Introduction
This article covers everything you need to know about zinc die casting and its applications.
You will learn:
- What Zinc Die Casting Is
- Zinc Die Casting Methods
- Products Made by Zinc Die Casting
- Zinc Alloys Used in Casting
- And much more...

Chapter One: What is Zinc Die Casting?
Zinc die casting is a manufacturing process where molten zinc is injected into precision steel molds to create products with exact dimensions. The resulting zinc parts inherit zinc's excellent mechanical properties, known for their strength, durability, and aesthetic appeal. Zinc alloys are preferred for this process due to their flexibility, impact resistance, and lower melting point, making them ideal for efficient casting.
This process operates at lower temperatures because of zinc's relatively low melting point. Before starting, molds are carefully prepared and lubricated. Various zinc alloys are used, including zamak and zinc-aluminum-copper blends, with zamak 3 being particularly popular for its dimensional accuracy and structural strength.
Among casting metals, zinc stands out for its ease of use and abundance. It appears as a brittle, silvery-white metal with a bluish tint that tarnishes when exposed to air. Typical zinc die-casting alloys contain about 78% zinc, mixed with lead, tin, copper, aluminum, and magnesium to enhance casting performance.
Zinc offers engineers unique design possibilities that may be difficult with other metals. Its inherent strength allows for thin-walled designs with less material. Additionally, zinc's excellent bearing and wear resistance make it perfect for producing bushings and complex components.
Chapter Two: What are the Different Methods Used in Zinc Die Casting?
Die casting methods are crucial in metalworking, involving high-pressure injection of molten metal into molds to capture intricate details. In zinc die casting, the mold (or die) is designed in negative relief to shape the final part precisely. This method uses zinc alloys—combinations of zinc with metals like aluminum, copper, or magnesium—to improve material properties and castability. Zinc is chosen for its excellent fluidity, low melting temperature, dimensional stability, and ability to produce detailed, repeatable cast parts, making it vital for industries like automotive, electronics, and consumer goods.
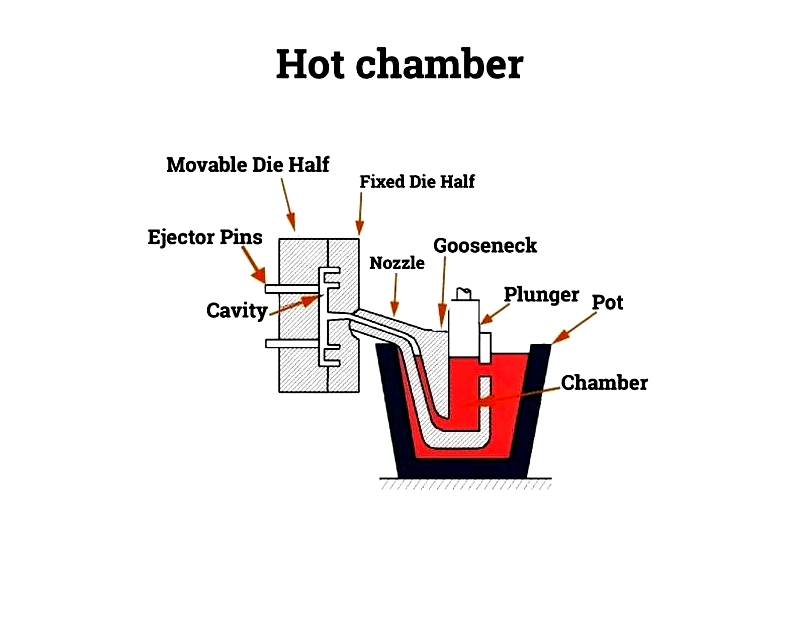
Hot Chamber Zinc Die Casting
Die
During the injection stroke in hot chamber casting, the plunger forces molten zinc alloy through the gooseneck channel into the nozzle. At each cycle's start, the plunger retracts, drawing molten zinc into the shot cylinder. The CNC machining system powers the shot cylinder, ensuring precise casting.
Injection pressures range from 700 psi to 5000 psi (5 MPa to 35 MPa), with higher pressures possible due to molten zinc acceleration. The plunger maintains hydraulic pressure until the casting solidifies, ensuring low-porosity, high-strength parts. This process supports both precision zinc castings and high-volume production.
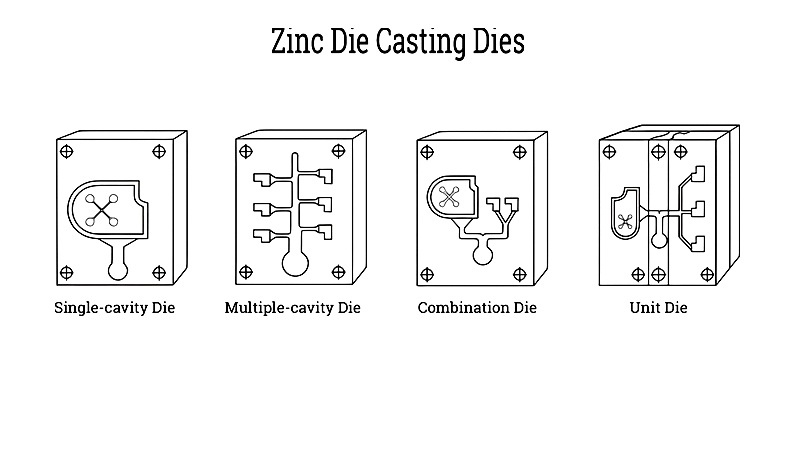
- Single Die – Produces one component per cycle, ideal for low-volume runs, prototypes, or custom parts. Single dies offer cost-effective tooling and simple design.
- Multiple Die – Features several identical cavities, enabling simultaneous production of multiple parts. This reduces per-unit costs and boosts throughput for high-volume manufacturing.
- Combination Die – Includes cavities for different parts, allowing varied components to be cast in one operation, reducing costs and increasing productivity.
- Unit Die – Modular dies inserted into a master holder, suitable for small-to-medium batches and quick die changes.
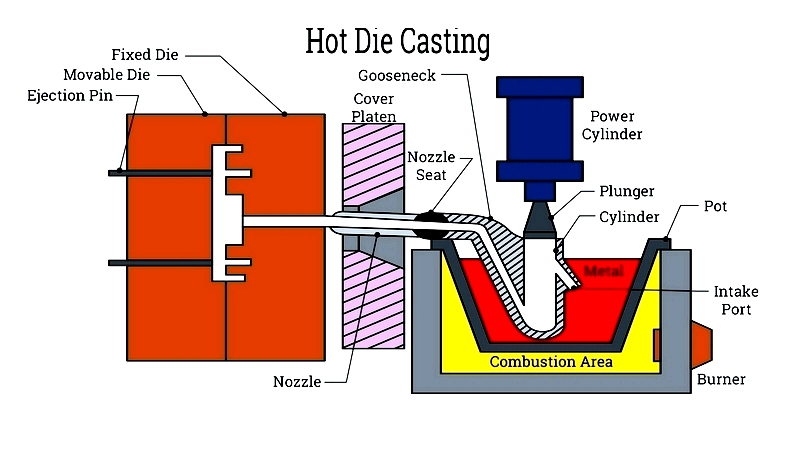
Hot Chamber Zinc Die Casting
Hot chamber casting is the most common method for zinc alloys due to zinc's low melting point and excellent castability. Key components—the furnace, gooseneck, nozzle, and plunger—work together for continuous casting, making it efficient for small-to-medium parts. The stationary die half mounts onto a plate connected to the casting machine, ensuring alignment and accuracy.
Furnace
The integrated furnace melts zinc alloy, maintaining optimal temperature to prevent impurities and ensure fluidity. Its intake port connects to the gooseneck beneath the shot cylinder. When the plunger rises, it opens the port, allowing heated zinc to fill the gooseneck. Automated temperature controls and refractory linings ensure consistent alloy quality.
Gooseneck
The gooseneck channels molten zinc from the furnace to the die with minimal air exposure, reducing oxidation. Made from heat-resistant materials, its design is crucial for high-speed operation and reliability in zinc die casting equipment.
Nozzle
The nozzle delivers molten zinc into the die cavities, ensuring uniform filling and precise mold replication. After each cycle, excess zinc flows back for recycling, supporting sustainable production.
Plunger or Piston
The plunger drives the high-pressure injection phase. In hot chamber systems, a hydraulic motor powers it, ensuring precise movement and sealing to prevent leaks and achieve tight tolerances in precision zinc castings.
During each cycle, regulated pressure ensures rapid, complete filling for intricate parts, contributing to short production cycles and exceptional accuracy.
Die
The die consists of two halves: the stationary half fixed to the cover platen and the movable (ejection) half. The ejection half has pins to release the solidified part after casting. Advanced designs, including multi-cavity molds, maximize output and quality for high-consistency components.
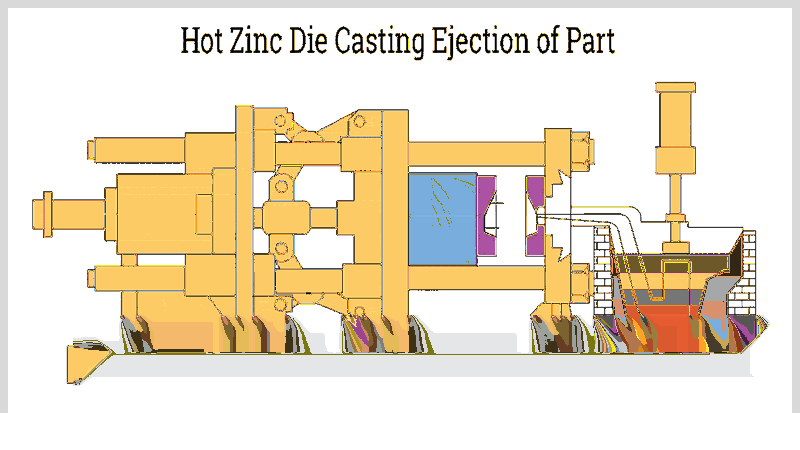
Complete Hot Chamber Zinc Die Casting Process
The hot chamber cycle offers rapid turnaround and consistency, involving:
- Chamber Filling – The plunger rises, allowing molten zinc to fill the cylinder and gooseneck, reducing air entrapment.
- Injection – The plunger forces zinc into the sealed die, ensuring high precision for complex geometries and thin walls.
- Pressure – The plunger maintains pressure to minimize porosity and maximize strength, tailored to alloy content and part requirements.
- Cooling – Zinc solidifies quickly due to its low melting point, with rapid cooling enhancing productivity.
- Finishing – Trimming, deburring, and surface treatments refine parts for performance and appearance.
Mastering these steps ensures cost-effective, repeatable results, making zinc die casting ideal for custom components and high-volume production.
Cold Chamber Zinc Die Casting
Cold chamber casting differs in handling molten metal. Zinc alloy is melted separately and ladled into an unheated shot chamber, reducing contamination and extending die life. This method suits zinc alloys with higher melting points and is used for aluminum, magnesium, and copper alloys.





