Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of laser coolers and laser cooling technology.
Key topics covered include:
- Principles of Laser Cooling & Laser Coolers
- Laser Cooling Instruments and Chiller Types
- Applications of Laser Coolers & Laser Cooling
- And More...

Chapter 1: Principles of Laser Cooling and Laser Cooler Operation
This chapter examines the fundamentals of laser cooling, discusses various cooling techniques, and explains the working principles of laser coolers.
What is Laser Cooling?
Laser cooling refers to techniques that reduce atomic and molecular sample temperatures near absolute zero. These methods utilize photon re-emission momentum changes to decrease overall kinetic energy.
Thermodynamic temperature relates to particle velocity distribution - more uniform distributions indicate lower temperatures.
Laser cooling combines atomic spectroscopy with light's mechanical effects to narrow velocity distributions, thereby cooling particle groups.
Laser Cooling Methods
Doppler cooling is the most practical and widely used technique, often synonymous with laser cooling itself.
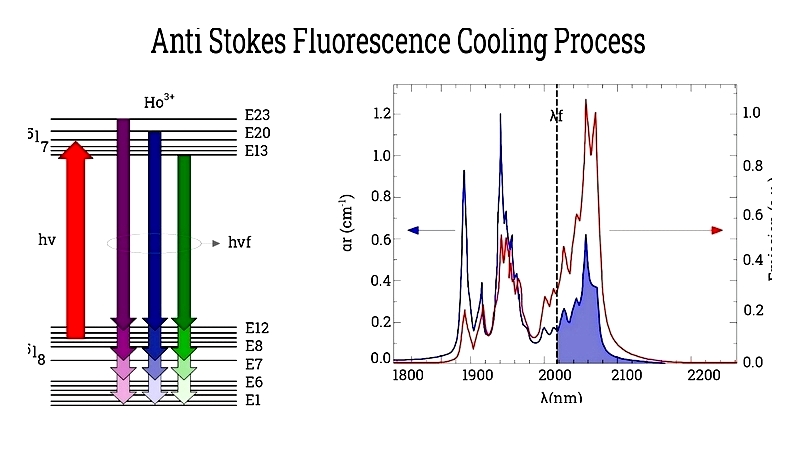
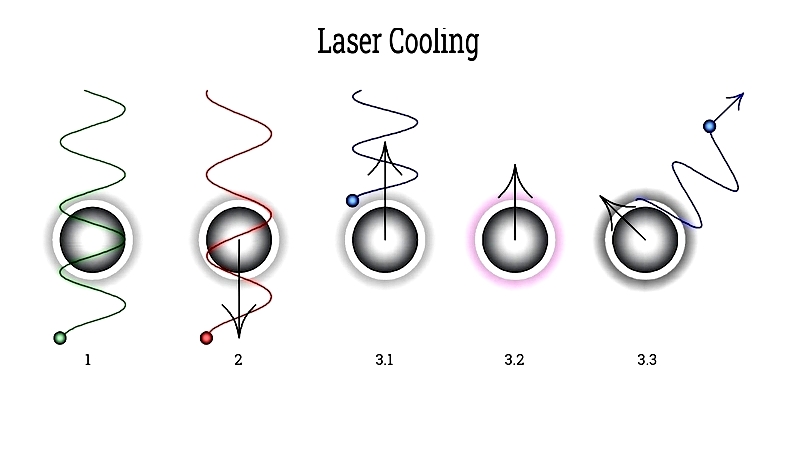
Other techniques include Sisyphus cooling, resolved sideband cooling, Raman sideband cooling, VSCPT, gray molasses, cavity-mediated cooling, polarization gradient cooling, anti-Stokes cooling in solids, EIT cooling, and Zeeman slower applications.
Doppler Cooling
This method traps and reduces atomic motion to cool substances. Stationary atoms don't absorb photons, while moving atoms experience frequency shifts that enable selective absorption and deceleration.
When atoms absorb photons moving toward the laser, they slow down. Subsequent photon emissions in random directions create no net momentum change over multiple events.
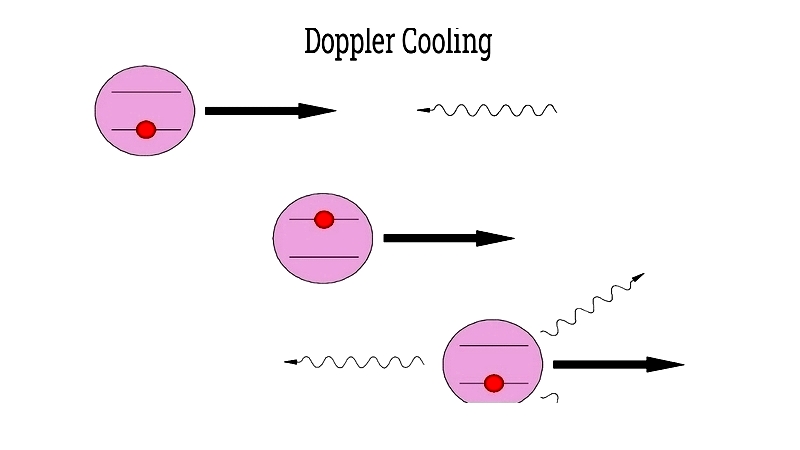
The technique relies on atoms being transparent to most photon frequencies, interacting only at specific resonant bands. Carefully tuned laser frequencies below resonance allow selective interaction with moving atoms.
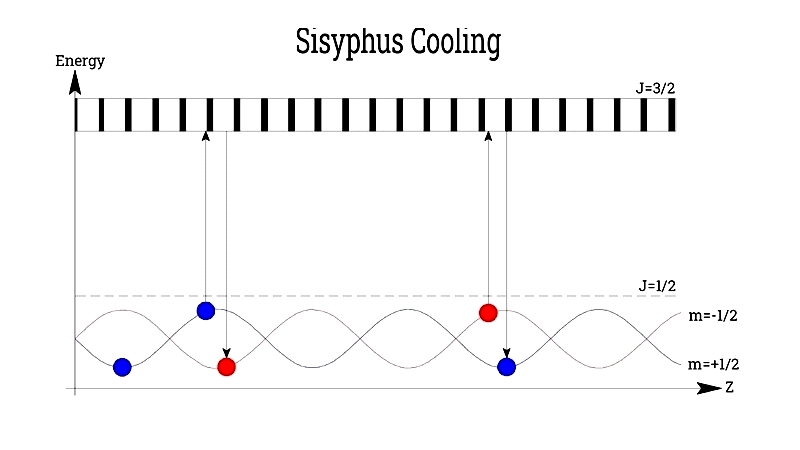
Sisyphus Cooling
This sub-Doppler technique uses counter-propagating orthogonally polarized lasers to create potential landscapes where atoms lose kinetic energy through optical pumping.
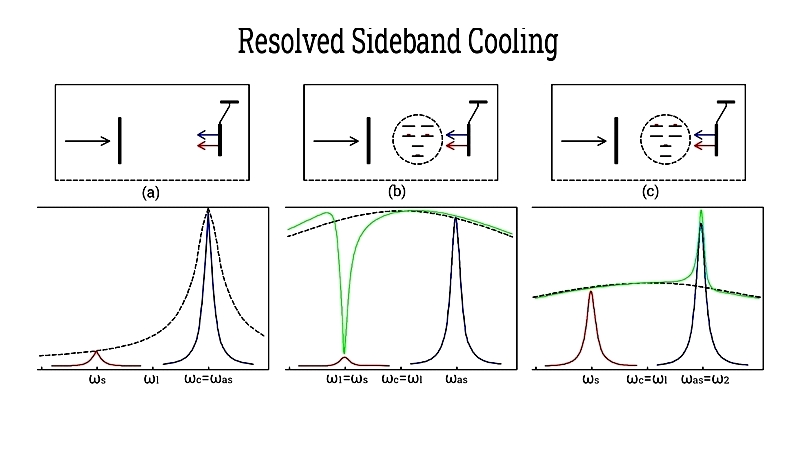
Resolved Sideband Cooling
This method cools tightly bound atoms beyond Doppler limits by aligning laser frequencies to red sidebands, enabling transitions to lower vibrational states.
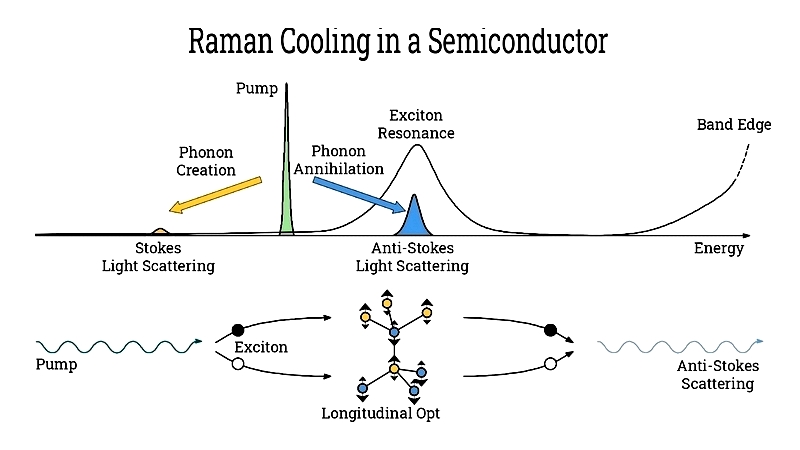
Raman Cooling
Raman cooling surpasses Doppler limits using optical molasses or optical lattices for precise atomic temperature control.
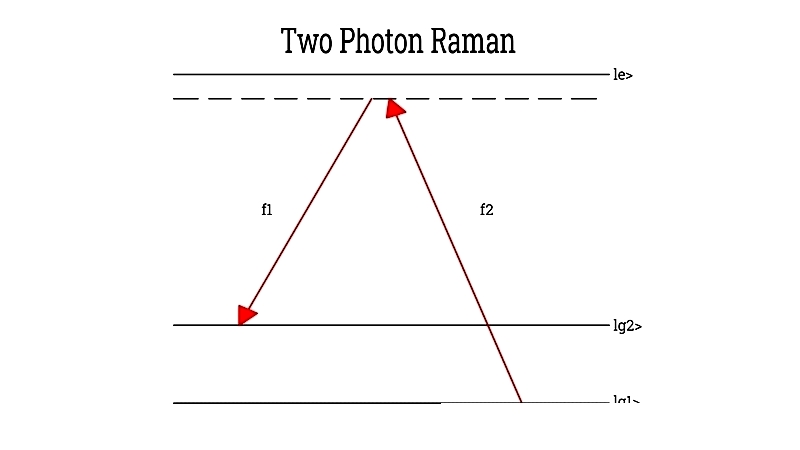
Two Photon Raman Process
Uses dual lasers to transition atoms between hyperfine states via virtual states.
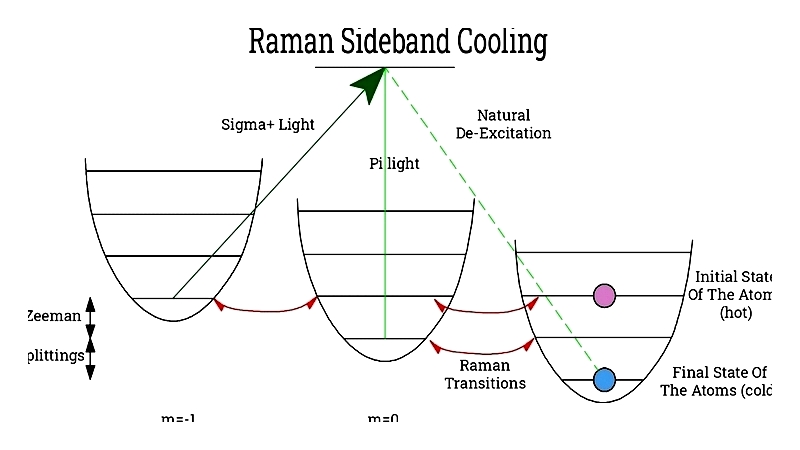
Raman Sideband Cooling
Begins with magneto-optical trapped atoms, transferring them to ground states through carefully controlled Raman processes.
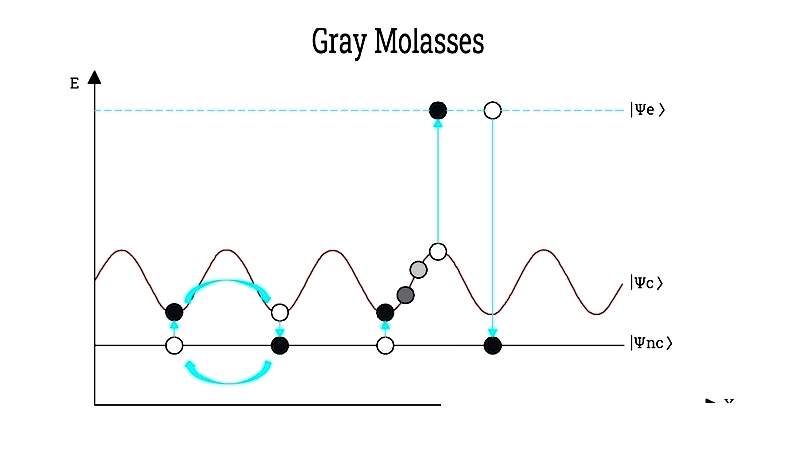
Gray Molasses
Combines Sisyphus cooling with dark states to achieve sub-Doppler temperatures for difficult-to-cool species.
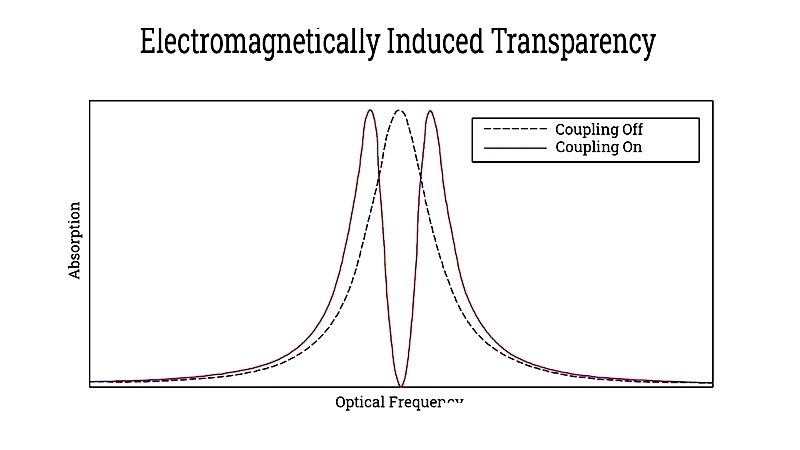
Electromagnetically Induced Transparency
Creates narrow transparent windows in opaque media using quantum interference between three atomic states.
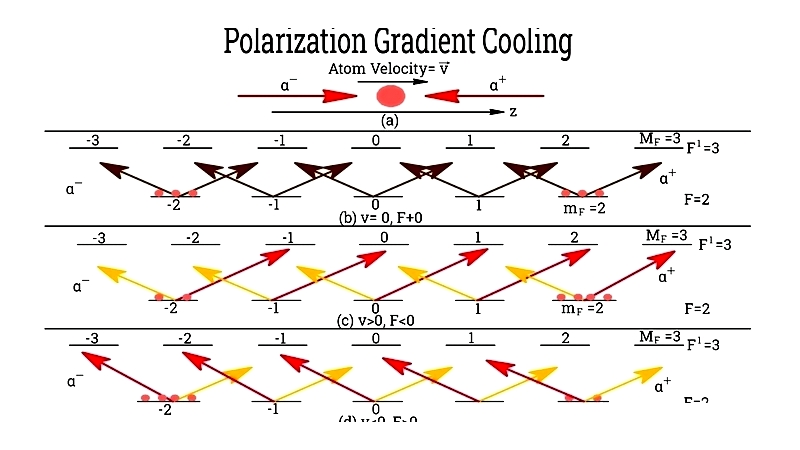
Polarization Gradient Cooling
Achieves ultra-low temperatures through spatially varying polarization states created by orthogonal laser beams.
Chapter 2: Laser Cooling Instruments and Chiller Types
This chapter examines common laser cooling devices and chiller types used for temperature control in laser systems.
Laser Cooling Instruments
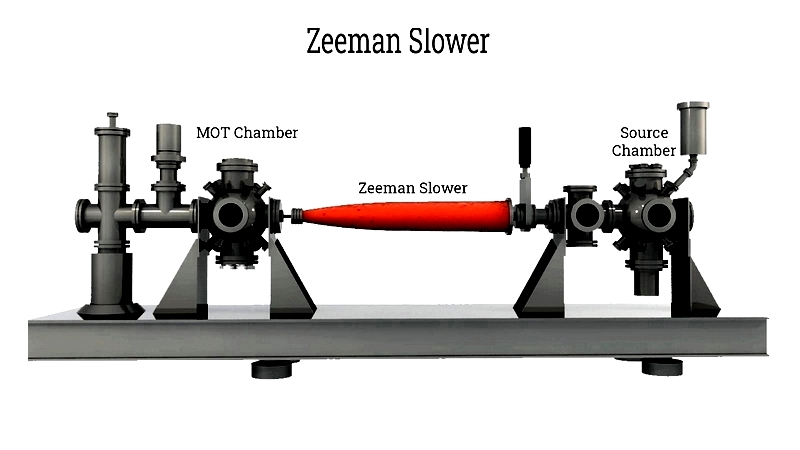
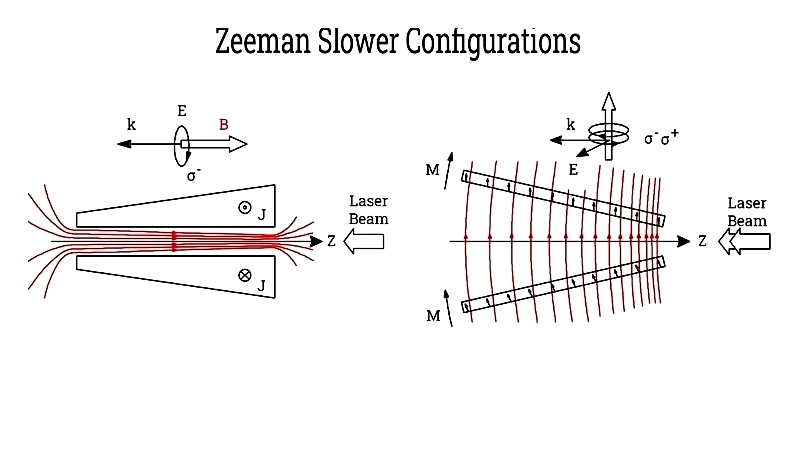
Zeeman Slower
Reduces atomic beam velocities from hundreds of m/s to a few Kelvin using Doppler cooling principles.
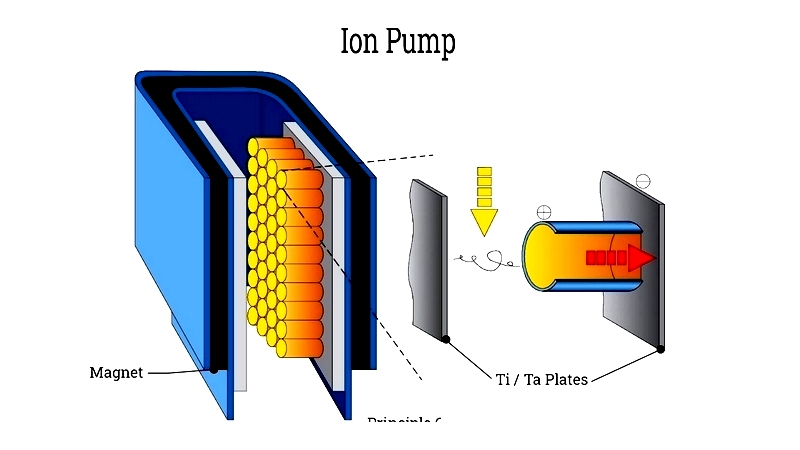
Ion Pump
Creates ultra-high vacuum environments (10-11 mbar) through sputtering for laser cooling experiments.
Laser Chiller Types
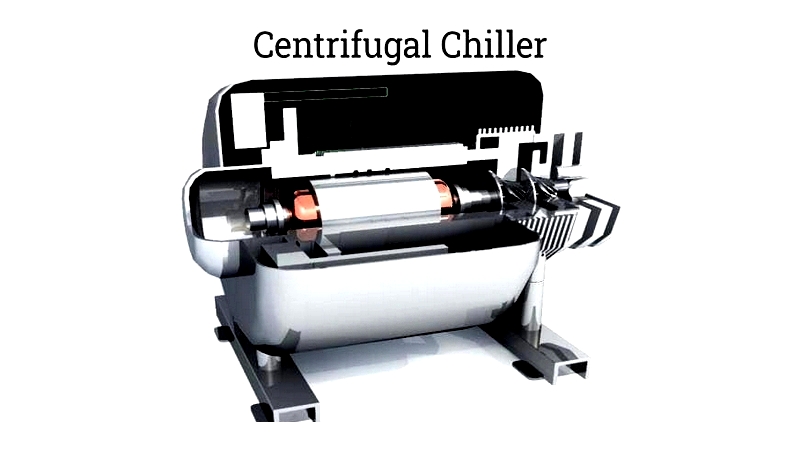
Centrifugal Chiller
Uses centrifugal compression for high-capacity cooling in industrial laser applications.

Laser Chiller System
Maintains precise temperature control for various laser types with advanced monitoring features.
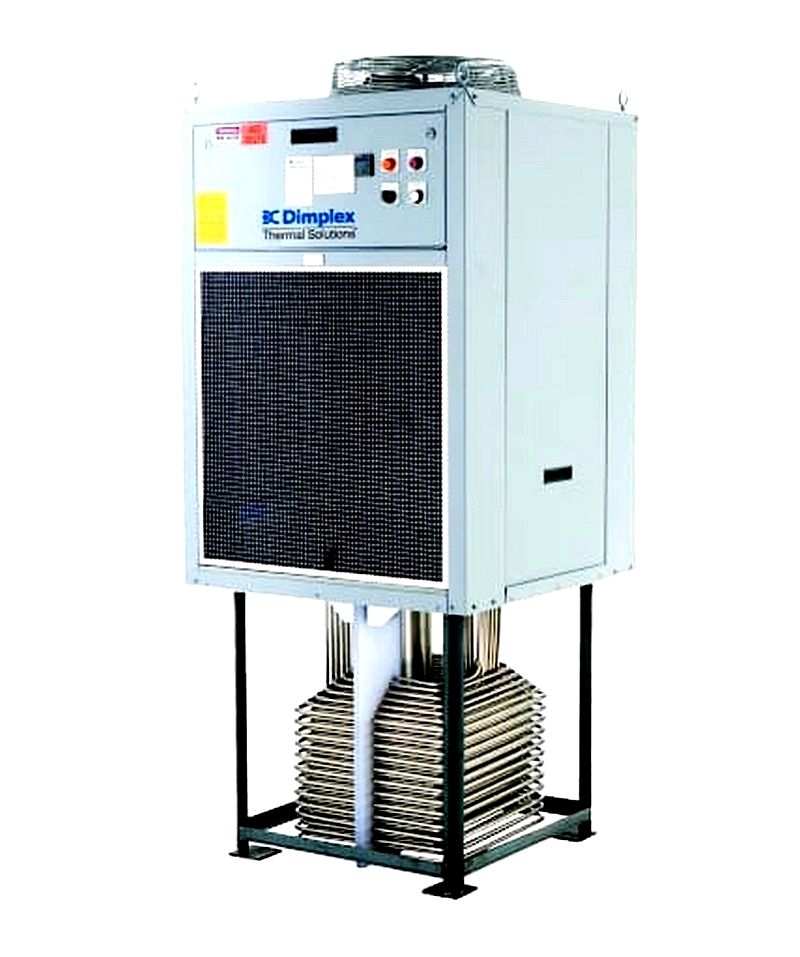 Dimplex Thermal Solutions Drop-in Chiller
Dimplex Thermal Solutions Drop-in Chiller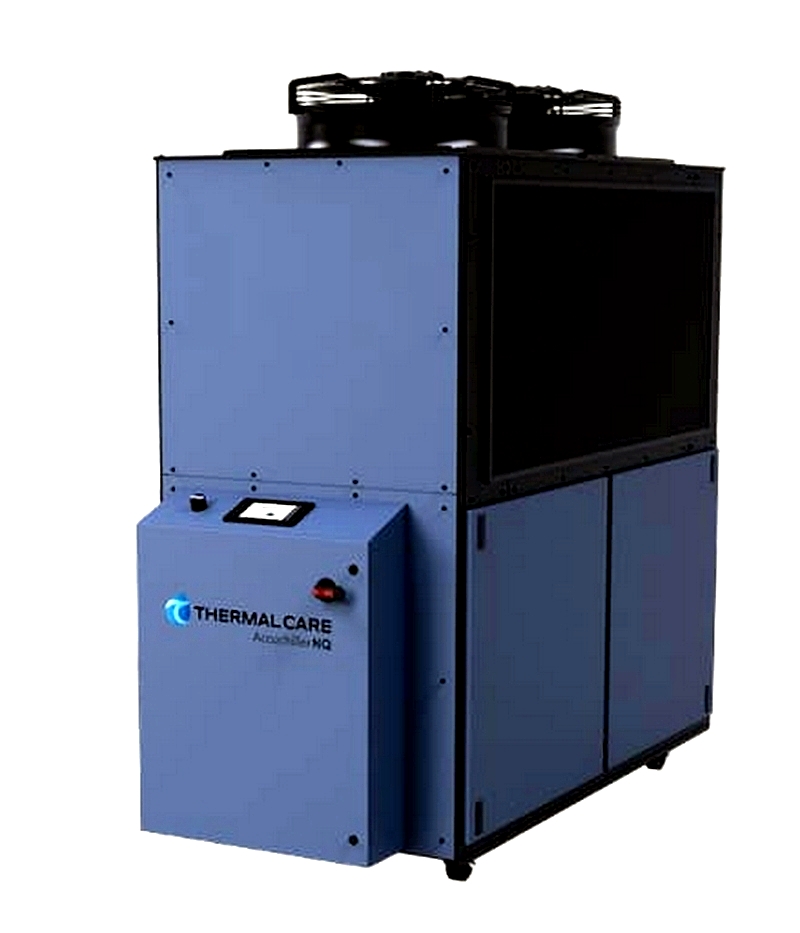 Thermal Care Dual Zone Chillers
Thermal Care Dual Zone Chillers




