Introduction
This article provides a comprehensive overview of metering pumps and their applications.
You will explore key topics including:
- What is a Metering Pump?
- How Metering Pumps Work
- Applications of Metering Pumps
- Types of Metering Pumps
- And More...
Chapter One – What is a Metering Pump?
A metering pump is a precision device that delivers a specific volume of fluid at a controlled rate, ensuring accurate volumetric flow. The term "metering pump" refers to various pumping technologies, each designed to meet specific application and process requirements. The choice of metering pump depends on the particular needs of the application.
When selecting a metering pump, key considerations include fluid viscosity, temperature, discharge pressure, flow rate, and wetted path materials. A typical metering pump consists of a pump head and motor, which may feature manual or electronic control systems.
Many metering pumps use piston-driven positive displacement mechanisms, where the piston moves liquid within the chamber. While piston-driven pumps are common, alternative designs are available for specialized applications.
Chapter Two – Types of Metering Pumps
A metering pump is a reciprocating positive displacement pump that delivers precise liquid volumes with each stroke. These pumps are vital for dosing, blending, and injecting fluids across industrial, municipal, and laboratory settings. Their rotary motion converts to reciprocating movement through a wheel and worm shaft mechanism, though designs may vary. Metering pumps are prized for their accuracy and repeatability in controlling chemical and process fluid flow rates.
The primary role of a metering pump is to ensure accurate liquid transfer in processes like water treatment, chemical dosing, pharmaceutical production, and food processing. Precise dosing helps maintain product quality, regulatory compliance, and process efficiency.
Metering Pump Types
Various metering pump types serve specific applications in industries such as water treatment, chemical injection, oil and gas, food and beverage, and pharmaceuticals. Selection depends on factors like liquid viscosity, corrosiveness, required flow rate, pressure, and automation needs.
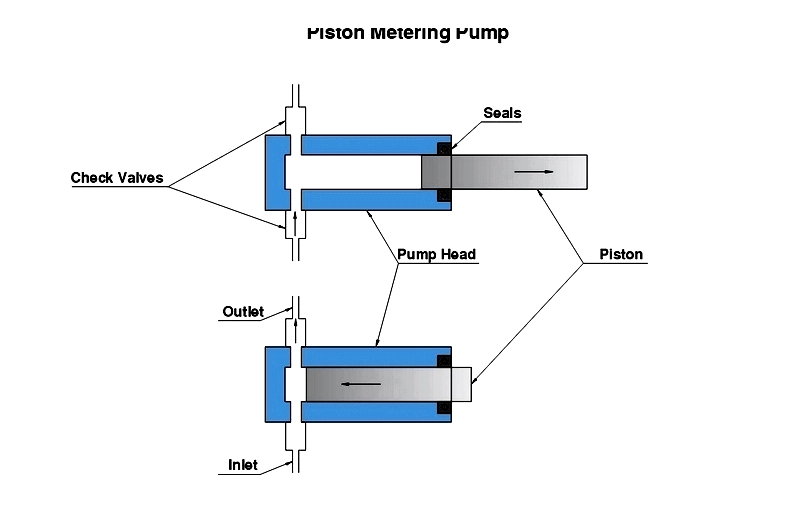
Piston Metering Pumps
Piston metering pumps use reciprocating pistons to move fluid within the chamber. Flow rate and volume are determined by the chamber's diameter and stroke length. Check valves at the inlet and outlet ensure directional flow.
As the piston retracts, it creates a vacuum that draws fluid into the chamber. During discharge, the piston pushes fluid through the outlet valve. These pumps excel in high-pressure applications and are ideal for precise dosing in laboratory, industrial, and petrochemical settings.
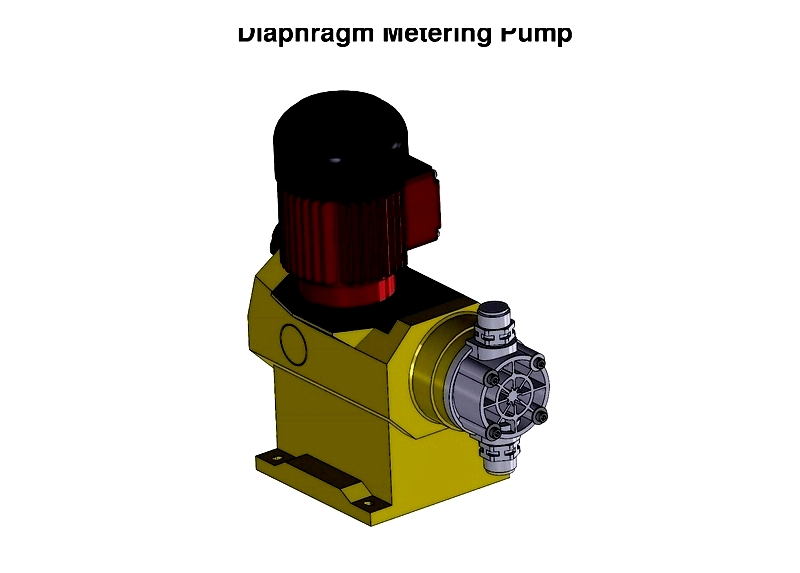
Diaphragm Metering Pumps
Diaphragm metering pumps use flexible diaphragms to move liquid, offering leak-free operation for corrosive or hazardous chemicals. Diaphragms may be mechanically or hydraulically actuated.
The diaphragm's movement creates suction, drawing fluid through the inlet valve and discharging it through the outlet valve. These pumps are widely used in water treatment, agriculture, and chemical processing where accuracy and chemical compatibility are critical.
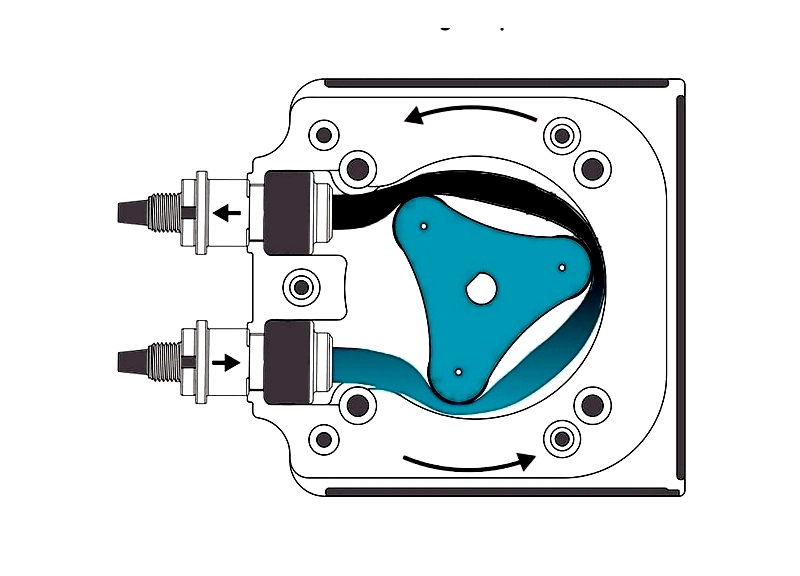
Peristaltic Metering Pumps
Peristaltic pumps use rotating rollers to compress flexible tubing, creating a vacuum that draws in and propels fluid. This gentle action suits shear-sensitive fluids, slurries, and viscous media.
Since the fluid only contacts the tubing, these pumps minimize contamination and wear. They're commonly used in pharmaceuticals, food processing, and laboratory applications.
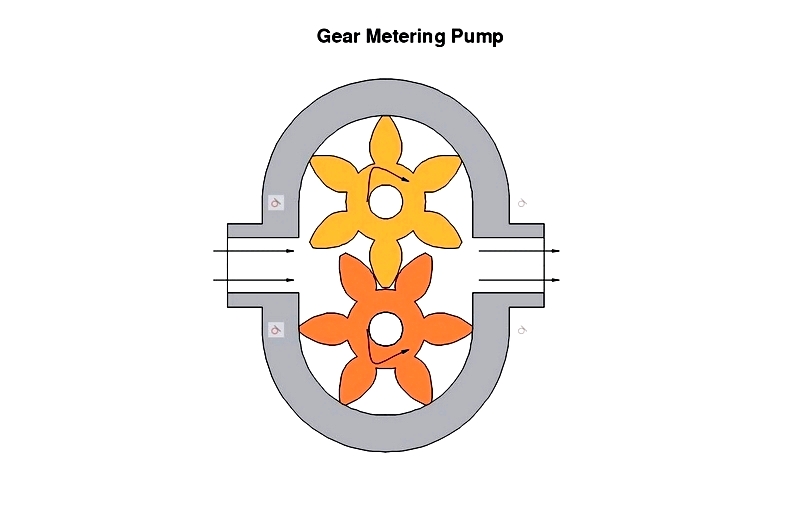
Gear Pumps
Gear pumps use intermeshing gears to create vacuum and move fluid between gear teeth, producing steady flow. They're ideal for high-viscosity fluids in hydraulic systems, lubrication, and chemical dosing.
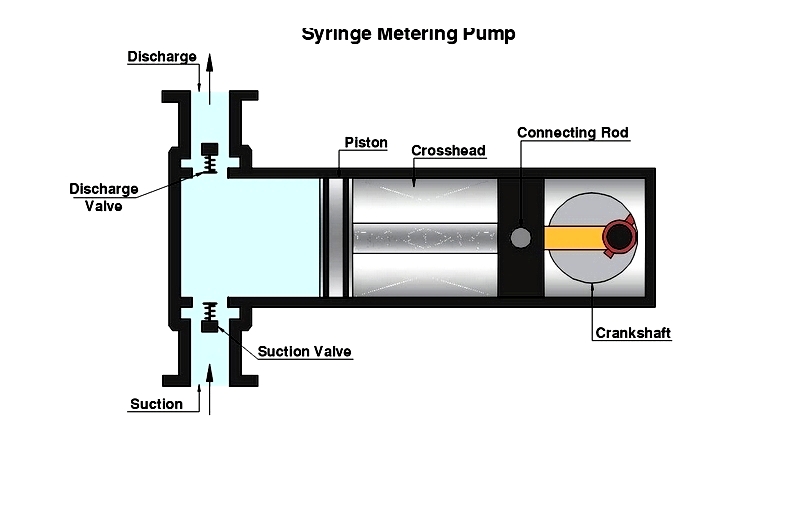
Syringe Pumps
Syringe pumps deliver ultra-precise micro- and nano-liter quantities for medical, laboratory, and research applications. Their slow metering rates suit specialized uses rather than bulk transfer.
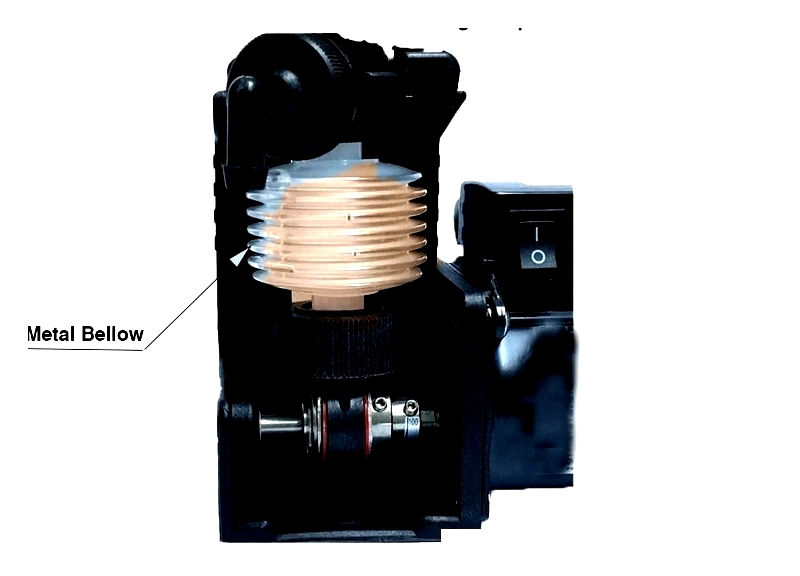
Bellows Pumps
Bellows pumps use expanding and contracting bellows to displace fluid, ideal for precise dosing of low- to medium-viscosity liquids in medical devices and instrumentation.
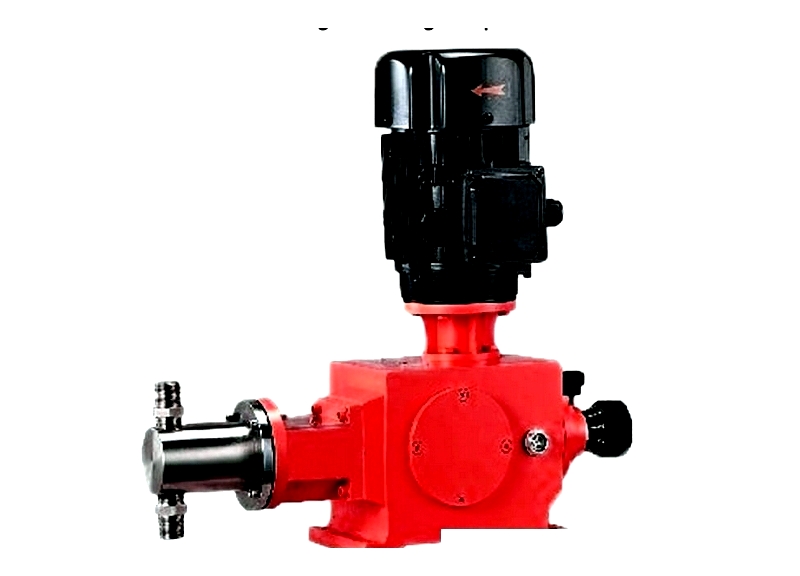
Plunger Pumps
Plunger pumps achieve ultra-high pressures (exceeding 50,000 psi) for oil and gas, process engineering, and industrial cleaning applications.

Small Metering Pumps
Compact micro pumps offer precise fluid transfer in confined spaces for dosing, sampling, and instrumentation. Their modular design allows customization for specific applications.

Chemical Metering Pumps
These pumps precisely dose chemicals in demanding industrial processes. Constructed with chemically resistant materials, they're essential for water treatment, boiler feed, and mining operations.

Electronic Metering Pumps
EMPs feature digital controls for automated flow adjustment, ideal for continuous dosing in water treatment, chemical manufacturing, and food production.

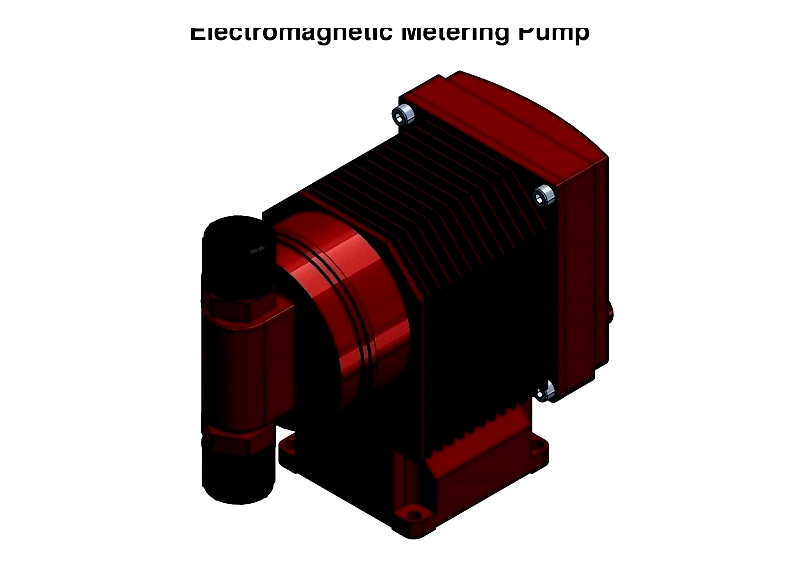
Solenoid Pumps
Electromagnetic pumps use solenoid coils to actuate diaphragms, offering reliable, low-maintenance dosing for water treatment and laboratory applications.

Chapter Three – How Metering Pumps Work
Metering pumps precisely control fluid dispensing in critical applications like water treatment, chemical processing, and pharmaceuticals. They handle various fluids while maintaining accuracy and repeatability.
Working Principles
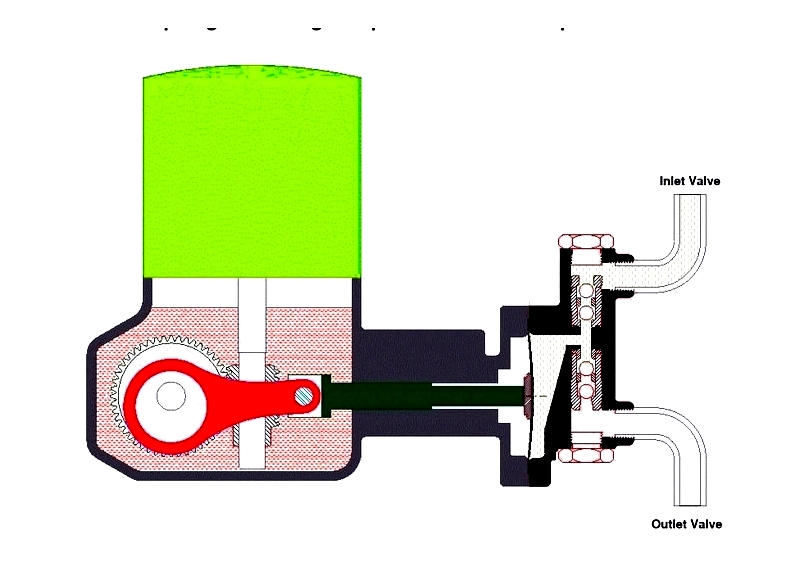
Pump Driver
Drivers power the pump assembly using electric motors, pneumatic




