Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of Stainless Steel Fabrication.
You will learn about:
- The fundamentals of Stainless Steel Fabrication
- Various fabrication methods for stainless steel
- Different types of stainless steel used in fabrication
- Applications of fabricated stainless steel products
- How to select the appropriate stainless steel for fabrication
- And much more...

Chapter 1: Understanding Stainless Steel Fabrication
Stainless steel fabrication encompasses various manufacturing techniques that manipulate, form, and transform metal into durable stainless steel products. These methods aim to utilize stainless steel's beneficial properties, enhancing product durability, aesthetics, resilience, and lifespan.

While steel has been valued for centuries for its strength, stainless steel is a relatively modern alloy developed just over a century ago to address issues like gun barrel wear. Since its invention, the stainless steel industry has rapidly advanced, introducing numerous production techniques.
This evolution has resulted in a wide range of stainless steel alloys, each designed for specific applications. Depending on composition, stainless steel can vary from extremely hard and corrosion-resistant to more malleable forms. This diversity has led to three primary classifications: austenitic, ferritic, and martensitic, along with five main families: austenitic, ferritic, martensitic, duplex, and precipitation hardening.
The extensive variety of stainless steel families and classifications can be complex, potentially confusing newcomers to the material.
Each stainless steel family includes multiple grades, identified by numerical codes indicating their properties and quality. In the U.S., two primary grading systems are used: the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) with three-digit codes, and the American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) with six-digit codes for categorizing over 200 stainless steel alloys.
Beyond U.S. standards, international organizations like ISO and countries including Japan, Germany, the UK, Sweden, and China maintain their own grading systems. This multitude of standards can make finding specific information about stainless steel alloys challenging.
Under the SAE system, Grade 304 stainless steel is classified as follows:
- European Number (EN): 1.4305
- EN name: X8CrNiN18-9
- Unified Numbering System (UNS): S30400
- Deutsches Institut für Normung (DIN): X5CrNi18-9, X5CrNi18-10, X5CrNi19-9
- British Standards (BS): 304S 15, 304S 16, 304S 18, 304S 25, En58E
- Japanese Industrial Standards (JIS): SUS 304, SUS 304-CSP
EN numbers represent a European standard for classifying metal specifications, grades, and chemical compositions, originally developed by the British during World War II to standardize products. The German equivalent is called the Deutsches Institut für Normung.
Chapter 2: Methods for Fabricating Stainless Steel
Stainless steel is widely used in manufacturing diverse products, appearing in both everyday items and industrial applications. Its popularity stems not only from its attractive appearance but also from its durability and corrosion resistance. Consequently, stainless steel fabrication has become essential across industries, from construction to food processing and medical equipment manufacturing. Its non-reactive nature, strength-to-weight ratio, and ability to withstand harsh conditions make it ideal for demanding engineering projects.
Various stainless steel grades can be shaped and processed, with austenitic grades being the most commonly used. Fabrication involves traditional techniques to form metals into components, tools, and products. The chosen method depends on the steel grade, alloy composition, and end-use requirements. Factors like machinability, weldability, formability, and heat resistance influence method selection to ensure products meet desired specifications.
Each stainless steel grade offers unique properties tailored to specific applications. While selecting the right grade may seem complex, grading systems like AISI and ASTM provide detailed descriptions to simplify the process for engineers and fabricators.
Stainless steel adapts well to traditional forming techniques including machining, punching, cutting, bending, and welding. Despite its strength and hardening ability, it remains ductile, allowing for cold forming in both custom and high-volume manufacturing. Fabricators adjust methods based on the grade being processed, as varying element combinations affect properties and require different approaches.
Work Hardening
Work hardening rates vary by stainless steel grade. Austenitic grades (like 304 and 316) harden quickly during processes like cold rolling, while 400 series grades harden slightly faster than carbon steel. This characteristic benefits applications requiring increased strength, wear resistance, and improved fatigue life.
Grades with the highest work hardening rates typically have elevated magnetic permeability. Cold working can enhance tensile strength up to 2000 MPa, though its efficiency decreases with larger components. Proper annealing between forming steps helps manage excessive hardening, maintaining ductility and performance.
Welding
Welding properties vary significantly among stainless steel grades, with austenitic types offering superior weldability for pressure vessels and piping. Martensitic grades require careful handling to prevent cracking, while ferritic grades offer good weldability when properly managed.
- Welding Austenitic Stainless Steel – Most austenitic grades weld well, except grade 303. Grades like 304 and 316L exhibit excellent weldability, especially with low-carbon fillers. TIG and MIG welding provide precise, high-quality welds for architectural applications.
- Welding Martensitic Stainless Steel – Austenitic filler rods improve ductility, though grade 416 is prone to cracking. Post-weld heat treatment may be necessary to restore toughness.
- Welding Ferritic Stainless Steel – Controlled heat input and proper fillers help maintain weld strength and prevent embrittlement.

Weld quality depends on proper shielding gases and filler metals. Experienced fabricators ensure optimal results for standard and custom projects.
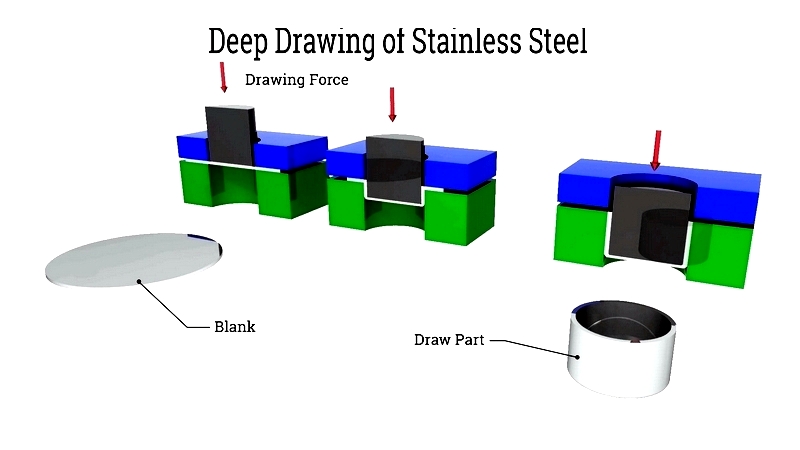
Deep Drawing
Deep drawing is a cold working method, often followed by heat treatment. It's primarily used with 400 series ferritic and 300 series austenitic stainless steels. Grade 304 is preferred for its ductility and corrosion resistance, making it ideal for kitchen sinks and automotive components.
Stainless steel requires about double the pressure of carbon steel for effective forming. Specialized lubricated tools help reduce friction and achieve quality finishes.
Process efficiency depends on lubrication, tool geometry, and draw depth. Slow speeds prevent defects, and selecting formable grades improves productivity.
Punching
Punching positions stainless steel between hardened tool steel or tungsten carbide punch and die. The press cuts precise holes and can create decorative patterns. CNC machining enables complex, multi-stage operations in a single setup, reducing production time.

Cutting
Cutting methods include shearing, sawing, waterjet, plasma, and laser cutting. Austenitic grades require different approaches than ferritic grades due to work hardening. High-speed steel or carbide-tipped blades with proper lubrication extend tool life and improve finishes.





