Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of road cases and their applications.
You'll discover information on various topics including:
- What constitutes a Road Case
- Different Road Case varieties
- Road Case manufacturing processes
- Practical applications of Road Cases
- Regulatory standards for Road Cases
- And additional relevant information

Chapter One – Understanding Road Cases
A road case is a robust, durable protective container specifically engineered to endure the demanding conditions of transportation. With varying wall thicknesses, it offers impact resistance suitable for both air cargo and commercial shipping needs.
Typically constructed from high-quality black laminated plywood, these cases feature recessed steel handles, aluminum edges, and reinforced steel corner protection. Their interior configurations can be customized to accommodate specific contents.
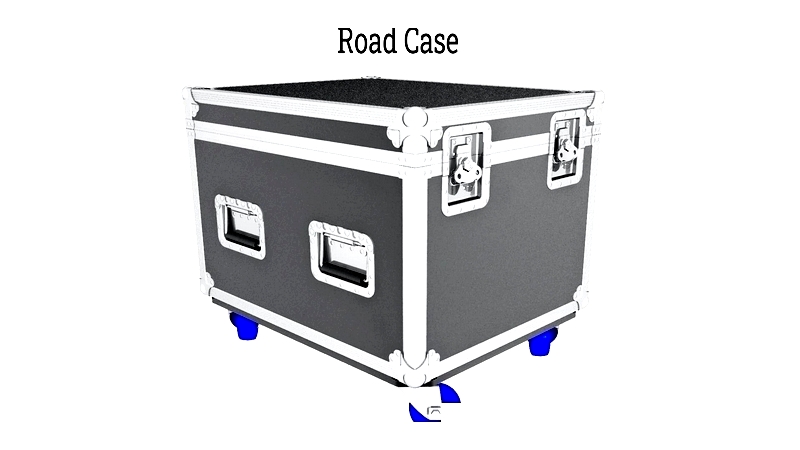

Premium road cases provide comprehensive protection against impacts, temperature fluctuations, shocks, vibrations, and environmental contaminants. They ensure safe transportation of delicate equipment through custom foam and rubber inserts.
Chapter Two – Road Case Varieties
Road cases, alternatively called flight cases or equipment transport cases, are precision-designed to protect sensitive equipment during transit and storage. Using premium materials like plywood, aluminum, and ABS laminates, these cases guarantee equipment arrives in optimal condition. Selecting appropriate shock-absorbing foam, hardware, and locking mechanisms is crucial for safeguarding valuable items against damage or theft.
Modern road cases offer diverse sizes and configurations for various applications. Whether transporting musical instruments, industrial equipment, or medical devices, their durability and protective qualities make them indispensable across industries. Below we examine the primary road case types addressing different transportation challenges.
Ramp Road Cases
These specialized cases incorporate ramps for easy loading of wheeled equipment like amplifiers or generators. Their designs range from simple wooden panels to retractable aluminum tracks, reducing injury risks and improving efficiency during setup.
Particularly useful for moving medical equipment or audiovisual carts, ramp cases often include custom foam inserts and locking features for enhanced security.

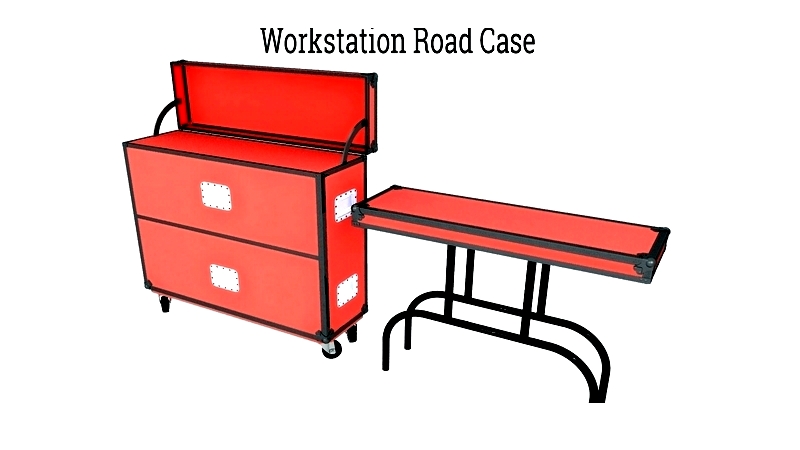
Workstation Road Cases
Combining storage with work surfaces, these mobile units feature tool organization systems, power strips, and cable management. They're ideal for field repairs, event production, or content creation.
Essential for field engineers and production crews, their rugged design with organized compartments ensures efficient operation in various environments.
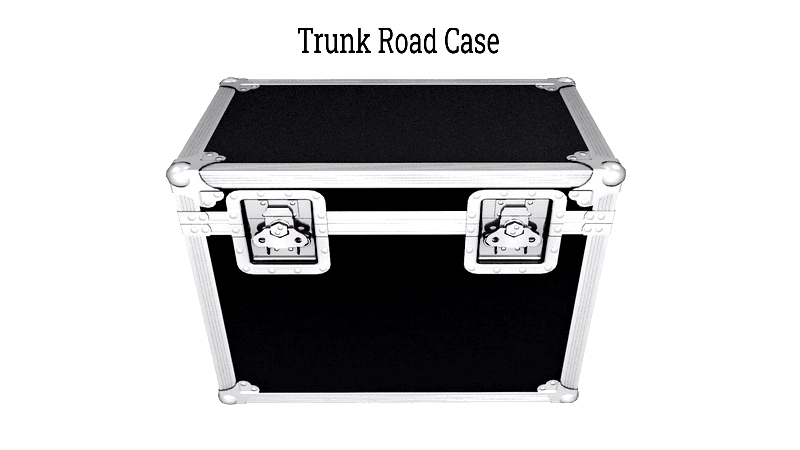
Trunk Road Cases
The most versatile option, trunk cases protect items from cables to delicate lenses. Their customizable interiors accommodate various equipment shapes while providing maximum protection.

A4A Road Cases
Meeting strict airline standards, these flight-approved cases undergo rigorous testing for durability. They're designed to withstand at least 100 trips without failure.
When selecting A4A cases, verify certification to ensure airline acceptance and optimal protection during transit.

Rack Mount Road Cases
Essential for transporting rack-mounted electronics, these cases provide vibration isolation and climate protection for sensitive equipment.

Workbox Road Cases
These mobile cabinets offer secure storage for tools and small parts, featuring locking drawers and wheels for easy transport.
Available in various configurations, they help professionals maintain organization during complex projects.

Selecting the Appropriate Road Case
Consider equipment size, transportation frequency, security needs, and shipping environment when choosing a case. Budget and compliance requirements should also inform your decision.
Understanding different road case types helps you select solutions that protect equipment and ensure reliable performance.




