Introduction
You will learn about:
- The definition of O-Rings
- O-Ring manufacturing processes
- Design and material considerations for O-Rings
- Various sizes and types of O-Rings
- And more...

Chapter 1: What is an O-Ring?
An O-ring is a circular, flexible gasket used in both static and dynamic applications. Its primary function is to create a seal between components such as pipes, tubes, pistons, and cylinders. Made from various materials to suit different applications, O-rings exhibit excellent flexibility. When placed between two surfaces, they effectively prevent gas or liquid leakage.
In static applications, O-rings remain stationary to maintain pressure or create vacuum seals. In dynamic applications, they accommodate movement including reciprocating or rotating motions. As self-sealing components, O-rings generate internal pressure within tubes or pipes to ensure secure sealing.
Chapter 2: O-Ring Manufacturing Process
The production of O-rings—essential sealing components used in hydraulic systems, automotive engines, medical devices, aerospace assemblies, and industrial equipment—involves specialized manufacturing techniques. Common methods include extrusion, injection molding, compression molding, and transfer molding. During extrusion, high-performance elastomers are shaped to precise tolerances before undergoing molding processes to meet specific O-ring requirements for advanced engineering applications.
Mold Selection
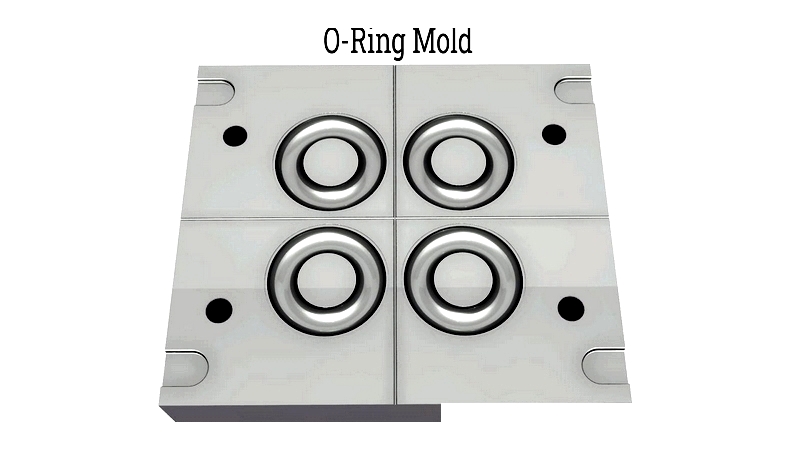
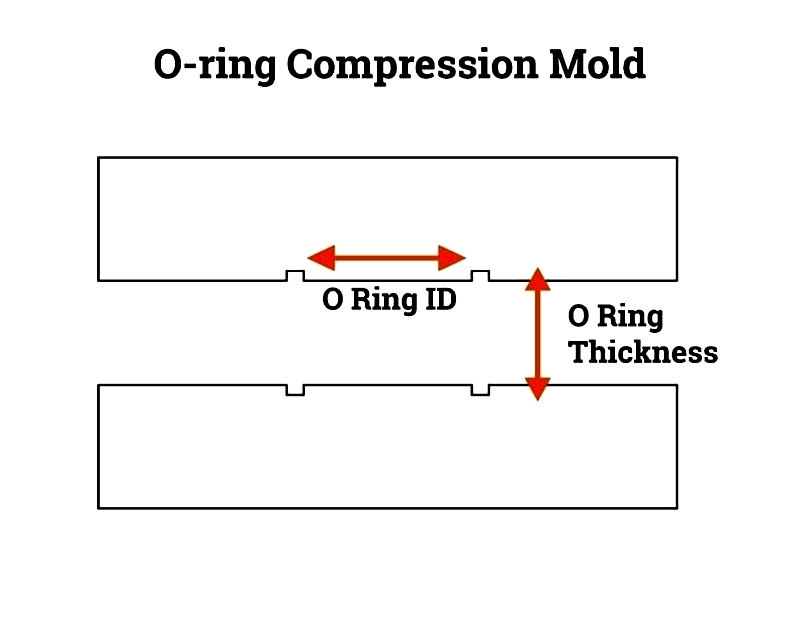
O-ring molds consist of two halves that compress elastomer compounds to form precise seals. Selecting the appropriate mold is crucial for achieving accurate inside diameters (ID), outside diameters (OD), and cross-sections. Mold choice depends on design factors including required dimensions, cross-sectional thickness, and application type (static or dynamic sealing). Since materials expand during compression, groove width should be 1.5 times the O-ring's diameter. For custom O-rings requiring non-standard sizes, CAD-designed molds ensure dimensional accuracy and performance.
For prototyping or low-volume production, spliced and vulcanized methods offer efficient alternatives without dedicated tooling, using extruded elastomer cord for custom sizes and profiles.
Material Selection
Choosing the right O-ring material is essential for optimal sealing performance, durability, and cost-efficiency. Key considerations include chemical compatibility, temperature resistance, pressure ratings, abrasion resistance, and regulatory compliance. Proper material selection ensures reliable performance across diverse environments—from harsh chemicals to sterile processes.
Common O-ring materials include:
- PTFE: Offers chemical inertness and high-temperature resistance for corrosive environments.
- Nitrile (Buna-N): Provides excellent oil and fuel resistance for hydraulic systems.
- Neoprene: Features moderate chemical resistance for refrigeration and automotive uses.
- EPDM: Delivers superior weather resistance for outdoor and steam applications.
- Fluorocarbon (Viton™): Ideal for high-temperature and chemical exposure in aerospace applications.
- Silicone: Suitable for extreme temperatures in food and medical industries.
The table below compares key properties of common O-ring materials:
Note: Always consult with O-ring specialists for material recommendations based on specific application requirements.
Extrusion Process
Extrusion forms continuous elastomer cords with controlled cross-sections. The material is heated and forced through a die to achieve precise diameters critical for sealing performance. Uniformity and surface finish are carefully monitored to prevent defects.

Molding Techniques
Three primary molding methods shape O-rings:
Compression Molding: Cost-effective for small to medium production runs, using heat and pressure to form seals.
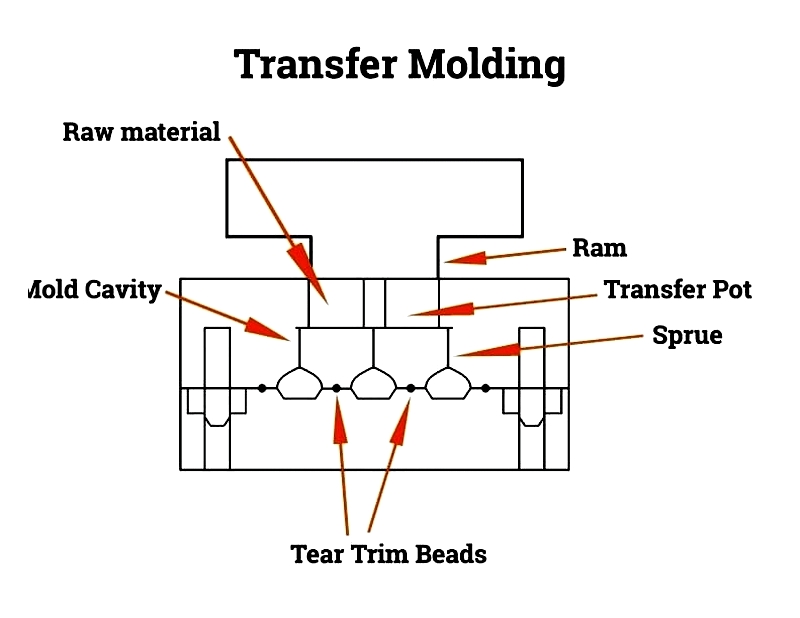
Transfer Molding: Combines features of compression and injection molding for precise, complex shapes.
Injection Molding: Ideal for high-volume production with tight tolerances, commonly used in critical industries.
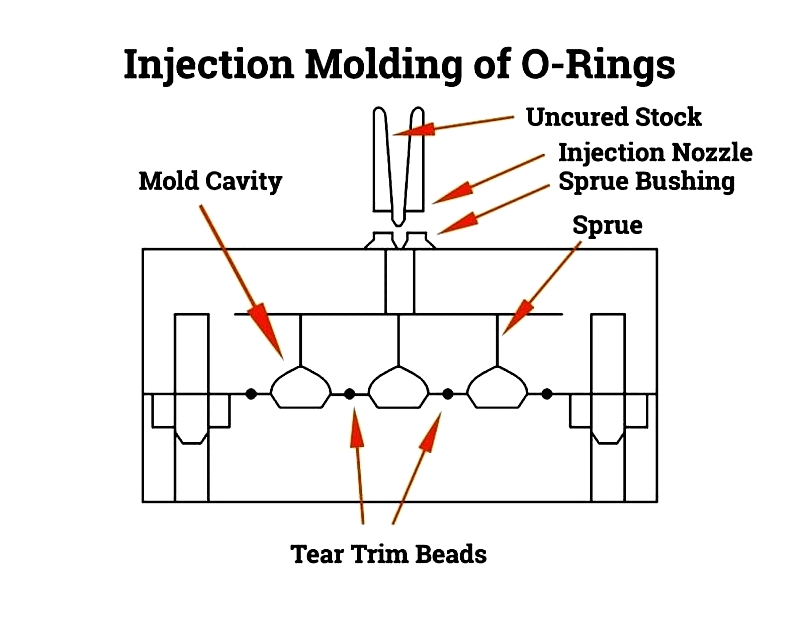
Finishing Processes
Post-molding steps include:
- Flash removal via drumming, buffing, or cryogenic methods
- Curing to enhance material properties
- Quality testing for dimensional accuracy and performance
Chapter 3: O-Ring Design and Materials
Modern O-rings serve critical sealing functions across industries, with material selection being paramount for performance. Key factors include chemical compatibility, temperature range, pressure requirements, and application type (static/dynamic). Proper design ensures reliable sealing and system integrity.
Design Considerations
important design elements include:
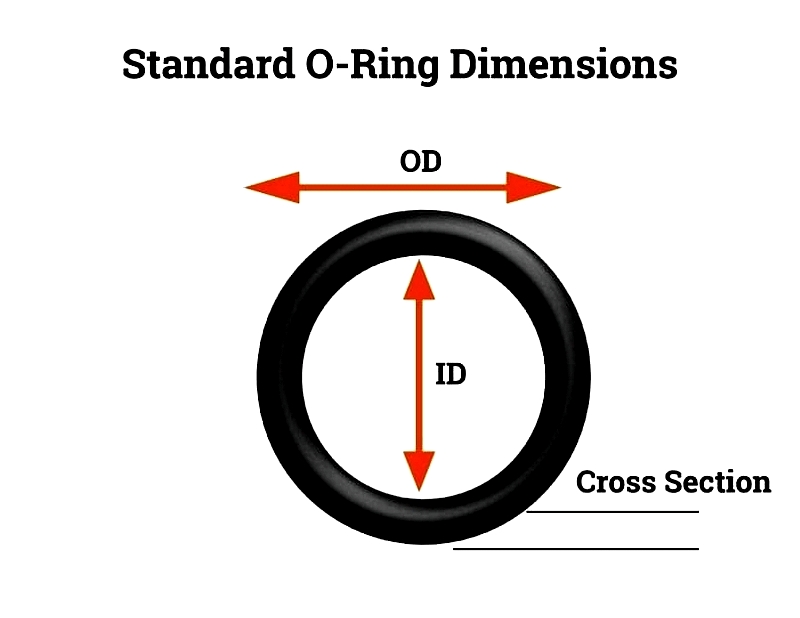
- Inner diameter (ID) and cross-section (CS) dimensions
- Shore hardness and tensile strength
- Groove design for optimal compression
Material Options
Common O-ring materials and their characteristics:
- PTFE: Chemical inertness, high-temperature resistance
- Silicone: Biocompatibility, wide temperature range
- Viton™: Extreme chemical and temperature resistance
- N




