Introduction
This article provides comprehensive information about rubber overmolding, covering topics such as:
- Different Rubber Overmolding Processes
- Key Design Considerations for Rubber Overmolding
- Rubber Types and Grades for Overmolding
- Regulatory Standards for Rubber Overmolding
- Quality Control in Overmolding
- Additional Factors in Rubber Overmolding
- Challenges and Limitations of Rubber Overmolding
- Advantages of Rubber Overmolding
- Industrial Uses of Rubber Overmolding
- Future Trends in Rubber Overmolding
- And more...
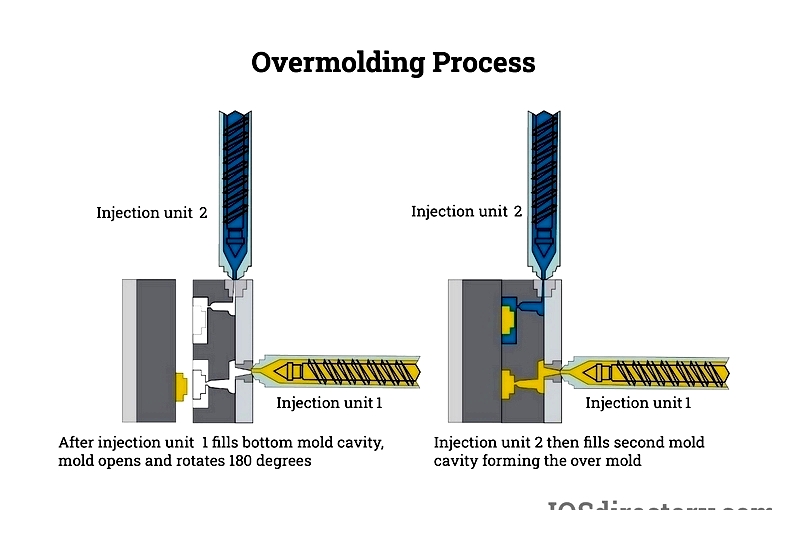
Chapter 1: What are the different rubber overmolding processes?
Rubber overmolding can be performed using various techniques, each with unique advantages and limitations. The optimal method depends on factors like material properties, product design, production volume, budget, and required precision.
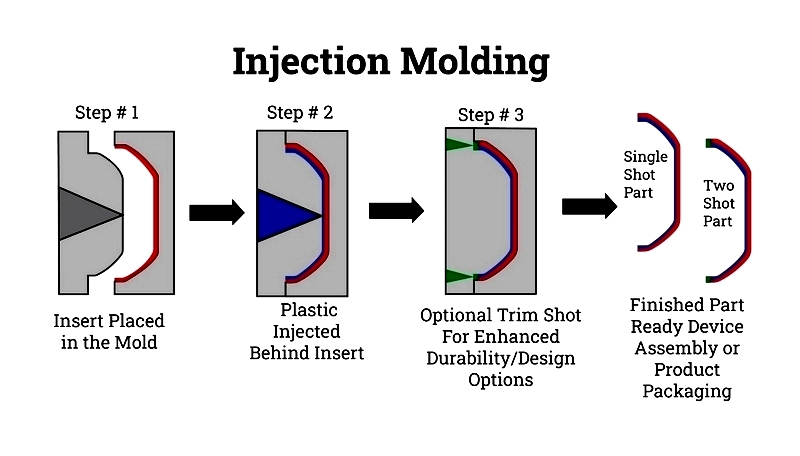
Injection Molding
Injection molding is the most common rubber overmolding technique. It involves injecting molten rubber into a mold containing the substrate (typically plastic or metal). After cooling and solidification, the mold opens to release the finished part. This method offers high accuracy and consistency, making it ideal for large-scale production.
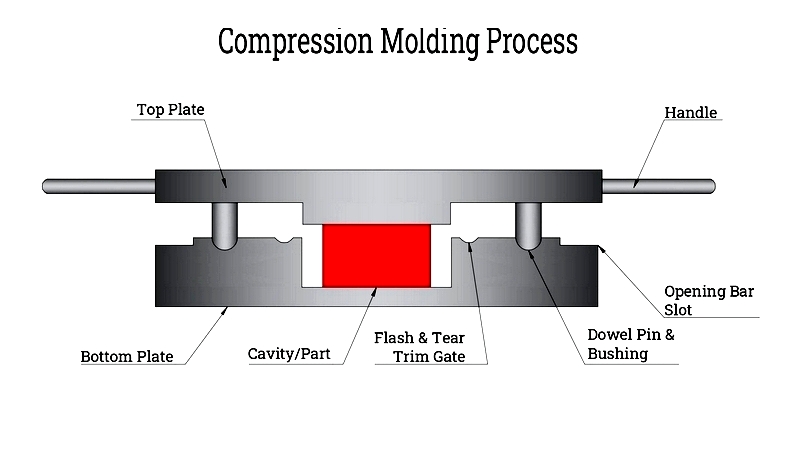
Compression Molding
Compression molding places the substrate in a mold that's then sealed and heated. Molten rubber is applied under pressure to conform to the substrate. After cooling, the finished product is removed. This method works well for complex shapes and small production runs.
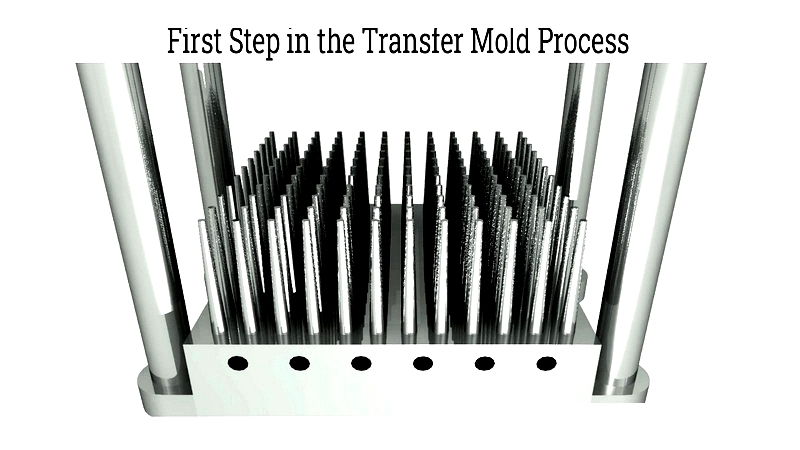
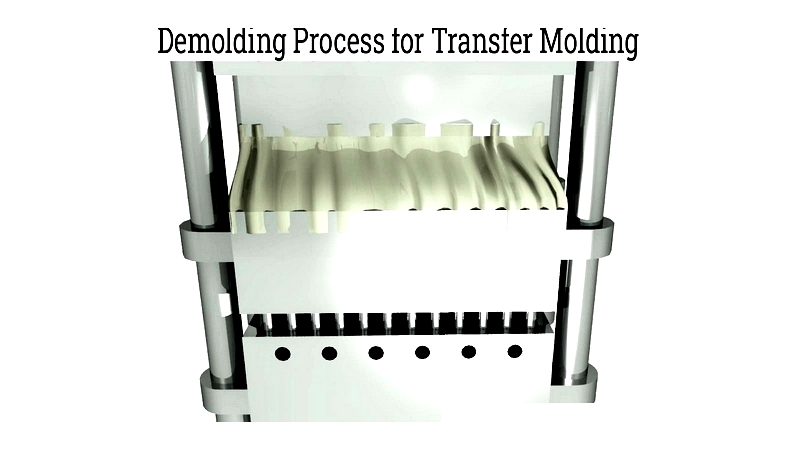
Transfer Molding
Similar to compression molding but with an added transfer pot, this technique injects molten rubber through a channel into the mold. Transfer molding is suitable for high-precision components with intricate designs.
LIM (Liquid Injection Molding)
LIM injects liquid rubber into a mold where it cures. This method features fast cycle times, exceptional precision, and is particularly effective for delicate substrates or electronic components.
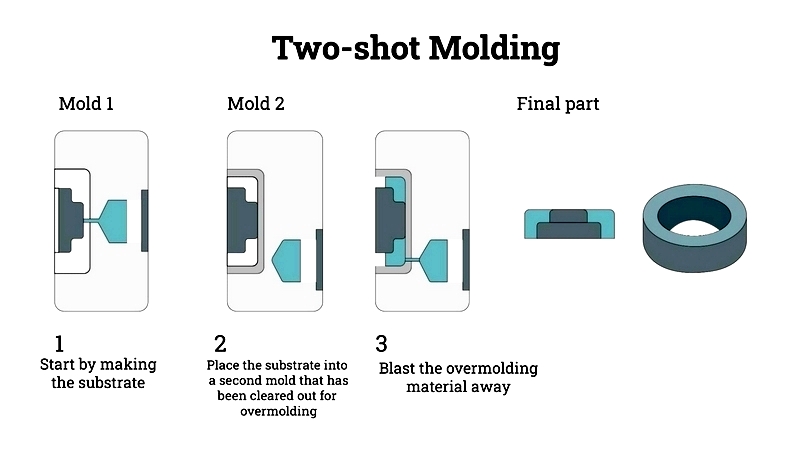
Two-Shot Molding
Also called dual-shot molding, this process injects two different materials into a single mold. It's commonly used to create multi-material products with complex designs, offering production efficiency and cost benefits across various industries.
Selecting the appropriate rubber overmolding technique requires evaluating factors like product complexity, production requirements, precision needs, and budget constraints. Each method offers distinct advantages and challenges, so the decision should align with specific manufacturing goals.
Chapter 2: What design factors should be considered for rubber overmolding?
Design considerations significantly impact the quality, functionality, and durability of rubber overmolded products. Whether creating automotive seals, medical device grips, or industrial handles, understanding these fundamentals is crucial for optimal results. Key design factors include:
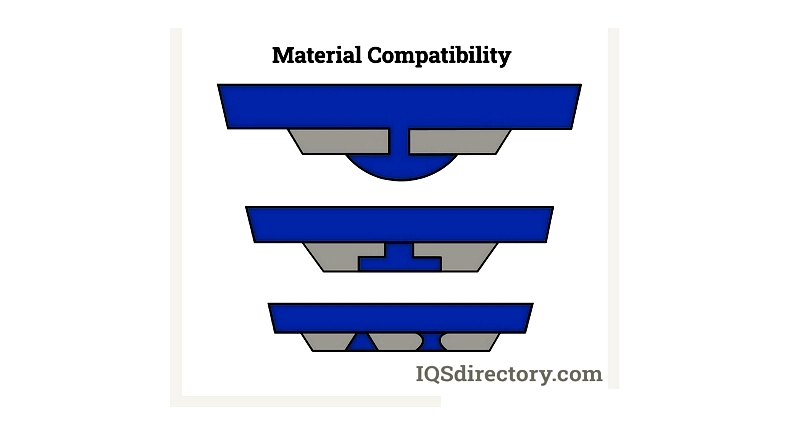
Material Compatibility
Choosing compatible materials ensures strong bonding between the substrate and rubber layer. important considerations include hardness, thermal expansion, and resistance to chemicals and environmental factors. Common materials include TPEs, silicone rubber, EPDM, and natural rubber, each suited for specific applications.
Surface Finish
A proper surface finish enhances adhesion strength. The substrate surface should be smooth and free from contaminants. Pre-treatments like plasma treatment may improve bonding in demanding applications.
Tolerances
Precise dimensional tolerances ensure proper fit and minimize defects like flashing or warping. Inaccurate tolerances can weaken the bond and cause product failure.
Undercuts
Undercuts complicate mold release and should be minimized. Advanced techniques like collapsible cores can help when undercuts are unavoidable.
Wall Thickness
Optimal wall thickness balances performance and cost. Thicker walls offer better impact resistance but increase material usage and weight.
Draft Angles
Proper draft angles (typically 0.5-1.5 degrees) facilitate part ejection and prevent damage to the rubber layer.
Additional Design Factors
Other important considerations include:
- Gate Location: Affects material flow and cosmetic appearance
- Venting: Prevents voids and incomplete filling
- Bonding Methods: Mechanical interlocks or chemical adhesives
- Environmental Exposure: Temperature, UV, moisture, and chemical resistance
Attention to these design factors enhances product quality and longevity. Collaboration with experienced overmolding specialists ensures compliance with performance specifications and industry standards.
Chapter 3: What rubber types and grades are used in overmolding?
Various rubber materials offer different properties for overmolding applications. Selection depends on product requirements and intended use. Common rubber types include:
Silicone Rubber
Known for thermal stability and chemical resistance, silicone is ideal for medical and food-grade applications due to its biocompatibility.
EPDM Rubber
Excellent weather and ozone resistance make EPDM suitable for outdoor and automotive applications.

Neoprene Rubber
Offers good oil and chemical resistance for industrial applications.
Natural Rubber
Provides excellent elasticity and tear resistance for dynamic components.

Nitrile Rubber
Superior oil and fuel resistance makes it ideal for automotive and industrial uses.
Specialty Materials
Fluoroelastomers and TPEs offer unique combinations of properties for specialized applications.
Rubber Grades
Rubber grades follow standards like ASTM D2000, which classify materials by performance characteristics. Understanding these grades helps select materials that meet specific application requirements.
Choosing the right rubber type and grade ensures optimal performance and longevity. Consultation with material specialists can help match materials to application needs.
Chapter 4: What regulations govern rubber overmolding?
While no specific regulations exist for rubber overmolding itself, related standards ensure safety and quality. Key regulations include:
RoHS Directive
Restricts hazardous substances in electrical equipment, affecting rubber components.




