Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of balers.
You will learn about various topics including:
- The history of balers
- Different types of balers
- Safety and compliance standards and regulations
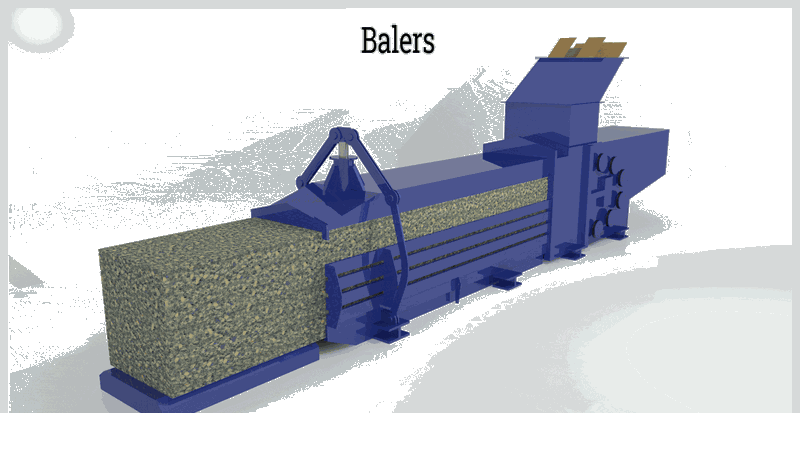
Chapter 1: What is the history of balers?
Modern balers trace their origins to mid-1800s hay presses, which revolutionized hay gathering and organization. These early stationary installations, often two to three stories high in barn haylofts, were powered by horses lifting and dropping weights to compress hay. Alternative designs used horse or mule-driven sweeps connected to geared presses or jackscrews. Before hay presses, farmers manually collected hay using forks and rakes. The development of stationary presses eventually led to portable versions.
During the 1860s, the first portable hay baler prototype required multiple operators. By the late 19th century, technological improvements enabled single-person operation through plunger mechanisms. Early baler designs lacked standardization until the early 20th century.
The 20th century introduced mechanical balers. George Innes developed the first automatic round baler in 1936, featuring a self-tying mechanism with Appleby knotters from John Deere grain binders. Ed Nolt improved this design in 1939, creating a more reliable model that set industry standards. Today, round balers remain the most common type.
As farming mechanization increased and farmer populations decreased, equipment manufacturers faced shrinking markets. With durable machinery requiring fewer replacements, these companies sought alternative revenue streams.
Manufacturers identified waste management as a promising new market. Industries generated substantial waste—boxes, paper, and cardboard—that occupied significant space in trash receptacles. In the 1940s, the first industrial baler adapted hay baler designs to compact industrial waste, saving space and simplifying disposal.
The environmental movements of the 1970s and 1980s boosted baler production. Businesses appointed waste management directors to oversee recycling and proper disposal. This sustainability focus led to the invention of recycling balers, initially designed for cardboard.
Chapter 2: What is the design of balers?
Waste balers are specialized recycling equipment crucial for managing and reducing waste volume in industrial, commercial, and municipal settings. These heavy-duty machines efficiently compress waste into dense, manageable bales for easier transportation and storage. Their robust construction handles diverse materials including cardboard, foam rubber, plastic, paper, textiles, and metals from manufacturing and distribution centers.
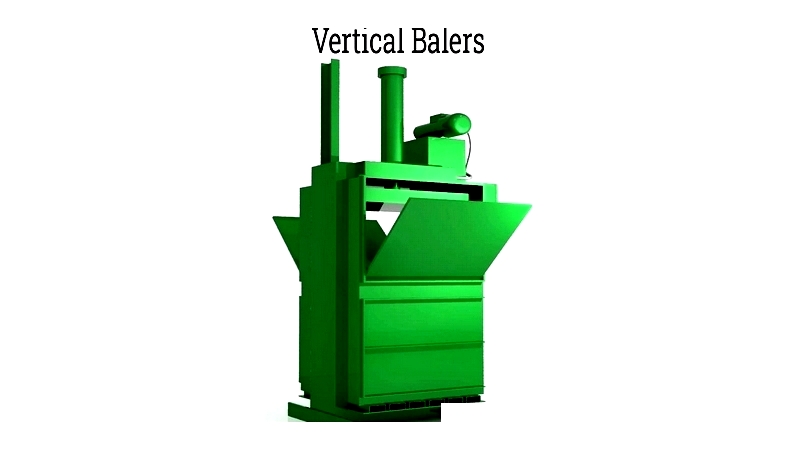
Modern waste balers, also called recycling balers or compactors, feature three main components: the bin (hopper), compaction mechanism, and motor unit. Waste accumulates in the bin until reaching a set threshold, when the hydraulic or electric-powered compaction mechanism forms dense bales. This process saves space, supports sustainability, and reduces transportation costs. Bales are secured with wire, plastic strapping, or wrap to protect against moisture, wind, odors, pests, and hazards.
Baler designs have diversified to meet industry-specific needs. Choosing the right baler maximizes recycling efficiency, regulatory compliance, and workplace safety. Common types include vertical, horizontal, auto-tie horizontal, closed-door horizontal, and two-ram balers, each optimized for different waste volumes, materials, and facility spaces.
Vertical balers are popular in retail, restaurants, small manufacturers, and supermarkets handling moderate recyclables like cardboard and shrink wrap. Their vertical compression suits spaces with limited floor area and approximately eight-foot ceilings, supporting sustainable waste management.
Horizontal balers serve high-volume operations like distribution centers and recycling facilities. Their side compression with hydraulic rams allows continuous or semi-automatic feeding via conveyors, processing large quantities of cardboard, paper, and plastics efficiently.
Advanced horizontal balers include auto-tie models that automatically secure bales, reducing labor costs, and closed-door models producing denser, more uniform bales for efficient stacking and transportation.
Two-ram balers handle intensive recycling of bulky materials like metals and rigid plastics. Their dual hydraulic rams—one for compression and one for ejection—enable faster processing of diverse materials, ideal for scrap metal recycling and material recovery facilities.
Manufacturers continue innovating with features like integrated conveyors, smart sensors, energy-efficient motors, and safety interlocks to enhance efficiency and compliance. When selecting a baler, consider your facility's waste output, material types, space, and sustainability goals. Comparing features, energy ratings, and total costs ensures optimal investment and workflow integration.
These baler designs address modern waste management challenges with tailored solutions. For detailed specifications, ROI analysis, and recommendations, consult reputable suppliers and request equipment demonstrations.




