Introduction
This article provides detailed information about capacitive touch screens.
It covers the following topics:
- What is a capacitive touch screen?
- How capacitive touch screens work
- Different types of capacitive touch screens
- An explanation of finger capacitance
- Pros and cons of capacitive touch screens
Chapter 1: What is a Touch Screen?
A touch screen is an interactive display that enables direct interaction with computers using fingers or a stylus. Serving as an alternative to traditional input devices like mice or keyboards, it operates through a graphical user interface (GUI). These interfaces are commonly found in devices such as computer monitors, laptops, smartphones, tablets, point-of-sale systems, and information kiosks. Some touch screens use infrared grids to detect finger presence instead of relying on touch-sensitive technology alone.
Types of touchscreen technologies
Various technologies enable smooth touch screen interaction. Some are designed specifically for finger input, while others support both fingers and tools like styluses.
Capacitive
Capacitive touchscreen displays feature an electrically charged layer. When touched, a small charge transfers to the contact point. Sensors at the panel's corners measure this charge and send data to the controller for processing. Unlike resistive and surface wave screens that accept both finger and stylus input, capacitive touchscreens respond only to finger touches. Known for high clarity, these panels are also resistant to environmental factors.
Infrared
Infrared touch displays use a grid of infrared beams produced by LEDs and detected by phototransistors. When a finger or object touches the screen, it interrupts these beams, allowing the device to determine the touch location.
Resistive
Resistive touchscreen panels have a thin, electrically conductive metallic coating that changes current when touched. This change registers a touch event and sends it to the controller. While generally more affordable, resistive panels offer only 75% clarity and can be damaged by sharp objects. However, they remain unaffected by external elements like water or dust.
Surface acoustic wave
Surface acoustic wave (SAW) technology employs ultrasonic waves that travel across the display. Touching the screen absorbs some waves, helping identify the touch location for controller processing. Although the most advanced among these types, SAW panels are vulnerable to environmental damage.
Chapter 2: What Is a Capacitive Touch Screen?
A capacitive touch screen is a highly responsive display technology that enables intuitive human-machine interaction by detecting touch gestures, typically from fingers or compatible styluses. Unlike resistive touch screens that rely on pressure, capacitive versions use the human body's natural electrical properties to alter the device's electrostatic field. This innovation has driven widespread adoption in modern digital devices.
Today, capacitive touch screen technology appears in various electronic devices, including smartphones, tablets, PDAs, all-in-one computers, automotive touch panels, and POS terminals. Its seamless interface supports multi-touch gestures like tapping, swiping, and pinching to zoom, delivering an intuitive user experience. Most capacitive touch screens integrate with high-resolution LCD or OLED displays for enhanced visual clarity and touch sensitivity.
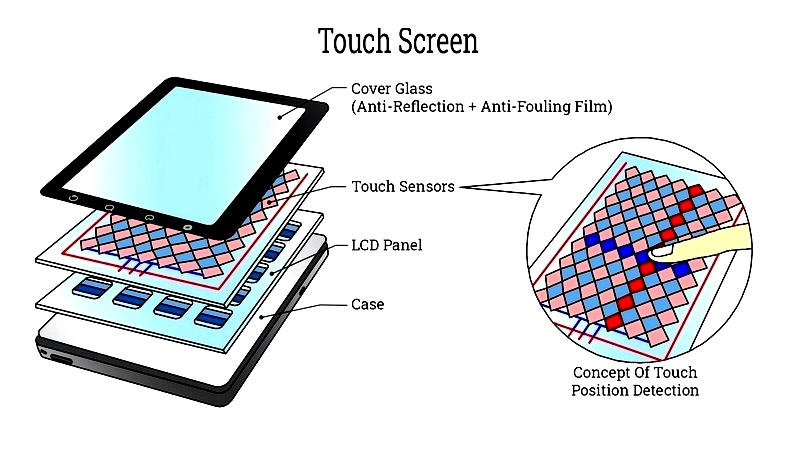
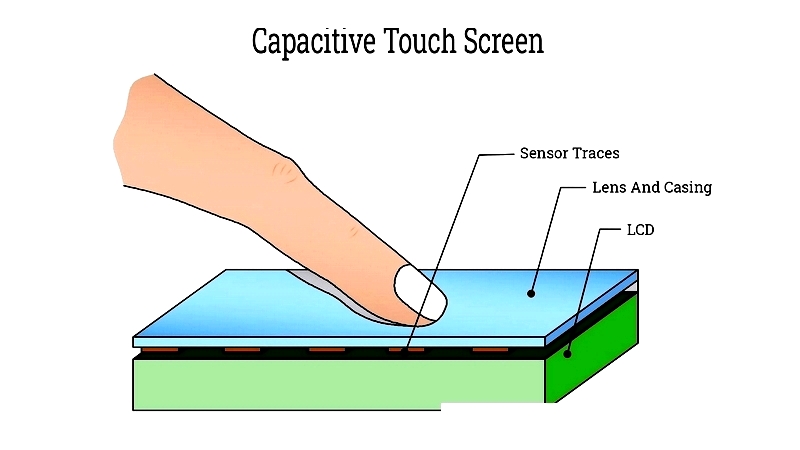
A standard capacitive touch screen panel consists of durable glass coated with transparent conductive material, usually indium tin oxide (ITO). This ITO layer identifies touch locations. When a finger touches the surface, it draws a small electrical charge, altering the touch sensor's electrostatic field. The device's touch controller processes this change to determine precise coordinates for accurate touch detection.
This design ensures high transparency and touch accuracy, making capacitive screens an industry standard for responsive applications. They also offer durability, scratch resistance, and vandal-proof options, making them ideal for commercial, industrial, and outdoor displays.
When evaluating capacitive touch screen displays, consider factors like responsiveness, multi-touch capability, glare reduction, water and dust resistance (IP ratings), and compatibility with gloves or styluses. Advances in projected capacitive technology (PCAP) have improved functionality, enabling smooth operation through protective glass or in demanding environments. OEMs should assess long-term reliability, supply chain consistency, and customization options when selecting manufacturers.
Whether for consumer electronics, workstations, medical devices, or industrial systems, capacitive touch screens offer superior usability and performance. Their scalable design, fast response times, and gesture recognition make them the preferred choice for modern interfaces.
Chapter 3: How Capacitive Touch Screens Work
Touch input technology transformed human-computer interaction by combining displays with responsive touch systems. Capacitive touch screens—common in smartphones, tablets, and industrial panels—use electrical capacitance principles to sense human touch accurately. Compared to resistive, infrared, or surface acoustic wave technologies, capacitive screens provide better sensitivity, multi-touch capabilities, and clarity, making them dominant in modern devices.
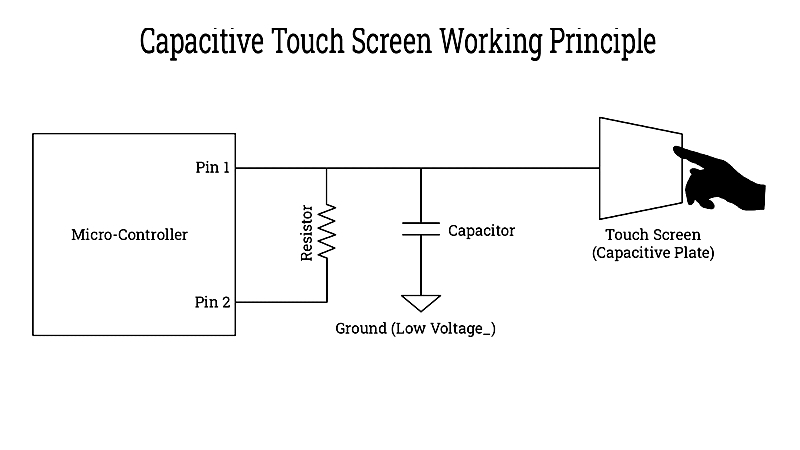
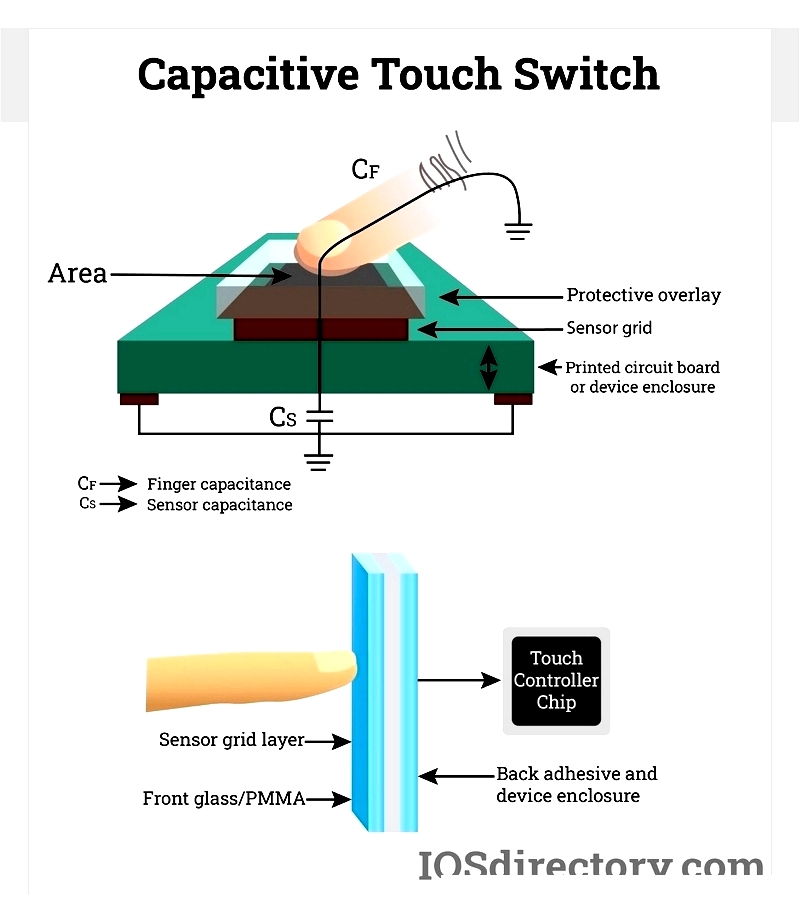
Capacitive technology centers on capacitance principles. A standard capacitor stores electric charge at a predictable rate when exposed to voltage. This timing—called the RC time constant—remains steady unless circuit parameters change. When a conductive object like a finger interacts with the circuit, it alters this timing, enabling touch detection.
A finger touching the screen adds capacitance because the human body conducts electricity. The skin acts as a dielectric material, increasing overall capacitance. This change in charging cycles is detected by precise sensors, enabling multi-touch recognition and fast gesture response.
The touch controller—a dedicated microcontroller—continuously charges the capacitive sensor grid and monitors charge fluctuations. When it detects a capacitance change (indicating a touch), it sends touch coordinates and gesture data to the device's operating system. Capacitive panels use ultra-thin, transparent conductive layers like ITO on glass or polycarbonate substrates for durability and accuracy.
Modern projected capacitive (PCAP) touch screens can detect multiple touches even through protective coverings or gloves, thanks to advanced sensing algorithms. Understanding this technology helps in selecting the right panel for consumer electronics, medical screens, or digital signage. Capacitive screens' longevity, low maintenance, and compatibility with high-resolution displays make them ideal for next-generation human-machine interfaces (HMI) and user experiences (UX).
When choosing capacitive touch screens, consider panel size, touch resolution, environmental resistance (IP/NEMA ratings), anti-glare coatings, and software compatibility. Reputable manufacturers offer customization for industrial HMIs or retail kiosks. Selecting the right technology ensures user satisfaction and long-term reliability.




