Introduction
This article provides a detailed discussion on expansion joints.
After reading this article, you should gain a better understanding of:
- The fundamentals of expansion joints: their definition, working principles, common materials, and selection considerations
- The manufacturing process of expansion joints
- Different types of expansion joints
- Benefits and applications of expansion joints
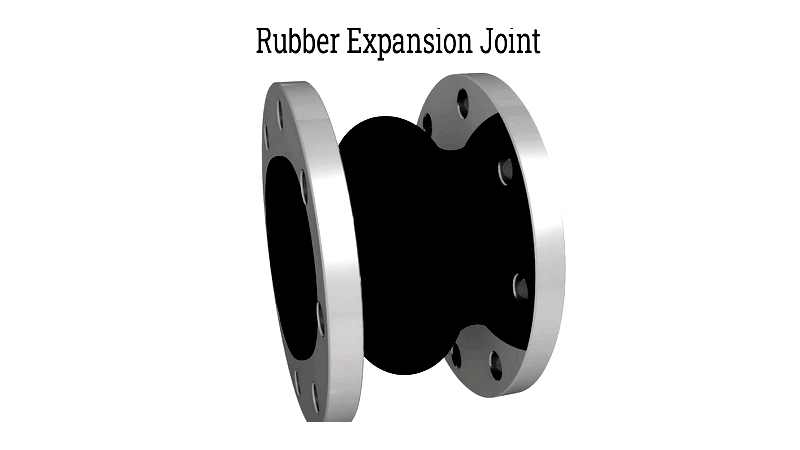
Chapter One: Overview of Expansion Joints
Expansion joints are specifically designed to accommodate movement in piping systems. They help manage thermal and mechanical vibrations in pipes, ducts, and other pipeline components caused by temperature variations. These joints expand with rising temperatures and contract when temperatures drop, providing secure support to piping systems. Some designs may incorporate mechanical components to allow for both rotational and linear motion.
Functioning as connecting elements between structures, expansion joints facilitate movement during thermal expansion and contraction. The term "expansion" refers to the increase in size or volume due to temperature rise. As temperature increases, atomic vibrations intensify, causing material expansion. Plumbing systems utilize these joints to absorb shocks and vibrations.
Additional benefits of expansion joints include noise reduction and alignment compensation. While most are designed for standard thermal movements, some specialized joints handle extreme external thermal expansions in high-temperature environments where surrounding temperature fluctuations affect piping systems.
Common materials for expansion joints include:
- metal (typically aluminum)
- Rubber
- Braided materials
Braiding involves mechanically intertwining three or more yarns without any two threads wrapping around each other. This continuous structure ensures even load distribution. Braids can be made from fiber or stainless steel, forming adaptable connectors with corrugated stainless steel bands wrapped around rubber or elastomer hoses.
Expansion joints also correct misalignment, reduce noise, and relieve anchor tension. Their designs vary according to specific applications, making them essential for preventing structural damage in systems prone to expansion or contraction, such as plumbing pipes, machinery, and hydraulic systems. These joints maintain effective seals even during surface movements between connected components.

Working Mechanism
metal expansion joints accommodate thermal expansion and relative movement in pipes, containers, and machinery. They may feature single or multiple metal bellows with end connectors and sometimes tie rods. The flexible bellows, made of rubber or metal, absorb pipe system movements by expanding and contracting with temperature changes. metal bellows compress to manage movement and reduce pipe stress, typically constructed from nickel alloys or stainless steel.
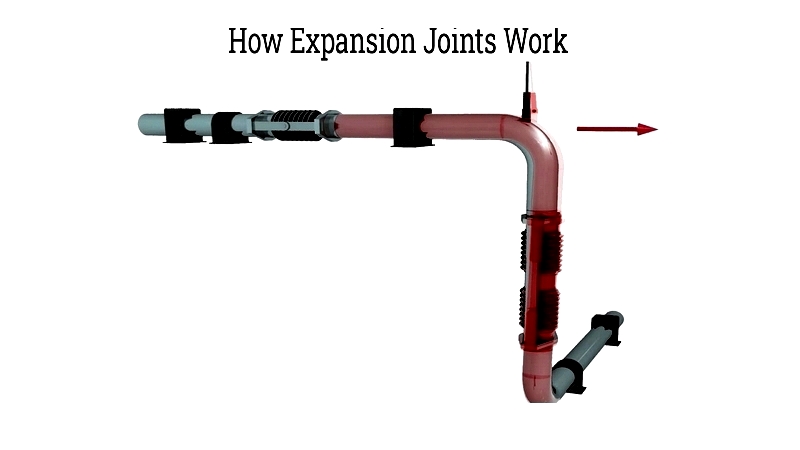
These joints serve various industries including energy production, paper manufacturing, chemicals, water treatment, and oil/gas sectors - anywhere pipelines experience thermal or vibrational movement.
Common Materials
metal
Ideal for significant thermal expansion applications, metal joints contract with rising temperatures to accommodate movement and reduce stress on anchors and pipes.
Rubber
Rubber joints excel in vibration and shock absorption, making them suitable for thermal expansion applications. They effectively protect equipment like pumps by minimizing noise and vibration transfer while serving as shock absorbers against seismic activity and pressure surges.
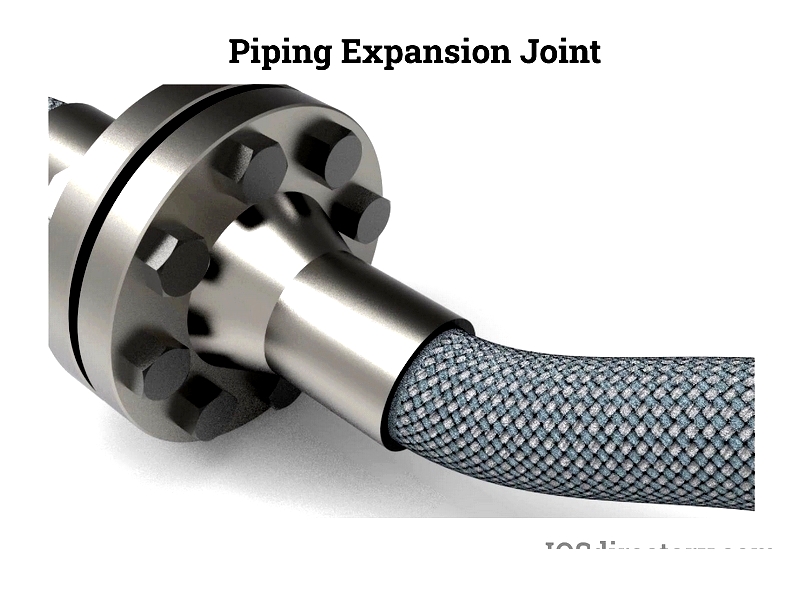
Braided Stainless Steel
More accurately described as flexible connectors, braided stainless steel hoses with flexible/metal liners perform well in vibration damping and pipe misalignment applications under high pressure and temperature conditions.
Selection Considerations
Given their use in demanding environments (steel, power, pulp/paper, mining, chemical industries), careful selection, installation, and maintenance ensure reliability, optimal performance, and extended service life.
Application Fields
The primary selection criterion is the intended application field. Expansion joints serve various industries, with common uses in plumbing, piping, and construction systems.
In piping systems, they accommodate pipe expansion from fluid pressure or temperature changes. In plumbing, they absorb shock/vibration while reducing operational noise.
Construction expansion joints act as structural gaps that alleviate material stress from building movements caused by:
- Thermal expansion/contraction
- Seismic shifts from wind forces
- Dynamic load bending
- Direct impact forces
Piping Scheme Considerations
Before installing expansion joints, ensure surrounding pipes and equipment follow proper piping engineering practices. Proper placement of anchors, guides, and supports is crucial for joint functionality:
- Anchors: Fix pipes to prevent movement
- Guides: Allow controlled directional movement
- Supports: Transfer pipe weight to structures
Placement
Optimal placement ensures adequate movement allowance, proper ambient cooling, and accessibility.
Joint Motion
Expansion joints and pump connectors absorb axial, lateral, and angular movements. Accurate movement calculations ensure joint longevity, as excessive stress causes premature failure. Construction joints may need to accommodate horizontal, vertical, or multidirectional movements while protecting against shear-induced degradation.
Media Flow
Design considerations depend on the flowing medium. Flow liners or insulation protect against contaminants/abrasives. Medium characteristics critically influence material selection, as condensation may cause chemical attacks. Improper




