Introduction
This article provides an in-depth look at photochemical etching. You will learn about topics such as:
- What is Photochemical Etching?
- The Photochemical Etching Process
- Uses and Benefits of Photochemical Etching
- And Much More...
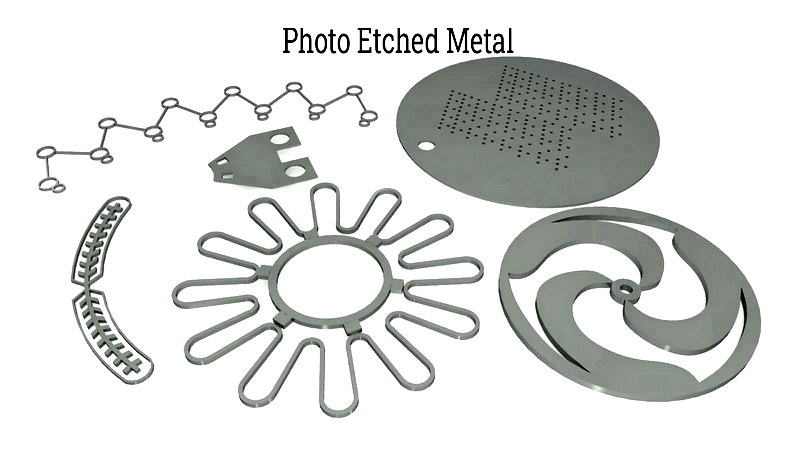
Chapter 1: Understanding Photochemical Etching and Its Process
Photochemical etching, also known as photochemical machining (PCM) or metal etching, is an innovative subtractive manufacturing process that uses photographic and chemical methods to create metal components. The process begins by transferring a design onto a metal workpiece. A chemical solution then selectively removes material from areas not protected by the design, producing an accurate reproduction of the original image or component. Photographic methods, particularly photoresist imaging, define which areas to preserve or remove.
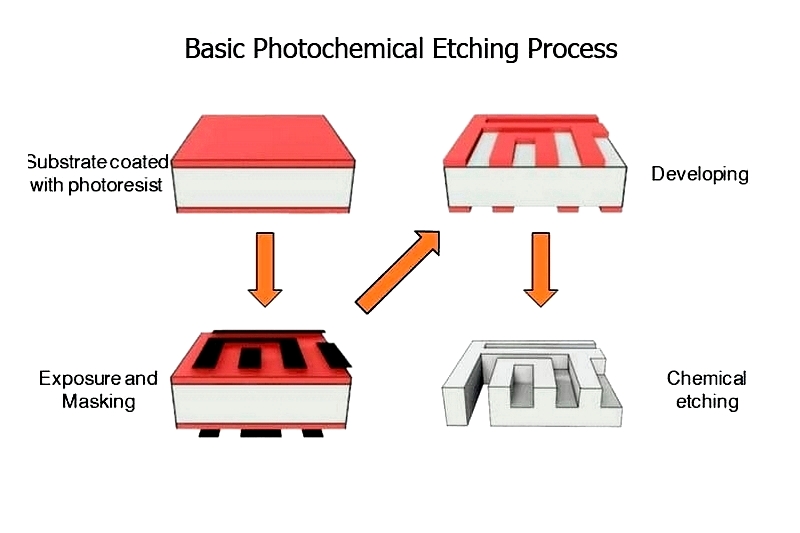
As a cost-effective alternative to laser cutting, water jet cutting, and stamping, photochemical etching allows for easy modifications and refinements, even during large-scale production. It produces parts with excellent dimensional accuracy, free from burrs and sharp edges, and requires no additional finishing. once the design is approved, the entire production process can be completed in under an hour.
The main advantage of photochemical etching is its ability to create highly precise components that are difficult or impossible to make with traditional machining. It is widely used in industries such as aerospace, medical, life sciences, automotive, and electronics. For example, it is essential for manufacturing printed circuit boards, silicon integrated circuits, pressure membranes, and various miniature electronic components.
Typically, parts made through this process are flat and thin, with dimensions as small as ten microns. For advanced applications, production can reach the nanoscale, enabling the creation of items like computer processors. The range of possible shapes is virtually unlimited, and adding intricate designs incurs minimal additional costs.
Chapter 2: The Photochemical Etching Process
Photochemical etching, also called chemical etching, photo etching, or photochemical machining (PCM), is an advanced precision metal fabrication process. By using controlled light exposure and selective chemical reactions, manufacturers can cut and etch metals into intricate patterns that traditional methods cannot easily achieve. This process employs specially formulated photoresists and etchants to create detailed designs on flat metal sheets, resulting in micron-accurate features across metals like stainless steel, copper alloys, brass, nickel, aluminum, and titanium. It is ideal for mass production and rapid prototyping of high-precision components in industries such as electronics, automotive, aerospace, telecommunications, medical devices, and microelectronics.
Compared to laser cutting, stamping, or CNC machining, photochemical etching offers key advantages: burr-free edges, no heat distortion or induced stress, and the ability to produce fine, repeatable features at scale with low tooling costs. It is commonly used in electronics to manufacture high-precision parts like computer processors (CPUs), MEMS components, circuit boards (PCBs), lead frames, EMI/RFI shielding, encoder discs, and meshes. It also supports specialized components for scientific, industrial, medical, and semiconductor applications—including filters, screens, coatings, optics, plasma generators, and vacuum chambers—where tight tolerances and complex geometries are essential.
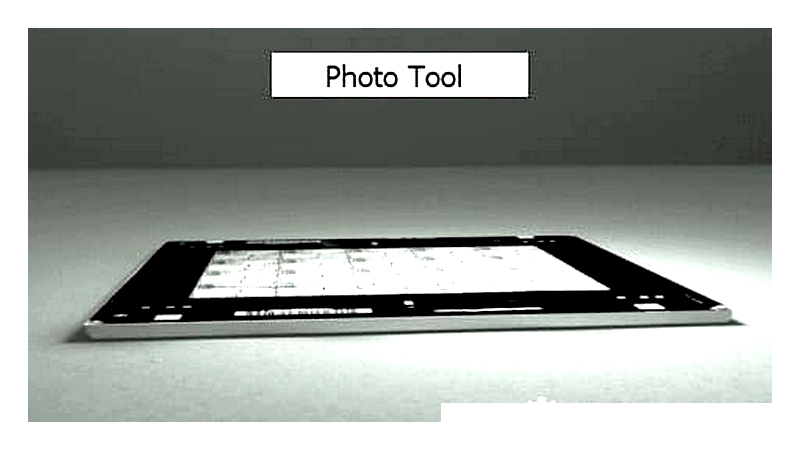
Photo-tool Plotting
The photo-tool, also called a photomask or artwork master, is the photographic negative or positive of the desired design. Accurate photo-tool creation is crucial for transferring CAD designs to metal substrates. Using software like DXF, Adobe Illustrator, Gerber, or CAD programs, engineers create technical drawings that are converted into a photo-tool. The design is then printed onto photographic film (silver halide or diazo) using high-resolution photoplotters or laser-imaging systems. Compensation factors are applied to the artwork to counteract dimensional changes from undercuts during etching. Optimizing the photo-tool ensures repeatable, micron-level accuracy in the final parts.
Temperature and Humidity Variations
Environmental fluctuations in temperature and humidity can cause dimensional variations during artwork plotting, affecting final product accuracy. For tight-tolerance applications, photo-tools may use thicker polyester films or glass plates, and plotting may occur in controlled cleanroom environments. Where environmental control is impractical, maskless direct-write techniques like laser direct imaging (LDI) or digital lithography offer superior precision, minimizing dimensional drift and enabling rapid design iteration—ideal for high-mix, low-volume manufacturing and prototyping.
Etch Factor
Most etchants attack metal substrates isotropically, producing undercuts—sideways etching beneath the photoresist—that increase with etch depth. The etch factor, defined as the ratio of lateral etch to vertical etch depth, must be calculated when preparing the photo-tool. By adjusting the design to compensate for undercuts, manufacturers ensure feature sizes meet specifications. Master images are then step-and-repeated across the photo-tool to maximize throughput and consistency.
After applying these compensation factors, the final master image is repeatedly plotted onto the film to optimize output and ensure consistency.
Material Preparation
Material selection is a critical stage in photochemical machining. Common choices include stainless steel, nickel, copper, titanium, brass, and beryllium copper alloys, selected based on mechanical, electrical, and corrosion-resistance requirements. Before applying photoresist, the metal workpiece is cut to size and thoroughly cleaned to remove contaminants like oil, dirt, rust, or grease. Proper cleaning ensures photoresist adhesion; poor preparation can cause defects, pinholes, or misalignments, reducing yield.
Two primary cleaning methods are used: chemical and mechanical. Chemical cleaning involves degreasing solutions and mild acid pickling to dissolve organic and inorganic contaminants, minimizing surface abrasion and preserving metallurgical integrity. Mechanical cleaning, such as abrasive scrubbing, is avoided when surface finish is critical. Some processes include de-ionized water or ultrasonic rinses for complete particle removal.
To enhance photoresist adhesion, a hexamethyldisilazane (HMDS) coating may be applied. This vapor-phase silanization creates a hydrophobic monolayer, improving bonding between the photoresist and metal substrate and reducing pattern defects.
Photoresist Coating
Photoresists are light-sensitive polymer coatings essential to photolithography. These formulations are designed for durability, high contrast, and etchant resistance. The photoresist is uniformly applied to the workpiece, creating patternable protection. The choice of photoresist (positive or negative, photopolymer or photodecomposing) affects feature definition, resolution, and cost.
After application, the photo-tool determines which areas will be protected or exposed during UV exposure. Exposure type, chemical structure, and process requirements define the following categories:
Positive Photoresists
With positive photoresists, UV-exposed regions become more soluble in the developer, allowing selective removal and exposing the metal for etching. Positive resists offer finer resolution and sharp edge definition, making them ideal for micro-scale manufacturing of ICs and MEMS devices.

Negative Photoresists
Negative photoresists polymerize and harden upon UV exposure. The exposed regions remain insoluble, staying on the substrate during etching. Negative resists offer higher chemical resistance and are useful for rapid etch processes, though their resolution is typically lower than positive resists.





