Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of stability chambers.
You'll gain insights into various aspects including:
- What stability chambers are
- How stability chambers operate
- Key selection criteria for stability chambers
- Different types of stability chambers
- ICH guidelines for stability chamber usage
- Standard features of stability chambers
- Applications of stability chambers
- Industries utilizing stability chambers
- And more...
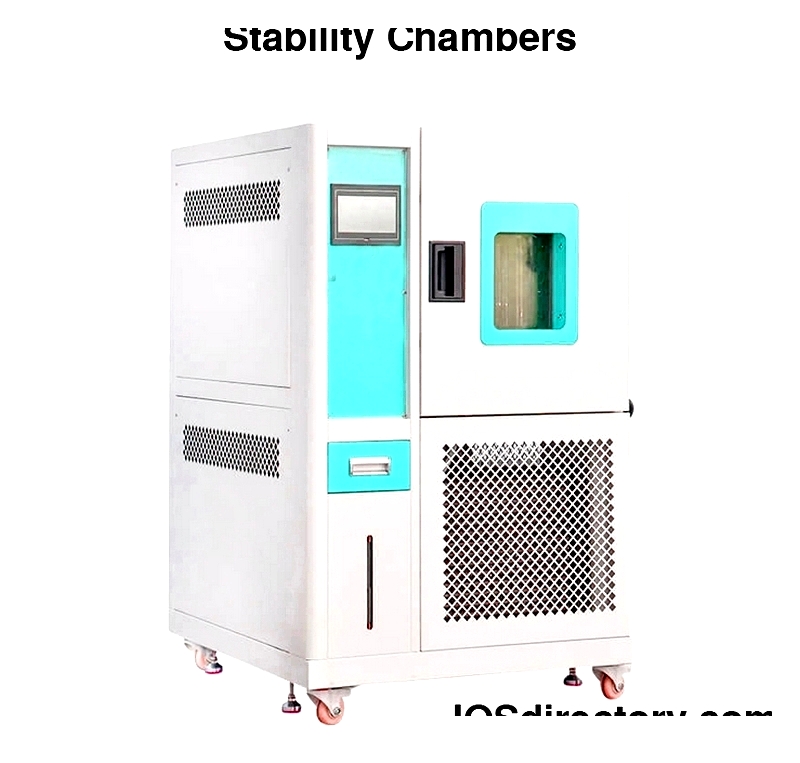

Chapter 1: How They Work and Selection Considerations
Climate-controlled stability chambers create stable environments for testing and storage by regulating temperature and humidity. These specialized facilities help determine product and packaging degradation over time. Some chambers focus on shelf life studies, while others specialize in stability testing, research, drug evaluation, and biomedical preservation. They're particularly valuable for pharmaceutical and biotech products, helping assess product stability, degradation rates, packaging durability, and container performance to meet regulatory standards.

The ICH and FDA establish specific guidelines for stability chambers. The FDA's Q1A standard provides stability testing guidance for new drug ingredients and products, covering stress testing, batch selection, container closure methods, testing frequency, and storage conditions. The standard also includes requirements for photostability testing and labeling. For stability commitment, primary batches should follow the same testing methods used in long-term studies.
Specialized chambers conduct rapid stability testing to evaluate product and package stability. These facilities assess drug stability, vitamin stability, and food stability. Some feature redundant heating/cooling systems and stainless steel construction, while others include NIST-compliant sensors. Various test chambers and cabinets meet different standards, often complying with NSF requirements.
Considerations When Choosing Stability Chambers
Selecting the appropriate test chamber is essential for accurate product testing. Key factors to consider include:
- Testing Capabilities: Chambers vary in adaptability and specialization. Ensure the selected chamber can create required conditions.
- Safety Features: Look for chambers with alarms and emergency shut-off valves to protect materials.
- Interfaces: Some chambers offer computer interfaces for remote monitoring and control.
- Controls: Choose chambers with intuitive, easy-to-understand controls.
- Maintenance: Select chambers designed for easy cleaning and upkeep.
- Size: Consider chamber dimensions, especially for testing large products.
How Stability Chambers Work
Stability chambers maintain consistent temperature and relative humidity. Relative humidity represents the air's moisture content relative to its maximum capacity. As temperature rises, air holds more water, decreasing relative humidity. This interaction ensures automatic, simultaneous adjustment of both parameters. Following ICH guidelines, humidity and temperature variations shouldn't exceed 5% and 2–3 degrees respectively.
The chamber features corrosion-resistant stainless steel construction with proper insulation and removable shelves. Sensors monitor conditions while controlled airflow maintains uniformity. Horizontal laminar airflow ensures even distribution across loaded shelves. Blowers facilitate circulation, while data loggers handle information transmission.
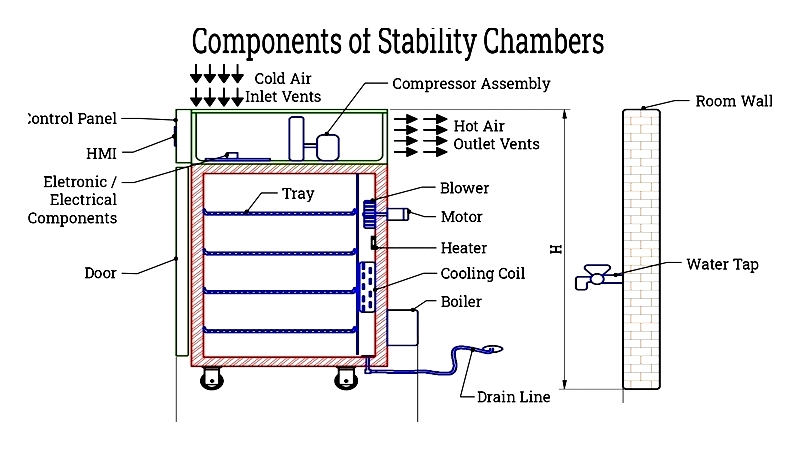
Glass doors allow observation without disrupting internal conditions, while ports enable exhaust air removal. Environmental chambers simulate various climate conditions for product testing, ranging from room-sized to benchtop units. They can create dry, humid, rainy, or corrosive environments as needed.
Photostability testing evaluates product reactions to white light and UV radiation. Safety features are crucial due to UV hazards. Choose chambers that automatically deactivate UV lights when opened.
Chapter 2: Types of Stability Chambers
Reach-in Chambers
Compact reach-in chambers suit situations with fewer samples and variable conditions.
Walk-in Chambers
Walk-in chambers accommodate large sample quantities and maintain consistent long-term conditions. ICH guidelines recommend these storage conditions:
Long-term studies: 60% ± 5% RH and 25 ± 2°C
Intermediate studies: 65% ± 5% RH and 30 ± 2°C
Accelerated stability studies: 75% ± 5% RH and 40 ± 2°C
Reliable stability data requires constant environmental conditions. Automated data logging and routine maintenance ensure proper chamber operation during extended testing periods.
Temperature-Humidity Chambers
Humidity chambers replicate environmental conditions to test product performance under extreme scenarios. These tests evaluate product longevity and durability, informing design improvements and material selection. Testing can be static or dynamic depending on requirements.
Extended testing chambers assess specimen responses to prolonged moisture exposure. Chambers introduce moisture via sprays or baths, while heat comes from coils or heating elements. Custom designs meet specific environmental requirements, with all chambers relying on fundamental heat and moisture principles.

Environmental Chambers
Environmental chambers evaluate products under various simulated conditions. Computer-controlled systems precisely replicate real-world scenarios, often exceeding typical usage conditions. These advanced tools provide valuable data for product improvement and development.

Photostability Chambers
ICH Q1B guidelines require photostability testing in specialized chambers. Available in benchtop and upright configurations, these chambers ensure uniform light, temperature, and humidity distribution.
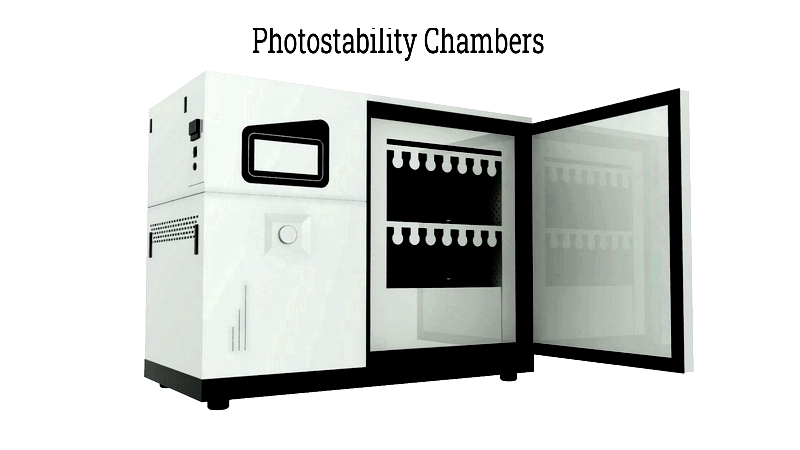

These chambers use cool white and UV-A fluorescent lamps, completing tests within 100 hours. Optimal testing requires quality equipment, precise sensors, and user-friendly controls.
Thermal Shock Test Chambers
These chambers evaluate product resilience to sudden temperature changes. Engineers use them to verify product performance under expected conditions.
Thermal shock testing subjects products to rapid 30°C+ temperature fluctuations, simulating extreme operational conditions.
Anechoic Stability Chambers
Anechoic chambers absorb electromagnetic and sound waves to eliminate echoes. Room-sized and soundproofed, they prevent external noise interference during product noise level testing.
Common applications include testing vehicles, appliances, and electronic devices.
Vacuum Chambers
Vacuum chambers create low-pressure environments by removing air, essential for aerospace and defense product testing. Sizes range from benchtop units to room-sized installations.




