Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of electroless nickel plating and its applications.
You will learn about:
- The fundamentals of electroless nickel plating
- The electroless nickel plating process
- Different types of plating processes
- Variations in electroless nickel plating
- Practical applications of electroless nickel plating
And much more...

Chapter One: Understanding Electroless Nickel Plating
Electroless nickel deposition (END) is a chemical process that creates a nickel-based coating through controlled chemical reactions. This technique reduces nickel ions to their metallic state using chemical agents like sodium hypophosphite. END significantly enhances corrosion resistance against elements such as saltwater, carbon dioxide, oxygen, and hydrogen sulfide. The process delivers uniform, smooth finishes across entire surfaces, including complex geometries like slots, holes, and tube interiors.
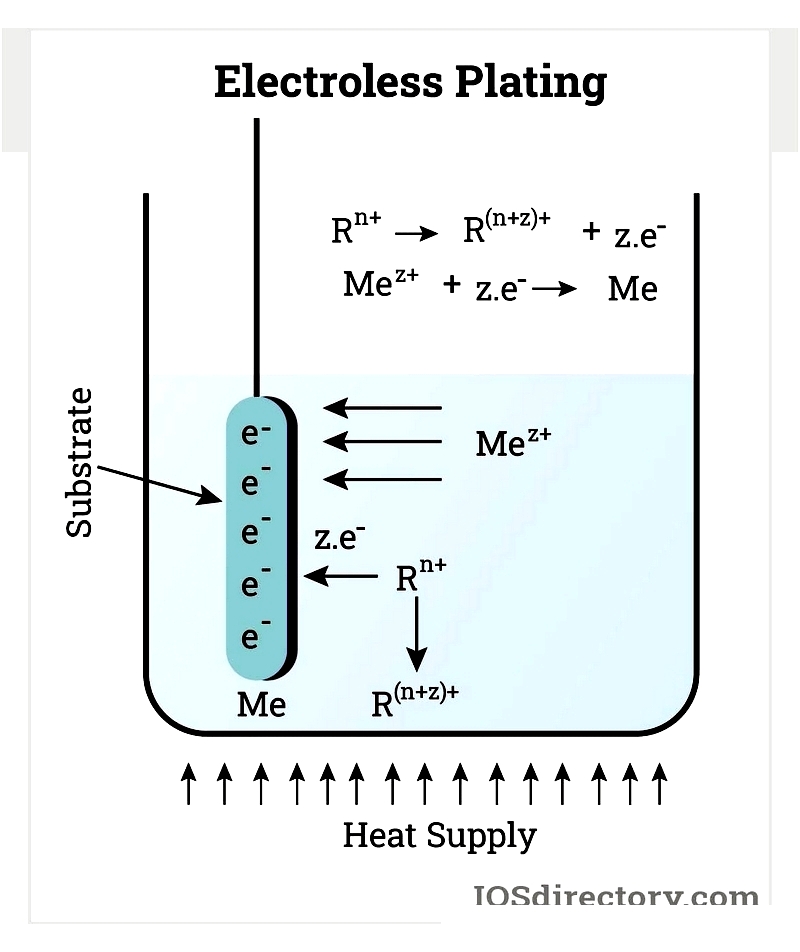
The success of electroless plating depends on thorough surface preparation, as uneven or rough surfaces can lead to bonding issues. This process provides protection against wear, abrasion, and corrosion while improving surface performance. It's an efficient, cost-effective method for achieving durable, high-quality finishes.
Chapter Two: The Electroless Nickel Plating Process
The electroless nickel plating process is a versatile surface finishing technique used across automotive, aerospace, electronics, and manufacturing industries. Unlike traditional electroplating, this auto-catalytic chemical deposition method creates uniform nickel-phosphorus or nickel-boron alloy coatings without electrical current. Process success depends on meticulous surface preparation, chemical activation, and precise control at each stage, ensuring optimal plating adhesion, corrosion resistance, and wear protection.
Surface Preparation
Before plating begins, surfaces must be thoroughly cleaned to remove contaminants that could affect coating adhesion. Industrial degreasers, alkaline cleaners, and ultrasonic techniques remove grease, oils, and other residues. Proper surface preparation ensures consistent plating thickness and coating integrity in corrosive environments.
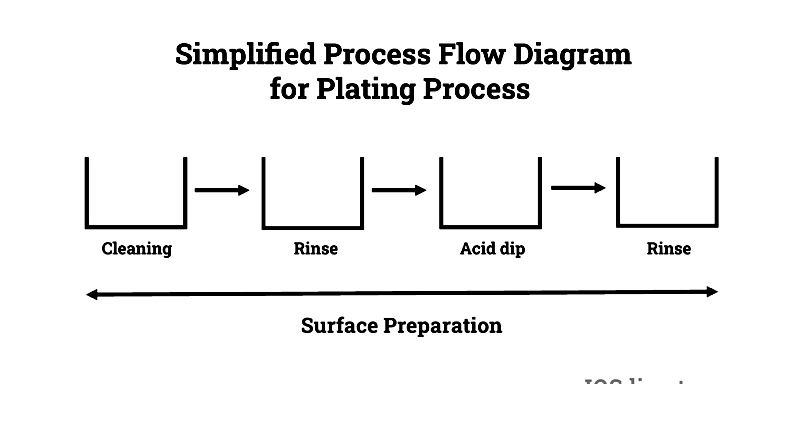
Activation
After cleaning, surface activation removes residual oxide films using acidic solutions. This step is particularly important for non-ferrous metals and alloys, ensuring proper adhesion of the electroless nickel-plated layer and preventing defects like pitting or delamination.
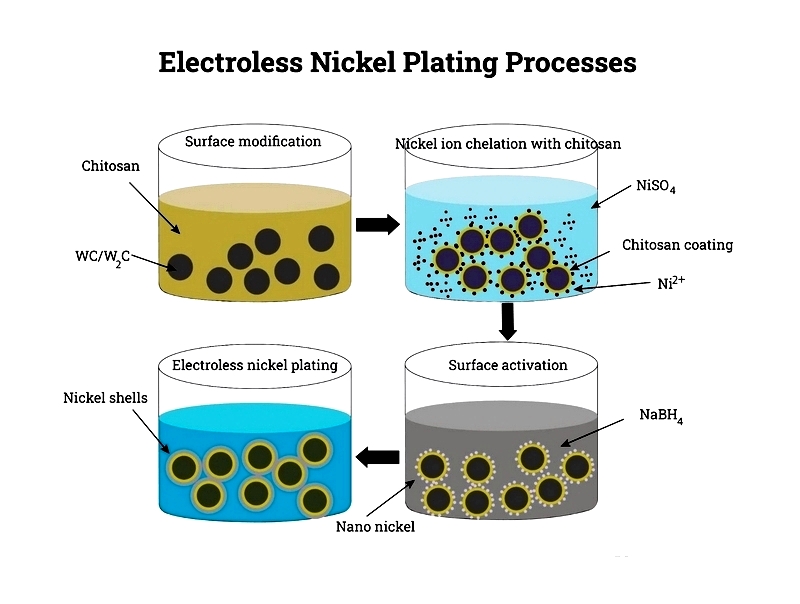
Pre-Treatment
Depending on the substrate material (steel, aluminum, copper, or plastic), specific pre-treatment techniques enhance adhesion and corrosion resistance. Zincate treatments for aluminum or palladium catalysts for non-conductive surfaces prepare materials for the plating bath stage.
Electroless Nickel Plating
During this stage, pre-treated substrates are immersed in a solution containing nickel ions and reducing agents. The chemical reaction deposits a dense, uniform nickel-phosphorus alloy layer across all surfaces, including complex geometries. This method achieves superior thickness uniformity compared to electrolytic plating.

Post-Treatment
After plating, components undergo post-treatment procedures like rinsing, drying, and heat treatment to enhance performance. Additional treatments may include passivation or protective topcoats to extend durability and meet specific industry standards.
By carefully following each process stage, manufacturers achieve reliable surface engineering solutions that meet stringent industry requirements for corrosion protection, hardness, and quality.
Chapter Three: Leading Electroless Nickel Plating Machine Manufacturers
Electroless nickel plating machines are essential for industrial finishing, providing uniform, corrosion-resistant coatings across various industries. These automated systems deliver robust plating solutions that enhance protection and component performance. Below are leading manufacturers and their flagship models in the United States and Canada.
Brand: SIFCO Applied Surface Concepts
Model: SIFCO Process® Equipment
Features: SIFCO offers industrial-scale to portable plating units with programmable controls for precise deposition. Their systems feature advanced filtration and solution circulation for stable bath chemistry and high throughput.
Brand: Technic Inc.
Model: Techni EN-BM Series
Features: These automated systems feature PLC controls for precise parameter regulation, including nickel ion concentration and temperature. Advanced solution management and filtration ensure consistent quality for aerospace and automotive applications.
Brand: C. Uyemura & Co., Ltd.
Model: Miralloy Series
Features: Flexible systems supporting various substrates and plating processes with intelligent controls for real-time monitoring. Advanced filtration extends solution life and improves efficiency.
Brand: Sharretts Plating Company
Model: Custom Electroless Nickel Plating Systems
Features: Custom-built systems with granular control over all plating parameters. Features include automated dosing, digital monitoring, and robust construction for diverse industrial applications.
Brand: metal Chem, Inc.
Model: Auto Catalyst 2000 Series
Features: High-volume production systems with fully automated operation, intelligent dosing, and in-line filtration. Designed to reduce cycle times while maintaining quality standards.
Selection Considerations: When choosing plating equipment, evaluate bath capacity, automation level, alloy compatibility, maintenance needs, and regulatory compliance. Consult manufacturers for detailed specifications and demonstrations.
Chapter Four: Types of Nickel Plating Processes
Nickel plating encompasses various methods, each with distinct applications. All methods aim to enhance nickel's corrosion and rust resistance properties.
Electroplating
This method uses electrical current to deposit metal coatings. The object connects to a power source's negative terminal while the plating metal connects to the positive terminal, with metal ions migrating through an electrolyte solution.
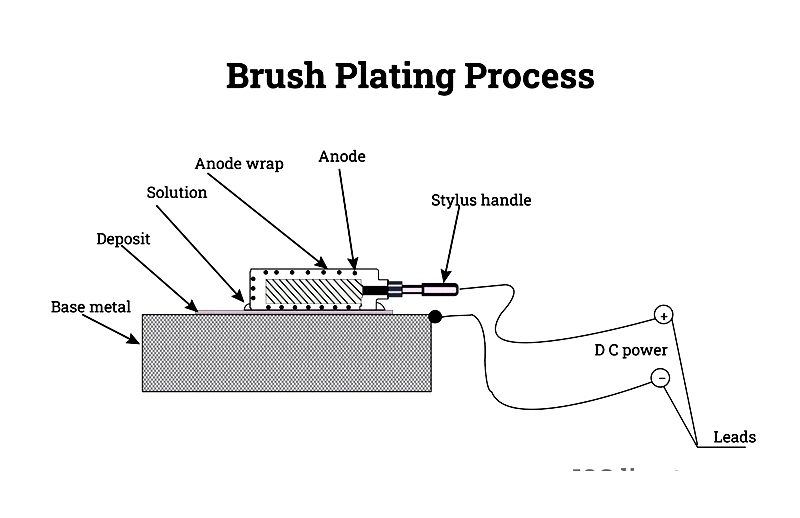
Brush Plating
A localized plating technique using a brush soaked in electroplating solution. Primarily used for repairs rather than full-surface coverage.
Hard Chrome Plating
Electroplating method that deposits thick chromium layers for enhanced wear resistance. Environmental concerns have led to alternative methods.





