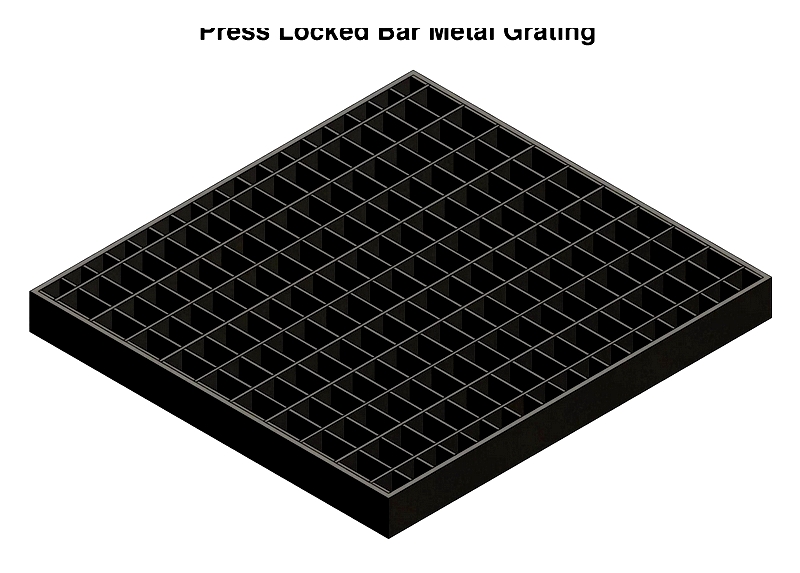
Press Locked metal Grating
Press-locked grating features notched bars pressed together for seamless surfaces. Used in architectural projects requiring both strength and aesthetics.





