Introduction
This article provides comprehensive information about steel fabrication. Continue reading to learn about:
- What steel fabrication is
- Raw materials used
- Initial processing steps
- Cutting, bending, and joining techniques
- And more...
Chapter 1: Understanding Steel Fabrication
Steel fabrication involves creating steel products through secondary metalworking techniques like cutting, bending, and assembling. Additional processes such as heat treatment and finishing enhance the metal's properties. This vital industry supports nearly all industrial sectors, with steel products being essential for construction, transportation, energy, mining, agriculture, and consumer goods manufacturing.
Skilled professionals perform steel fabrication using specialized techniques. These certified experts possess extensive training and thorough knowledge of steel's characteristics.

Primary vs. Secondary metal Manufacturing
Understanding steel fabrication requires distinguishing between primary and secondary metal manufacturing. Primary manufacturing produces basic semi-finished products like sheets, plates, bars, and tubes through casting, forging, rolling, extrusion, wire drawing, and sintering. These methods transform raw metal ingots into products for secondary manufacturing, typically performed in steel mills and foundries.

Secondary manufacturing, or fabrication, involves converting primary metal products into finished components. Fabricators customize semi-finished products to meet specific requirements, producing items like storage tanks, automotive frames, and metal enclosures. This work occurs in machine shops, fabrication facilities, or on-site.
Chapter 2: Essential Raw Materials for Steel Fabrication
Steel, an iron-carbon alloy, remains the world's most widely used metal due to its affordability, strength, and availability. In modern steel fabrication, raw materials determine product quality and suitability. While aluminum alloys, copper, and nickel alloys are also used, steel dominates construction and industrial applications because of its superior mechanical properties. Although aluminum is more abundant, iron ore smelting requires less energy than aluminum extraction, making steel more cost-effective.
Stainless steel deserves special attention for its corrosion resistance, making it ideal for food processing, medical devices, and architecture. Fabricated similarly to carbon steel through welding, cutting, bending, and machining, stainless steel comes in various grades. The 300 and 400 series are most common, with grade 304 being the industry standard. For high-temperature applications like exhaust systems, grade 321 is preferred for its titanium content and thermal stability.
In structural steel fabrication, material selection depends on strength, ductility, hardness, and impact resistance. Choosing appropriate steel grades—carbon steels, alloy steels, or weathering steels—ensures suitability for construction, automotive, and aerospace applications. While steel dominates heavy industry, aluminum suits lightweight needs, and copper and nickel alloys serve electrical and marine sectors.
The aerospace industry increasingly values stainless steel for its durability and temperature resistance in spacecraft components.
Castings
Castings form through melting and solidifying metal ingots via sand casting or investment casting. While they approximate final shapes, secondary processes like machining, precision finishing, and heat treatment ensure dimensional accuracy and improved properties.
Blooms
Blooms are semi-finished steel products with nearly square cross-sections (minimum 6 x 6 inches), created during primary rolling. They form the basis for structural profiles like beams and rails, crucial for heavy construction and infrastructure.
Slabs
Produced by rolling steel ingots, slabs (typically 8+ inches thick) become plates, sheets, and strips for shipbuilding, automotive panels, and industrial equipment requiring strength and flatness.

Billets
Billets (2 x 2 to 5 x 5 inches square) result from further processing blooms via rolling, forging, or extrusion. They produce long products like bars, rods, and wires for reinforcement and fasteners.
Plates, Sheets, and Strips
Rolling blooms and slabs creates these products. Plates (over 0.25 inches thick) serve construction and machinery, while thinner sheets suit automotive panels and appliances. Strips, narrower than sheets, feed stamped or rolled products. Sheet metal fabrication is fundamental for precision manufacturing.

Bars
Steel bars (0.5-2 inches) with square, round, or rectangular sections serve construction (rebar), machinery, and engineering. Their dimensional accuracy and finish ensure strength and precision.
Rods
Smaller than bars (0.2-0.5 inches), rods offer flexibility for forming and bending. Used in construction, fencing, and wire products, they often come coiled for efficient handling.
Beams, Channels, Angles, and Rails
These irregular-section products, made via hot rolling, provide structural support for buildings, bridges, and railways. Their designs optimize weight distribution and durability.

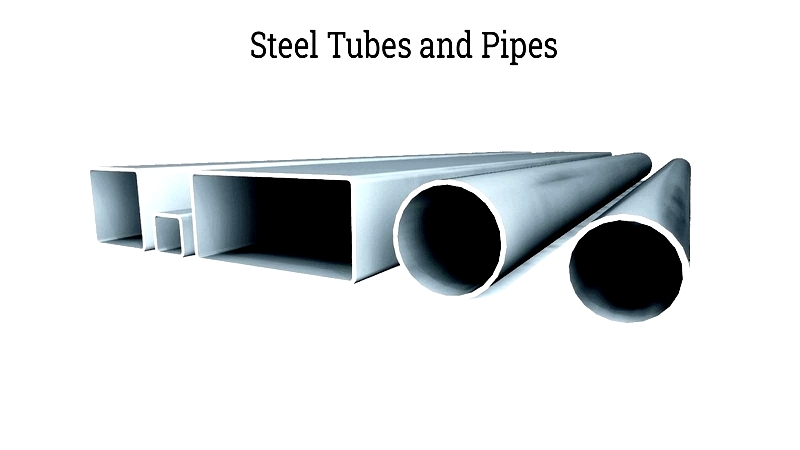
Tubes and Pipes
Hollow sections (round, square, or rectangular) come as welded or seamless. Welded types form by rolling and joining sheets, while seamless types pierce and elongate billets. Essential for pipelines, plumbing, and HVAC systems.

Wires
Produced by wire drawing, these thin, strong products serve electronics, construction reinforcement, and fasteners, benefiting from cold working's strength enhancement.
Selecting Raw Materials
Choosing materials involves evaluating mechanical needs, environmental factors, regulations, and costs. Comparing steel grades and considering options like HSLA steels or sustainable practices ensures optimal performance. Understanding materials helps engineers and buyers make informed decisions for custom fabrication projects.




