Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of shock, bungee, and elastic cords.
Key topics covered include:
- Definitions of Bungee Cords, Shock Cords, and Elastic Cords
- Varieties of Bungee Cords, Shock Cords & Elastic Cords
- Applications and Advantages of Bungee Cords, Shock Cords & Elastic Cords
- Additional Relevant Information
Chapter 1: What Are Bungee Cords, Shock Cords, and Elastic Cords?
This chapter examines bungee cords, shock cords, and elastic cords, including their manufacturing methods.
Understanding Bungee Cords
Bungee cords, also called shock cords or elastic cords, consist of multiple elastic strands encased in woven fabric. Each end typically features hooks for attachment and secure fastening.

Primarily made from rubber and covered with fabric, bungee cords offer ideal elasticity for various uses. They're commonly employed to secure luggage or loads on vehicle exteriors.
Bungee Cord Manufacturing
The elastic strands in bungee cords are made from rubber - natural, synthetic, or a combination - depending on intended use. The outer woven sheath may use materials like polypropylene, cotton, or nylon, providing protection and additional flexibility.
Materials in Bungee Cord Production
Bungee cords mainly consist of rubber, either synthetic or natural. Natural rubber (latex) is often preferred for its tensile strength and elasticity, though it degrades under UV exposure.

Synthetic rubber like neoprene offers better UV resistance but less tensile strength. Natural rubber remains the choice for military specifications and activities like bungee jumping.
The exterior coating typically features braided cotton or nylon fabric. Commercial cords usually have single-layer nylon, while military-grade versions often use double-layer cotton for durability.
Bungee Cord Design Specifications
Design varies by application. Commercial bungee ropes typically measure 0.25-0.62 inches in diameter, military versions 0.25-0.87 inches, and jumping cords 0.62 inches.
Stretch Characteristics
Bungee cords are engineered for specific stretch lengths and elongation percentages. Elongation is calculated by how much the cord extends beyond its original length.
Manufacturing Process
Bungee cord production involves several key steps:
Rubber Ribbon Production
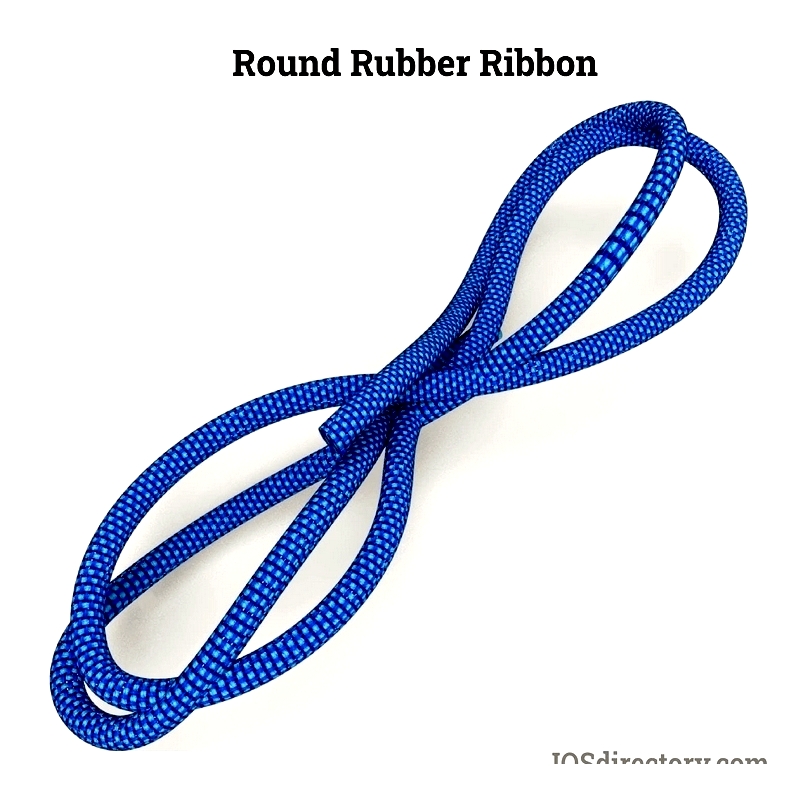
Manufacturing begins with extracting natural or synthetic rubber, formed into long ribbons (0.09-0.12 inches thick, 0.25 inches wide, up to 100 feet long). These pass through an extruder for shaping before cooling.
Rubber Ribbon Preparation
Tensile strength and diameter depend on strand quantity. During braiding, strands receive a talc or soapstone coating to prevent sticking in heat.

Outer Cover Braiding
A braider machine weaves rubber strands while maintaining light tension. Yarn forms the protective cover, with additional layers added as needed, often color-coded per client specifications.
Shipping Preparation
Finished cords are cut, coiled, and boxed. Dark plastic bags protect against sunlight, air, and UV rays during storage and transport.

End Fitting Attachment
Fittings are added based on specific needs. For luggage, cords are looped and wired with J-hooks. Jumping cords use waxed string whipping and may attach to non-metallic eyes or fabric webbing.

Quality Control
Rigorous quality checks include:
Visual Inspection
Examination for defects like rubber imperfections, incorrect coloring, sheath gaps, or damage.
Testing Protocols
Essential tests measure tensile strength, load capacity, and stretch rate under various loads for both commercial and military cords.
Color Coding & Labeling
Some manufacturers use color coding, particularly for military cords, to indicate production dates. Commercial cords mainly use color for aesthetic purposes.
Shock Cord Overview
Shock cords feature a quality rubber core with polyester sheath, known for compactness, durability, and stability. They're versatile for securing tools or gear but typically lack hooks.

The polyester sheath enhances abrasion resistance. While similar to bungee cords, shock cords are primarily used in military applications and bungee jumping.
Shock Cord Features
Key characteristics include:
- Versatile line for stringing or tethering accessories
- Ideal for securing objects or tie-downs
- Keeps personal items elevated
- High-quality rubber core
- Durable 100% polyester sheath
- Highly elastic for stretch applications
- Compact and lightweight
- Not suitable for life safety purposes
- Not certified for jumping, climbing, or rappelling
Elastic Cord Definition
Thinner than shock or bungee cords, elastic cords suit smaller projects like jewelry, headbands, and decorative items. Larger versions can secure tarps or tent items.

They're versatile for DIY projects including kitchen organization, toy bundling, or bike storage. However, shock cords may be preferable for heavier loads.
Elastic vs. Shock Cords
While made from similar materials, shock cords typically stretch more (up to 100% elongation) compared to elastic cords (usually 50% elongation).
Chapter 2: Types of Bungee Cords, Shock Cords, and Elastic Cords
This chapter explores various types, detailing unique properties, recommended uses, and features to inform purchasing decisions. Understanding available options helps select ideal solutions for specific needs, from UV-resistant outdoor cords to crafting-specific elastic varieties.
Bungee and Shock Cord Types
Different types are optimized for specific purposes, improving safety, equipment security, and performance across applications from automotive tie-downs to cargo




