Introduction
This article offers a comprehensive exploration of voice coils. You'll discover:
- Voice Coil Fundamentals
- Different Voice Coil Types
- Key Considerations for Voice Coils
- Voice Coil Applications and Advantages
- Additional Insights...

Chapter 1: Voice Coil Fundamentals
This section examines the design characteristics and functional principles of voice coils.
Understanding Voice Coils
A voice coil consists of wire, typically made from copper, aluminum, or copper-clad aluminum, wound around a bobbin. Attached to a speaker cone, it interacts with the magnetic field of the motor structure to move the cone.

When current flows through the coil, it creates a magnetic field that interacts with the permanent magnet, causing movement. This motion reproduces audio signals when music is played.
In actuators, current interacts with inductors in a magnetic field to generate force. This force follows the Lorentz equation:
F = B × I
Where ( F ) is Force (N), ( B ) is Magnetic Flux Density (Tesla), and ( I ) is Current (Amps).
The force remains relatively constant during operation, with minor reductions at stroke limits.
Actuators may feature either moving coils or moving magnetic assemblies.
Moving Coil Design
Most actuators use this design, where the coil moves within a stationary magnetic field housed in steel.
Moving Magnet Design
In this configuration, the magnet assembly moves while the coil remains fixed, often incorporating bearing systems for smooth operation.
Voice Coil Design Features
Key design aspects include:
Weight Considerations
Lightweight construction enables accurate high-frequency response while maintaining durability against stress.
Power Handling
Heat resistance depends on materials used. Cooling features like heat sinks help manage temperature.
Proper coil positioning enhances cooling. Ribbon wire improves heat dissipation compared to round wire.
Ferrofluid can aid cooling in some designs. Excessive power at low frequencies may cause damage.
Wire Material Selection
Copper is preferred for its conductivity and heat resistance. Aluminum offers weight savings but requires larger cross-sections.
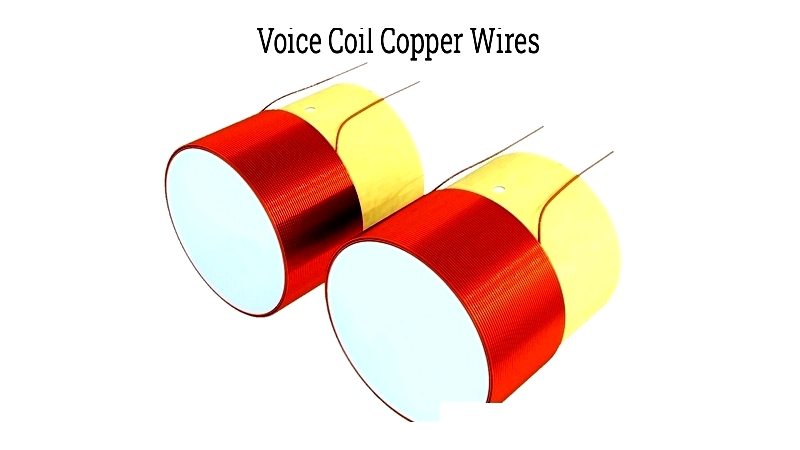
Modern designs use advanced materials to withstand high temperatures. Aluminum remains popular despite limitations.
New composites like Hisco P450 combine temperature resistance with structural integrity.
Impedance Characteristics
Lower impedance allows more current flow, increasing power delivery from amplifiers.
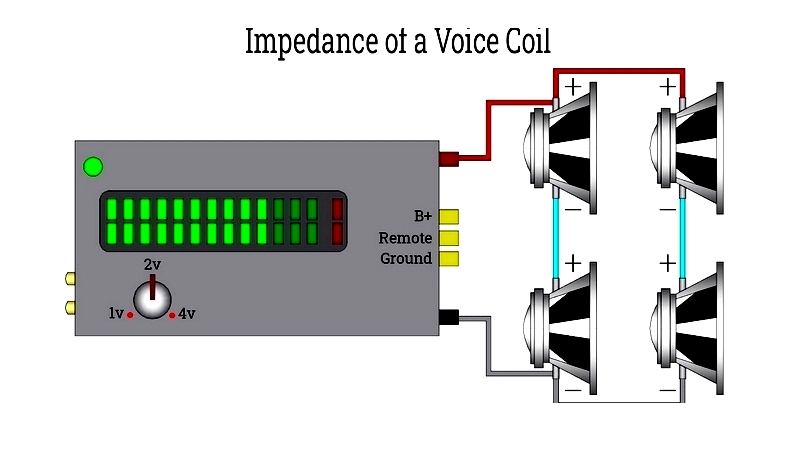
Configuration Options
Single and dual coil configurations offer different wiring possibilities to match amplifier capabilities.
Voice Coil Assembly
Proper alignment within the magnetic gap ensures accurate sound reproduction while allowing necessary movement.
Former Materials
Material choice affects performance, with options ranging from paper to advanced composites.
Dust Cap Function
Maintains gap clearance while influencing tonal characteristics through material and shape choices.
Coil Operation
The interaction between coil and permanent magnet fields drives movement, with applications extending beyond audio.
Performance Specifications
Key metrics include force constant, stroke length, peak force, and electrical time constant.
Chapter 2: Voice Coil Types
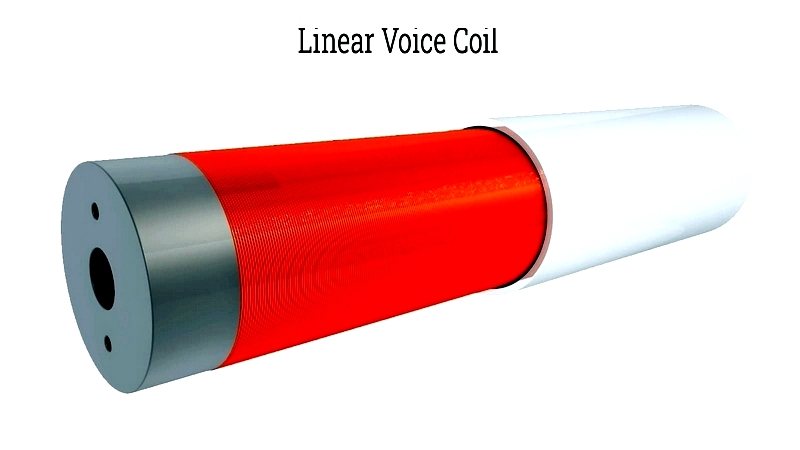
Voice coils serve critical roles in audio and motion systems. The two primary types are linear and rotary, each with distinct design configurations affecting performance.
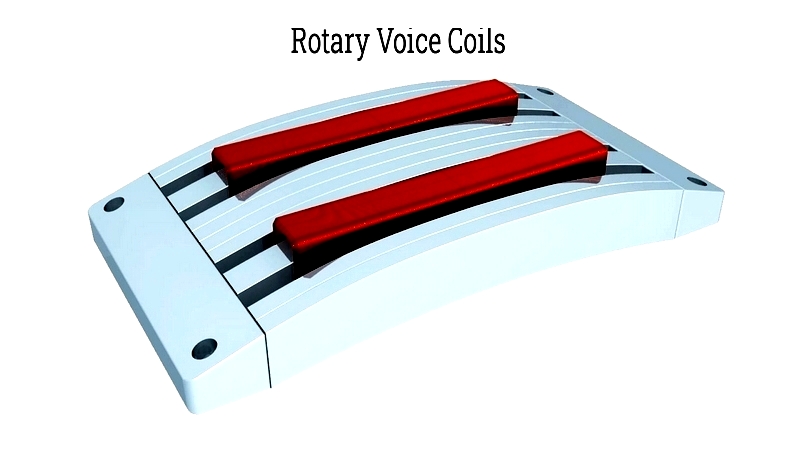
Linear voice coils convert electrical energy to precise linear motion, ideal for actuators and automation. Rotary voice coils enable controlled angular movement for applications like robotics.

Overhung Design
Features extended windings beyond the magnetic gap, offering stable force generation and good excursion.
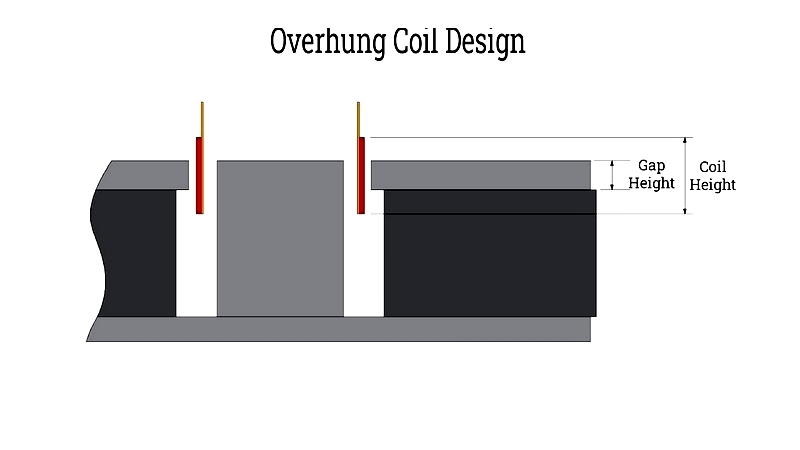
Provides robust performance in subwoofers with tradeoffs in transient response due to increased mass.
Underhung Design
Keeps all windings within the gap for superior linearity and low distortion, preferred for high-fidelity applications.
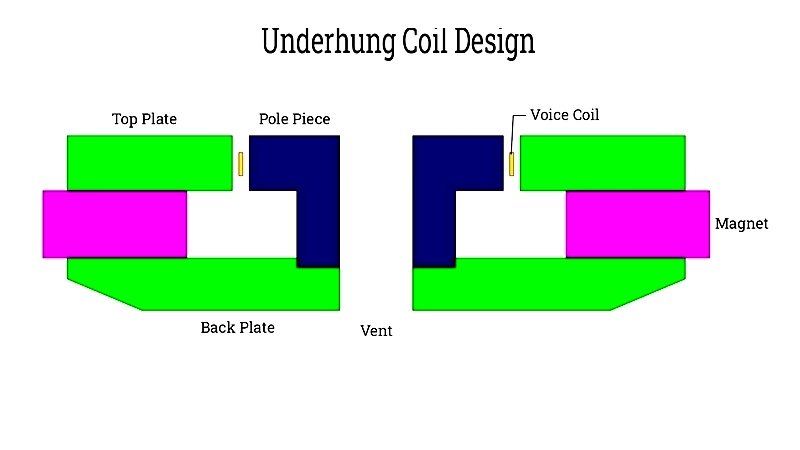
Excels in accuracy but has stricter excursion limits compared to overhung designs.
Selection Factors
Consider wire gauge, materials, thermal management, and application requirements when choosing voice coils.
evaluate specifications like BL product, power rating, and frequency response for optimal performance.




