Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of cord reels and their various configurations.
Continue reading to learn about key topics including:
- What Cord Reels Are
- Different Types of Cord Reels
- Configuration Options for Cord Reels
- How to Select the Right Cord Reel
- And More...

Chapter 1: What are Cord Reels?
Cord reels are indispensable tools for organizing and managing extension cords that supply power to devices located away from electrical outlets. These devices not only keep long cords neatly stored but also prevent tangling and damage when not in use.

How Cord Reels Work
Cord reels feature a cylindrical drum designed to hold extension cords efficiently. The drum has large discs or flanges at each end to secure the cord and is mounted on a sturdy frame with various attachment components. These components allow the reel to be installed on ceilings, floors, walls, posts, carts, or machinery.
To use a cord reel, simply pull out the required length of cord to reach your equipment (known as the payout position), then connect your device to the reel's receptacles or the cord end. The remaining cord stays wound on the drum. When finished, releasing the cord activates the winding mechanism to automatically retract it back onto the drum for storage.
Benefits of Using Cord Reels
Widely used across industries, cord reels significantly extend cord lifespan by preventing tangles and nesting. They protect cords from wear and damage by only exposing the necessary length during use. Beyond enhancing safety by reducing tripping hazards, cord reels offer practical convenience. Choosing the right specifications and proper installation makes them a valuable investment for organized and safe cord management.

Cord Reel Construction
Cord reels are typically constructed from durable materials like plastic (PVC/ABS), fiberglass, aluminum, or stainless steel. metal reels handle heavier cords and often feature corrosion-resistant coatings for outdoor use, while plastic reels suit lighter indoor applications. Premium models may offer water resistance, non-sparking designs, dust-proofing, and shock/vibration resistance for demanding environments.
Chapter 2: Types of Cord Reels
Available for residential, commercial, and industrial applications, cord reels can be categorized by design, features, capacity, and intended use. Selecting the appropriate type—whether for power cords, extension cords, or specialty cables—ensures safe management, operational efficiency, and reduced workplace hazards.
Commercial Cord Reels
Designed for light-duty power distribution in temporary setups, commercial cord reels are ideal for indoor use in non-corrosive environments. Typically made of non-metallic materials or stainless steel, these portable reels are common in offices, retail spaces, schools, and hospitality venues for easy cord storage and access.

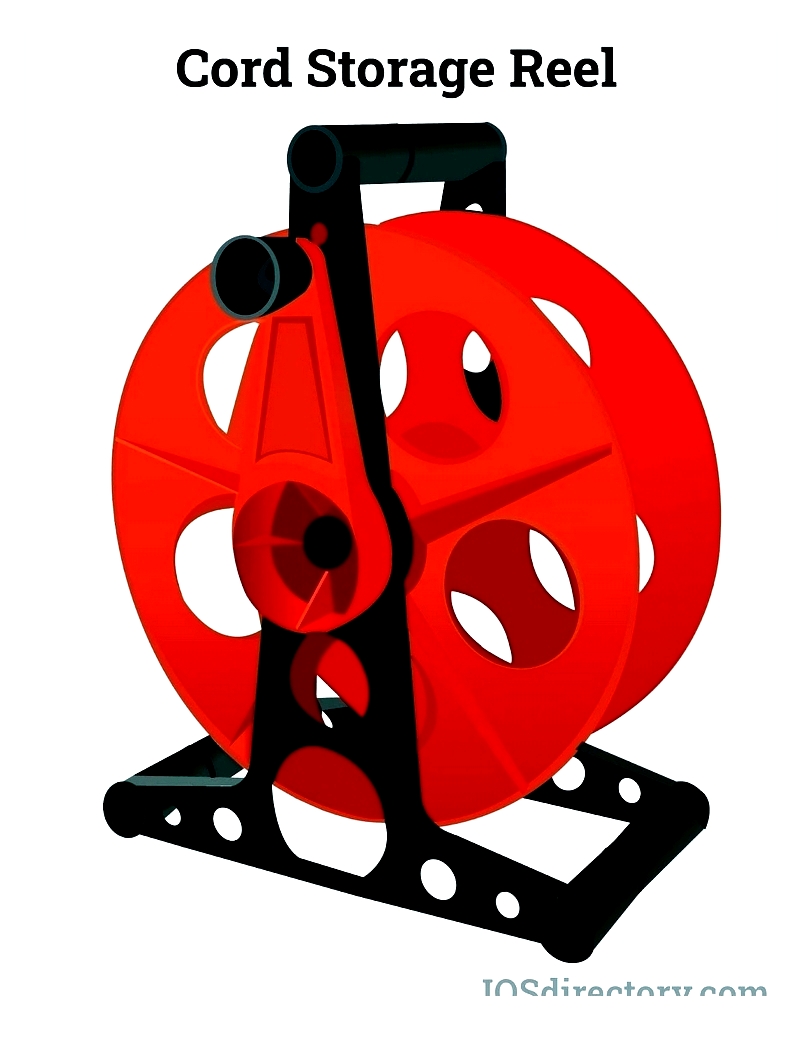
Cord Storage Reels
Specifically designed for cord storage, these reels feature a durable drum and mounting frame. Operated manually with a hand crank, they keep cords organized and tangle-free when not in use. important: These reels are for storage only—never use them with energized cords to avoid overheating risks.

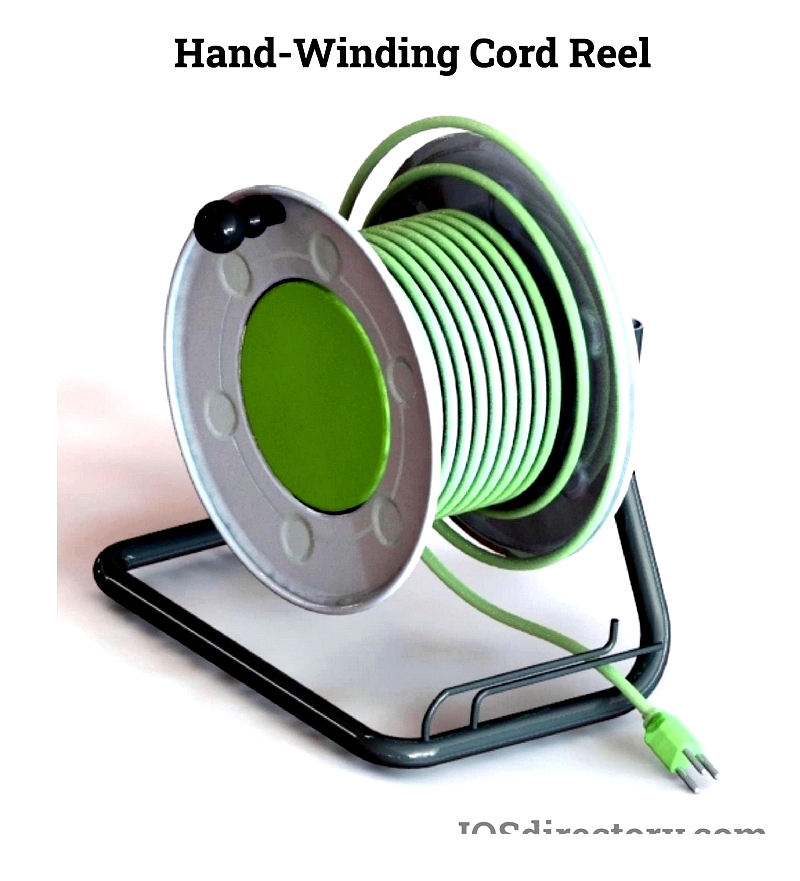
Hand-Winding Cord Reels
Manual operation via hand crank makes these lightweight reels ideal for shorter cables in portable applications. Cost-effective and easy to use, they're perfect for homes, offices, workshops, and retail spaces requiring simple cord deployment and storage.

Hazardous Location Cord Reels
Engineered for explosive environments, these reels feature spark-resistant mechanisms and explosion-proof enclosures. UL/ATEX certified, they're essential for mining, oil refineries, chemical plants, and other hazardous locations where safety is paramount.

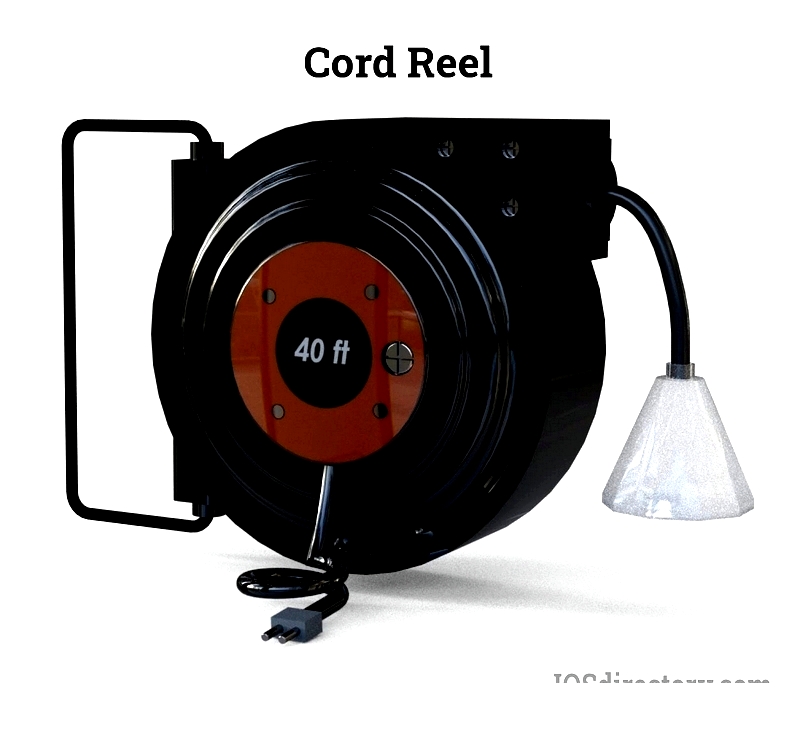
Lighted Cord Reels
Featuring integrated lamps, these reels provide both power and illumination for dark workspaces. The adjustable lighting is ideal for construction sites, garages, and maintenance areas where portable lighting is needed.
They're equally useful outdoors where power sources are limited, offering extended illumination capabilities for various applications.
Live Connection Cord Reels
These reels maintain continuous power flow through collector ring assemblies, making them ideal for industrial applications requiring uninterrupted operation. Heavy-duty contacts ensure reliable performance in continuous-duty environments.

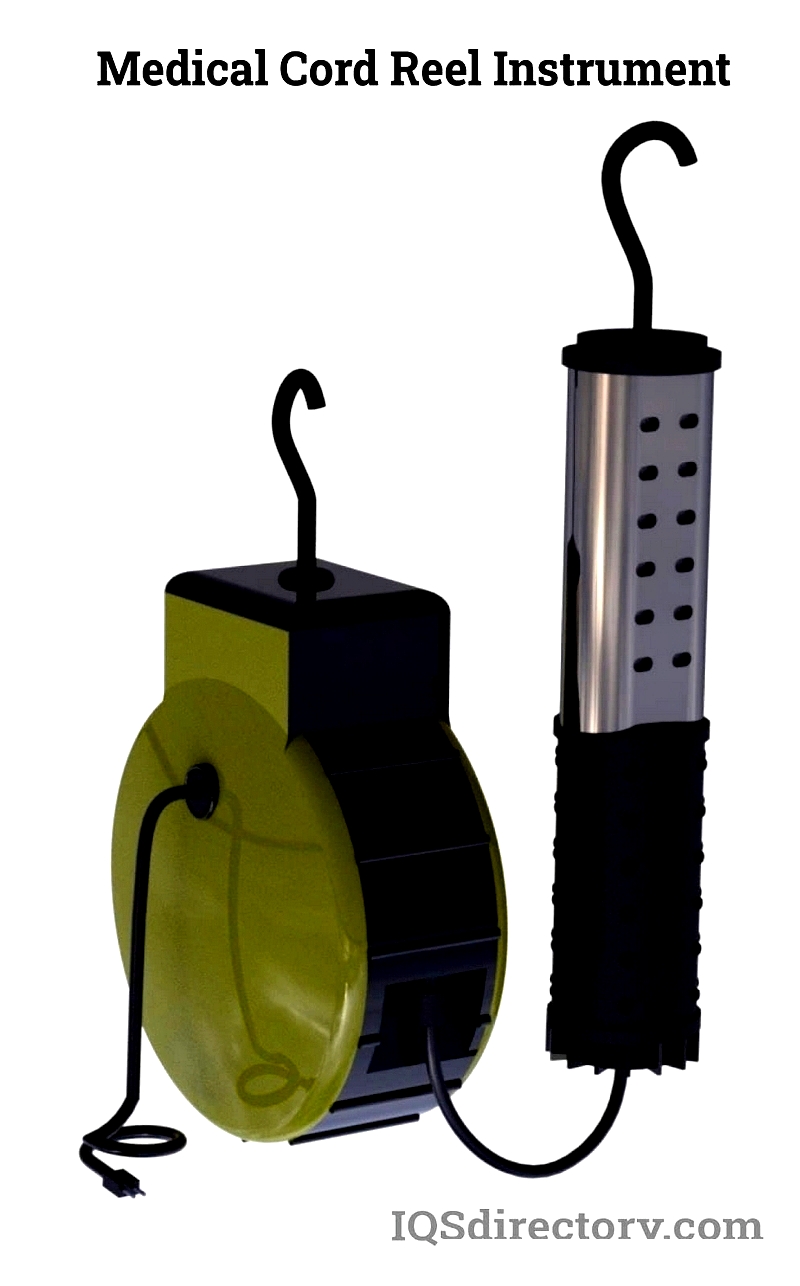
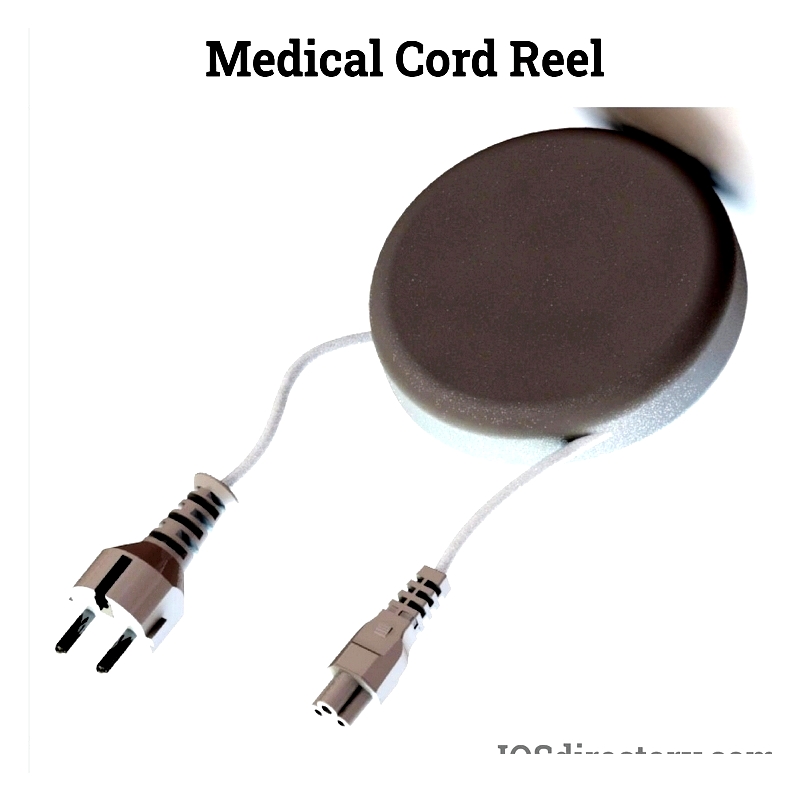
Medical Cord Reels
Specially designed for healthcare facilities, these reels ensure safe power delivery to medical equipment. They feature hygienic, durable construction with antimicrobial properties to meet strict infection control standards.
Compliant with healthcare regulations, these reels reduce tripping hazards and maintain critical equipment performance in hospitals, labs, and emergency medical settings.
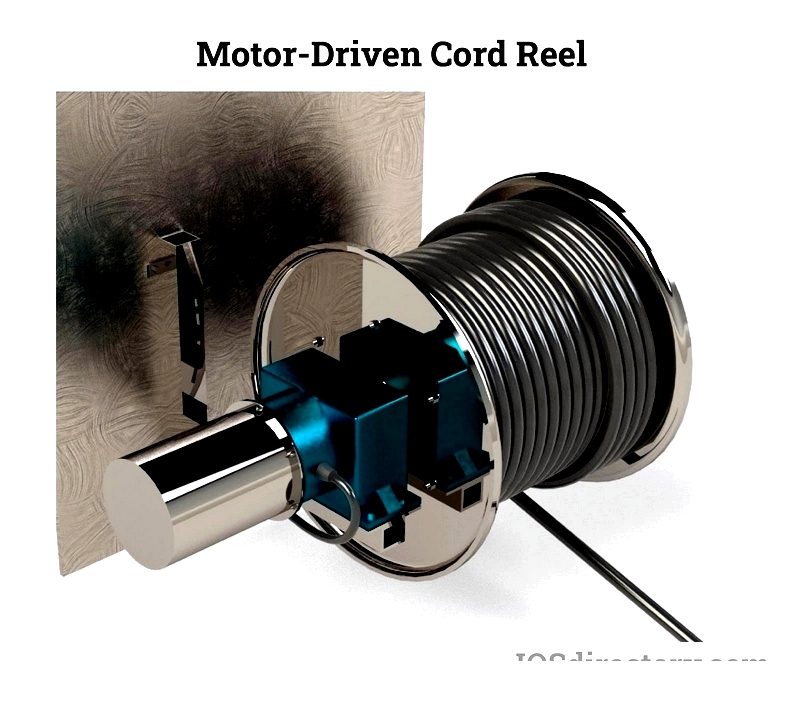
Motor-Driven Cord Reels
Automated winding/rewinding makes these reels perfect for heavy-duty applications. Available in electric, hydraulic, or pneumatic models, they're ideal for industrial settings where manual operation would be impractical.
Their consistent tension control prevents cord damage during frequent use, making them suitable for demanding environments like mining, construction, and shipyards.
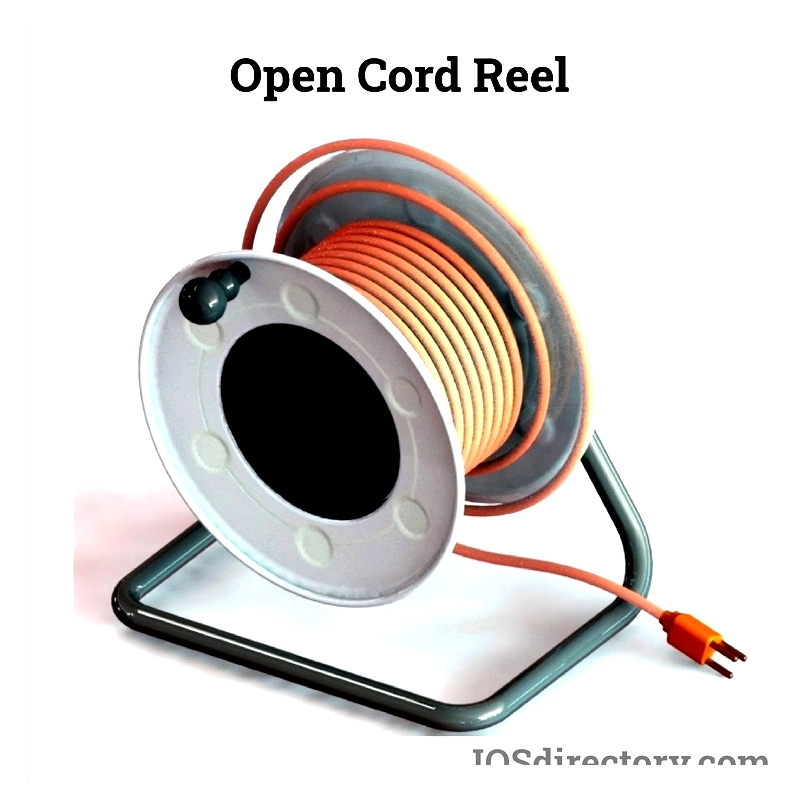
Open Cord Reels
With exposed mechanisms, these reels allow easy inspection and maintenance. Best suited for clean, dry indoor environments where full enclosure isn't necessary.

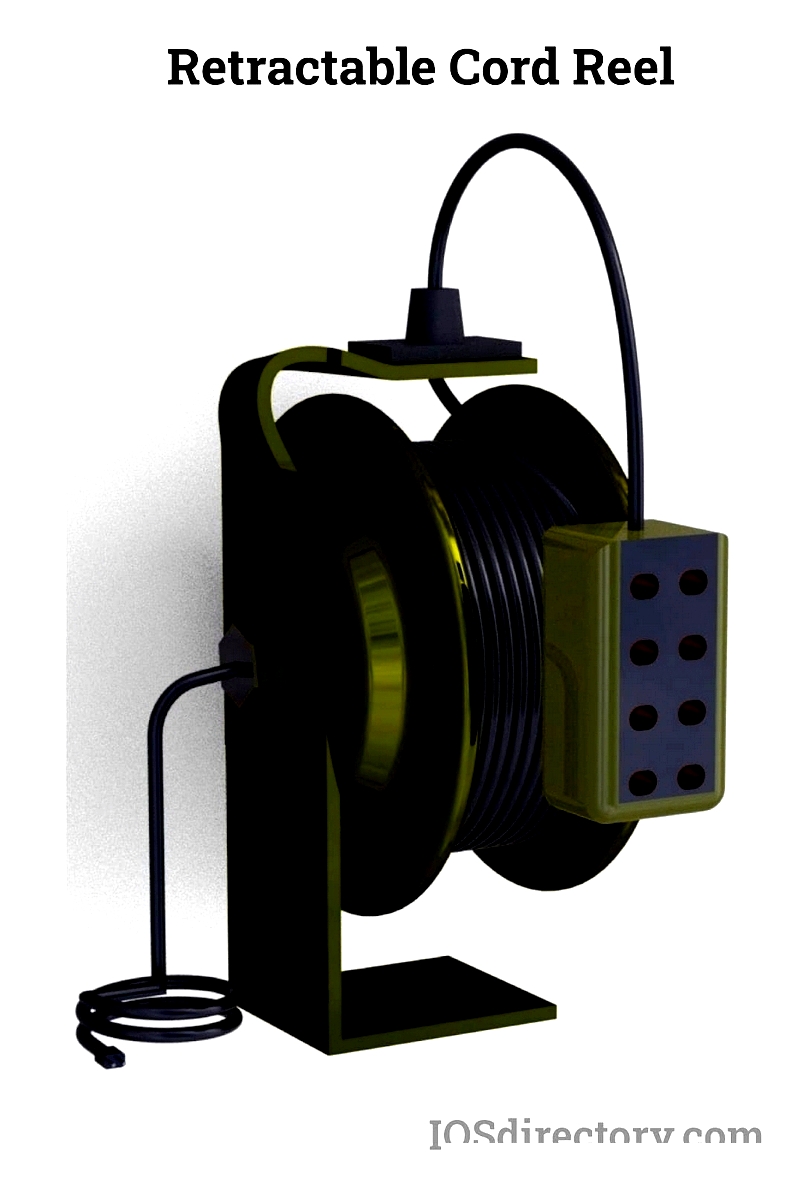
Retractable Cord Reels
Spring-loaded automatic retraction keeps cords neatly stored and prevents workplace hazards. The ratcheting system allows customizable cord lengths while ensuring secure retraction.
Widely used in automotive and industrial settings, these reels improve efficiency by reducing setup time and maintaining organized workspaces.
Stainless Steel Cord Reels
Constructed from corrosion-resistant 304/316 stainless steel, these reels excel in hygienic environments like food processing and healthcare. Their durable, non-porous surfaces simplify cleaning and resist bacterial growth.
Available in various sizes, they support heavy




