Introduction
This article covers everything you need to know about robotic system integration and its applications.
You will learn about:
- What Robotic System Integration is
- How to Select a Robotic System Integrator
- The Role of Robotic System Integrators
- Different Types of Robotic System Integrators
- And more...
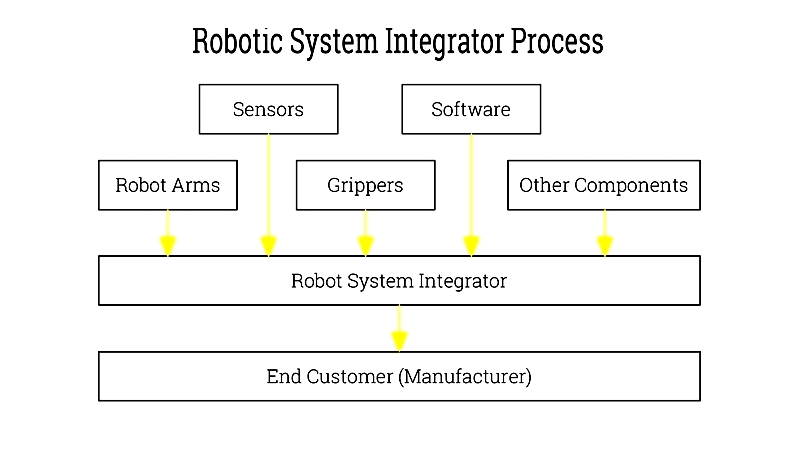
Chapter One: Understanding Robotic System Integrators
Robotic system integrators specialize in helping businesses automate various functions. They design customized robotic solutions tailored to specific operational needs, offering comprehensive strategies for integrating robotics into industrial processes. While robot manufacturers produce diverse robotic technologies for general use, these systems often require adaptation.
Robot manufacturers depend on system integrators for their expertise in helping end-users select the best robotic solutions for particular environments. Integrators play a crucial role in deploying, distributing, and advancing automated robotic systems.
Not all integrators can address every challenge, as each focuses on specific solutions. The right integrator is selected based on the integration requirements and their expertise in the relevant application. Their track record in handling similar applications is also a key consideration.
Robotic system integrators specialize in areas like material handling, warehouse automation, supply chain, manufacturing, and assembly tasks. Customers choose integrators based on their specialized knowledge.
Chapter Two: How to Choose a Robotic System Integrator
A robotic system integrator serves as a strategic automation partner, working with manufacturing and industrial clients to develop optimal robotic automation solutions for their production challenges. Leading integrators stand out through their deep expertise in robotics integration, industrial automation, control systems, and robotics engineering. After evaluating a client's processes, a qualified integrator proposes customized approaches to implementing advanced robotic solutions, including collaborative robots (cobots), industrial robots, vision systems, and end-of-arm tooling.
Experience
When selecting a robotic system integrator, industry experience and proven automation expertise are essential. This includes not only knowledge of robotic systems but also familiarity with specific sectors like automotive, electronics, food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, warehousing, or metal fabrication. For example, an integrator skilled in material handling automation may not be suited for robotic assembly line integration, just as a welding robotics expert might lack experience in pick-and-place or eCommerce fulfillment applications.
Early in the selection process, clients should identify automation specialists with relevant industry experience. Client references, case studies, and knowledge of sector-specific regulations can help verify an integrator's ability to deliver effective solutions.
- Inquire about their experience with similar projects and industries.
- Request performance data, such as improvements in throughput, downtime reduction, or ROI.
- Assess their understanding of standards like ISO safety protocols and industry best practices.
Solutions
An experienced integrator should be knowledgeable about the latest robotics solutions, including articulated robots, SCARA robots, machine vision, and flexible automation cells. Clients often rely on integrators to recommend technologies like AI-driven robotics or automated guided vehicles (AGVs) to enhance operations. The best solutions align with existing workflows while improving process efficiency, reducing labor costs, and boosting productivity.
Top integrators take a consultative approach, conducting process audits and presenting options that balance automation goals, ROI, and scalability. This may include robotic workcells, conveyor integration, safety systems, and IIoT connectivity.
The Plan
Developing a customized turnkey automation plan is a key challenge for integrators, as no single solution fits all environments. Leading manufacturers offer systems for robotic palletizing, parts inspection, assembly, packaging, and welding automation, each with unique strengths. Integrators must select the right combination of hardware and robotic control software to meet client objectives.
once selected, the integrator outlines a step-by-step implementation plan, detailing robot deployment and integration of conveyors, sensors, machine vision, and safety barriers to ensure seamless operation.
A well-structured plan clarifies how integrated technologies will improve throughput, reduce costs, enhance safety, and maximize uptime compared to manual processes. It may also include employee training and phased automation scaling.
The plan should address financial, technical, regulatory, and safety considerations. Financial analysis covers payback period, total cost of ownership (TCO), maintenance needs, and projected savings. Experienced integrators demonstrate how long-term productivity gains justify the initial investment.
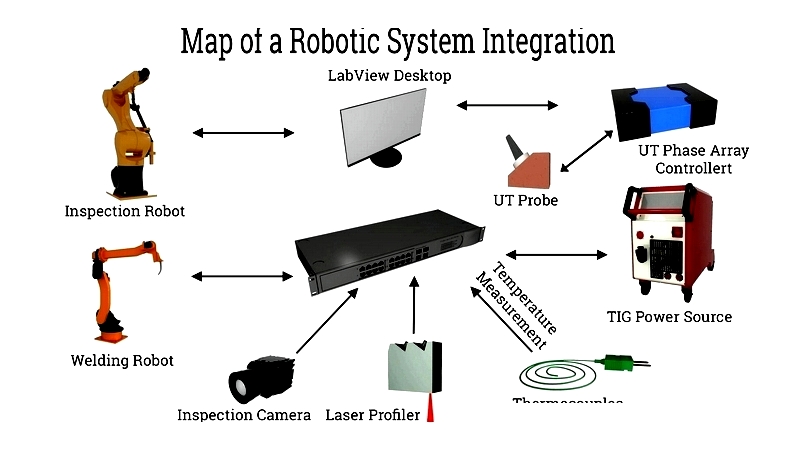
Execution
Real-world implementation often reveals unexpected challenges. Experienced integrators anticipate issues like robot programming errors, sensor misalignment, software integration problems, or safety compliance concerns and address them promptly. Rigorous testing ensures robotic arms, vision systems, conveyors, and safety protocols work cohesively to maximize uptime and performance.
Quality assurance processes—such as factory acceptance testing (FAT), site acceptance testing (SAT), and operator training—are critical for project success. Continuous collaboration ensures a smooth transition from manual to automated processes.
Support
Robotic system integration requires ongoing support, including maintenance, troubleshooting, and software updates. Clients should ensure their integrator offers comprehensive support services, such as remote diagnostics, on-site maintenance, spare parts availability, and training resources.
Reliable support fosters long-term partnerships and system uptime. Verify if the integrator provides 24/7 support, online resources, and maintenance agreements to protect your investment.
Certification
The Robotics Industries Association (RIA) established a certification process for robotic system integrators in 2012, setting industry standards for technical expertise and safety knowledge. RIA certification indicates an integrator meets high standards for project management and customer success.
The certification process includes on-site audits, technical evaluations, and safety training assessments, ensuring certified companies deliver safe, reliable, and efficient solutions. Clients gain confidence by choosing certified integrators.
When evaluating integrators, check certification status through organizations like RIA (now A3 – Association for Advancing Automation). This confirms their knowledge of safety standards, best practices, and emerging technologies.




