Introduction
This article covers everything you need to know about EMI Filters and their applications.
You will learn:
- What an EMI Filter is
- The different types of EMI Filters
- How EMI Filters are manufactured
- How EMI Filters are utilized
- And much more...
Chapter 1: What Exactly is an EMI Filter?
An electromagnetic interference (EMI) filter is a critical electrical component or circuit designed to eliminate unwanted frequencies from power lines or signals that could disrupt system operation. It processes AC or main power to filter out noise and delivers a clean output signal for optimal device performance. Commonly known as a choke, an EMI filter reduces high-frequency electromagnetic interference in power and signal lines. These filters are classified as low pass, high pass, bandpass, or band reject and typically include passive components like capacitors and inductors, arranged in LC circuits or more complex configurations.
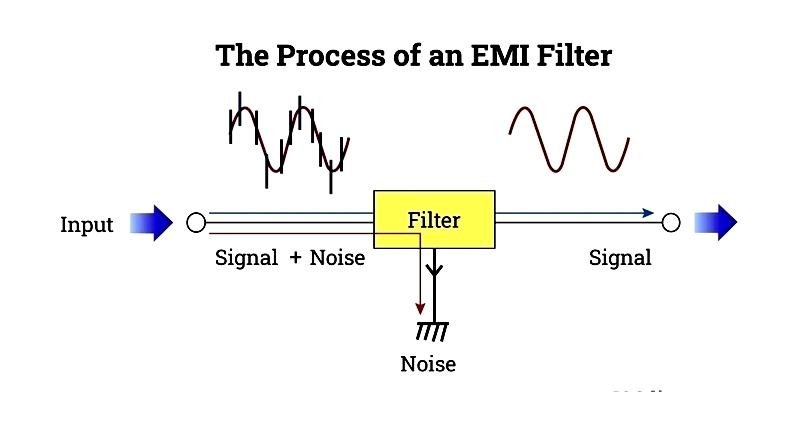
EMI filters use capacitive and inductive materials to remove high-frequency noise from signals. They work by absorbing or reflecting noise mixed with the genuine signal, producing a cleaner output.
Inadequate EMI protection can severely impact electrical device performance, causing unwanted currents and voltages in circuits. EMI can be conducted, traveling through physical paths, or radiated.
Radiated EMI spreads through the air without physical pathways. This interference occurs when a device emits electromagnetic energy as an electric field, potentially damaging other equipment by overwhelming their circuitry. Such emissions can travel long distances, disrupting device operation.
Internal EMI can also cause interference within a system. This occurs when sensitive components are placed near high-voltage or high-current circuits, leading to electromagnetic interference between different circuits.
Chapter 2: What are the different types of EMI filters?
EMI filters, also called electromagnetic interference filters or RFI (radio frequency interference) filters, are essential components in electronic devices and electrical systems to suppress unwanted electrical noise. They come in various sizes, designs, shapes, and configurations, each designed to protect sensitive equipment like medical devices, industrial controls, and consumer electronics from harmful electromagnetic disturbances. EMI suppression improves system safety, reliability, and performance. EMI filters are broadly categorized into two types: active and passive, each suited for different applications.
Active EMI Filters: Active EMI filters use an internal power supply to generate a counteracting current that neutralizes interference. These advanced filters monitor input voltage and emit a reverse current to cancel out electrical noise. Using active components like operational amplifiers and feedback circuits, active EMI filters effectively reduce both common mode and differential mode noise, especially at low and high frequencies.
Passive EMI Filters: Passive EMI filters absorb and dissipate unwanted energy instead of generating opposing currents. Made from passive components like capacitors, resistors, transformers, and inductors, passive filters create electrical resonance at specific frequencies to attenuate conducted and radiated electromagnetic interference. They suppress harmonic currents and minimize voltage distortion, making them ideal for power electronics, motor drives, solar systems, and industrial automation.
EMI filters are widely adopted for their effectiveness in protecting sensitive circuits from both conducted and radiated EMI. Quality EMI/RFI filters eliminate disruptive interference, allowing only desired signals to pass, which is crucial for compliance with international EMC standards.
Single Phase EMI Filter
Single-phase EMI filters are designed for single-phase AC power systems and are commonly used in household appliances, office equipment, and laboratory instruments. These filters suppress both common mode and differential mode noise, reducing conducted interference on power lines. They play a vital role in EMC compliance and ensuring reliable electronic equipment operation. Design engineers should consider insertion loss, rated voltage, rated current, and filter bandwidth when selecting a filter.
3 Phase EMI Filter
Three-phase EMI filters are built for robust noise suppression in industrial, commercial, and medical equipment using three-phase power. Designed to handle higher interference levels, these filters are suitable for applications operating between 47 Hz and 400 Hz. Typical uses include frequency converters, motor drives, CNC machinery, and automation systems. The two main three-phase filter topologies are Wye (star) and Delta:
- Wye Filter Types – Wye filters connect three hot wires to a single neutral point, creating a four-wire system. This configuration allows for versatile connections and is popular in sensitive environments for its voltage stabilization and current distribution.
- Delta Filter Types – Delta filters use a triangular configuration without a neutral point, requiring only three wires. This design ensures balanced power delivery and is ideal for heavy-duty industrial equipment.
When selecting a three-phase EMI filter, consider leakage current, filter attenuation, physical footprint, rated voltage, and safety certifications (UL, CE, RoHS).
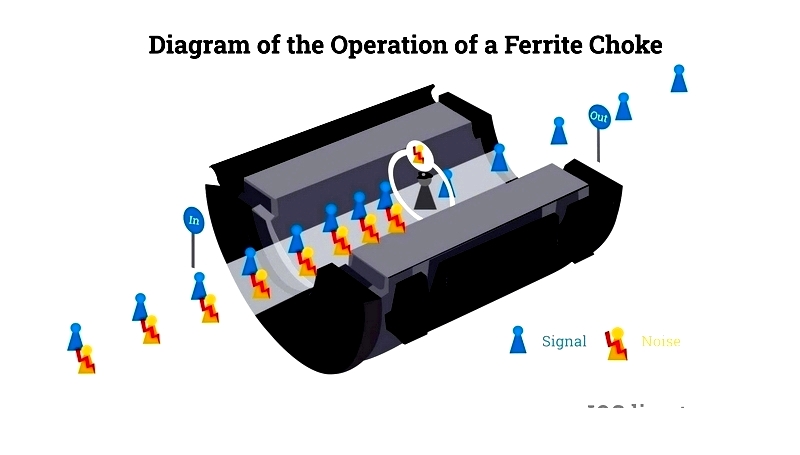
Ferrite Choke
Ferrite chokes, also known as ferrite bead filters or ferrite rings, are versatile and cost-effective passive EMI suppression solutions. They act as low-pass filters, attenuating high-frequency noise in data cables (HDMI, USB, Ethernet), audio/video wires, and power supply lines. Ferrite chokes are essential for compliance with FCC and CISPR standards.
The core of a ferrite choke is made of magnetic ferrite material, which resists high-frequency signals while allowing low-frequency currents to pass. Proper placement—typically 5 cm from the device's connector—enhances EMI attenuation efficiency. Selection depends on cable diameter, interference frequency range, rated current, and environmental conditions.
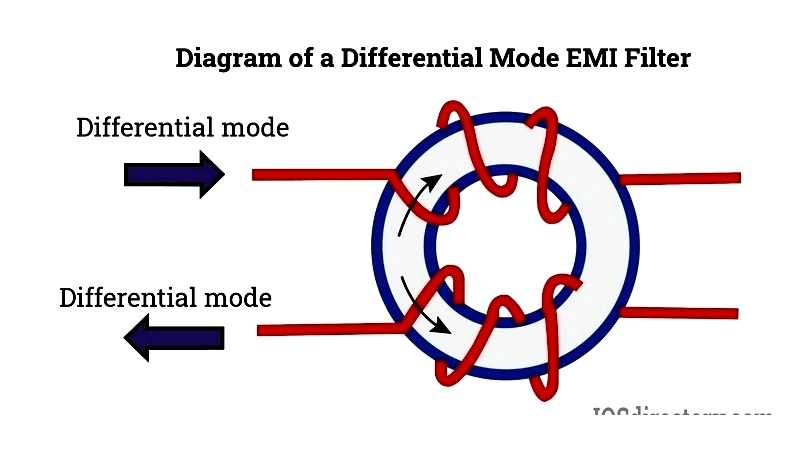
Differential Mode (DM) Passive EMI Filters
Differential mode passive EMI filters attenuate high-frequency AC currents (noise) flowing in opposite directions through conductors. Often implemented as LC filters or common mode chokes with added capacitors, these filters can be customized for specific interference mitigation needs.
These filters use magnetic cores with windings to impede differential signals while allowing common mode currents to pass. Differential mode EMI suppression is critical in power supplies, DC-DC converters, and telecommunications. Key selection criteria include impedance, current rating, insertion loss, and resonance frequency.
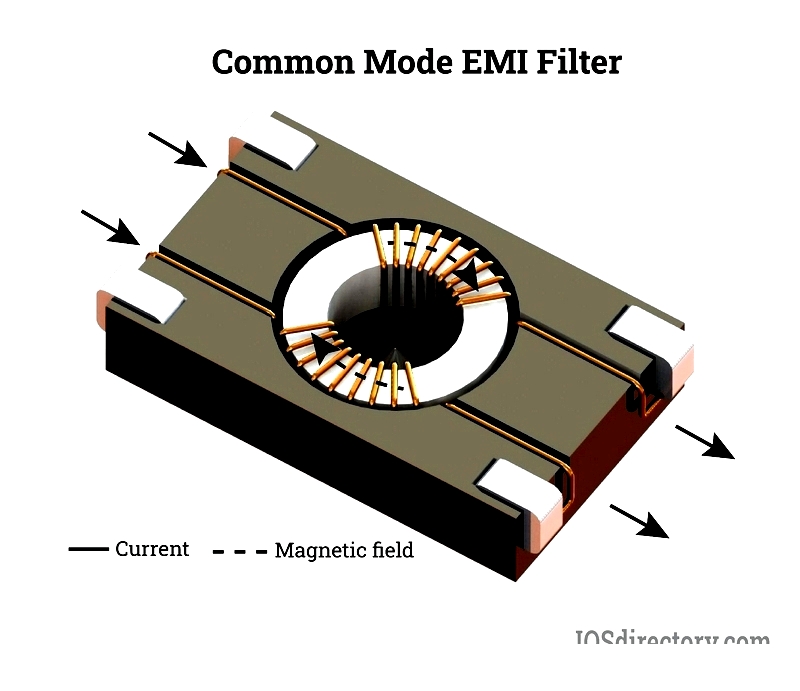
Common Mode (CM) Passive EMI Filters
Common mode passive EMI filters block high-frequency noise currents present in the same direction on both power lines. These disturbances can be radiated or conducted, originating from switching power supplies, inverters, and motors. The filters produce opposing magnetic fields, allowing only low-frequency signals to pass and providing effective RF filtering.
Common mode EMI filters are categorized by frequency band: RF EMI filters (above 30 kHz) and AF EMI filters (up to 30 kHz). RF EMI filters are used in digital communication devices, while AF EMI filters are found in switch-mode power supplies and rectifiers.
Core materials—solid iron for AF and powdered ferromagnetic alloys for RF—ensure optimal noise attenuation and compliance with EMI guidelines. Proper core and filter structure selection minimizes leakage current and optimizes EMI suppression.
Line Chokes
Line chokes, or AC line reactors, mitigate harmonic distortion and spikes from switching devices or variable frequency drives (VFDs). Installed in series with VFD inputs or outputs, they limit inrush currents, reduce transients, and protect drives and motors. Line chokes suppress harmonics and extend equipment lifespan by providing surge protection.
For long cable runs or multiple drives, output-side load reactors prevent voltage reflections and standing waves. Three-phase line chokes are essential for harmonic mitigation in AC to DC rectification, protecting sensitive electronics.
Proper sizing for voltage,




