Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of DC motors.
You'll discover key topics including:
- What is a DC motor?
- Different types of DC motors
- How DC motors operate
- Applications of DC motors
- And much more…
Chapter One – What is a DC Motor?
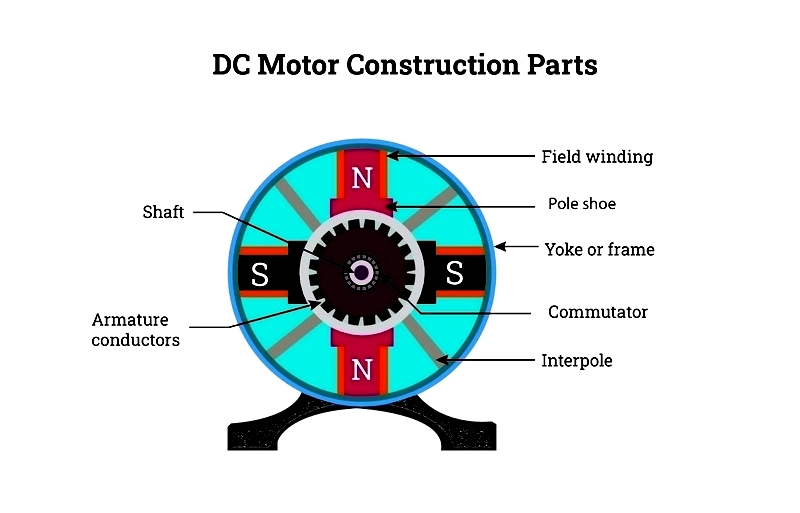
A Direct Current (DC) motor converts electrical energy into mechanical energy by generating a magnetic field when powered by direct current. When energized, the motor creates a magnetic field in its stator that interacts with rotor magnets, causing rotation. The commutator maintains continuous rotation by delivering current to the windings through power-connected brushes.
DC motors are preferred for their superior speed control, making them ideal for industrial use. They can start, stop, and reverse instantly, which is crucial for precise control of production equipment.
Chapter Two – Types of DC Motors
Understanding different DC motor types helps maximize their benefits in various applications. These motors are fundamental in industrial automation, robotics, appliances, and electric vehicles due to their controllability and versatility. Compared to AC motors, DC motors offer easier installation, precise speed control, and low maintenance requirements.
DC motors are classified by field winding connections: parallel (shunt), series, or compound. They also differ by rotor power method: brushed or brushless. Modern DC motors often incorporate permanent magnets for greater efficiency and compact size.
Used in countless products and industrial systems, selecting the right DC motor type enhances performance, lifespan, and efficiency. This chapter examines major DC motor types, their characteristics, and their suitability for different applications.
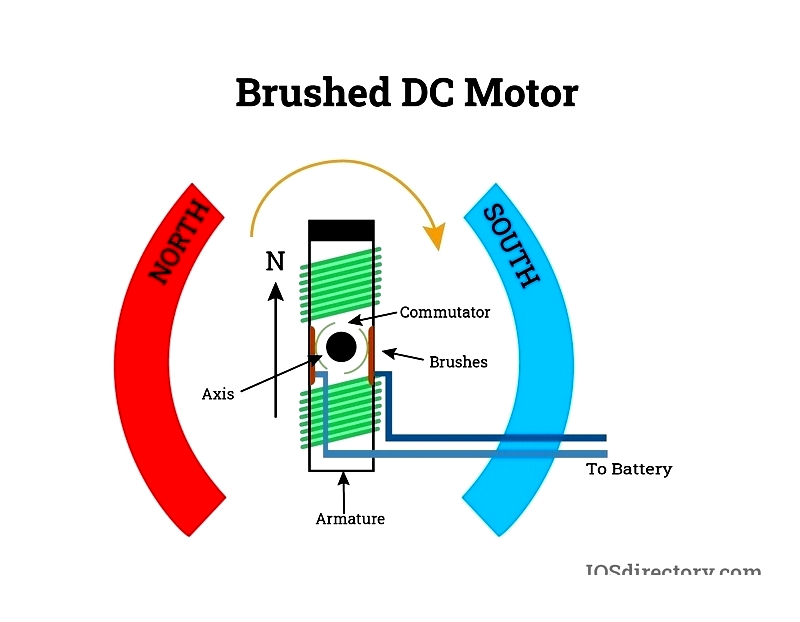
Brushed DC Motor
Brushed DC motors are widely used for their simplicity and affordability. They generate magnetic fields through current passing via commutator and carbon brushes to the rotor. Designs include separately excited and self-excited versions, with laminated steel stators reducing eddy currents.
The commutator acts as a rotary switch, reversing current flow to create continuous torque. This enables smooth speed control, essential for industrial machinery, electric traction, and battery devices.
Brushed DC motors are classified as separately excited, self-excited, or permanent magnet types. Self-excited versions include shunt-wound, series-wound, and compound-wound configurations, each suited for specific torque and speed requirements.
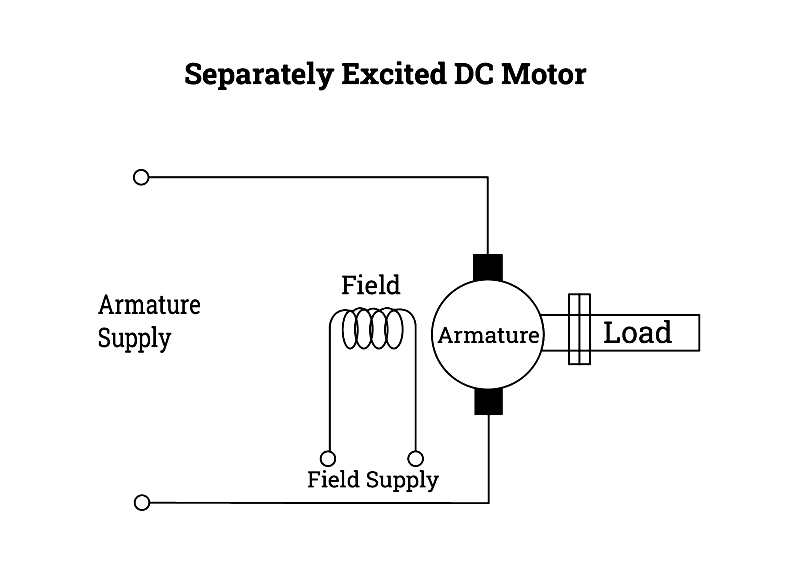
Separately Excited DC Motor
These motors use independent power sources for armature and field windings, enabling precise control. Ideal for automation systems requiring variable speed, they maintain consistent torque under load variations, making them suitable for precision machinery and laboratory equipment.
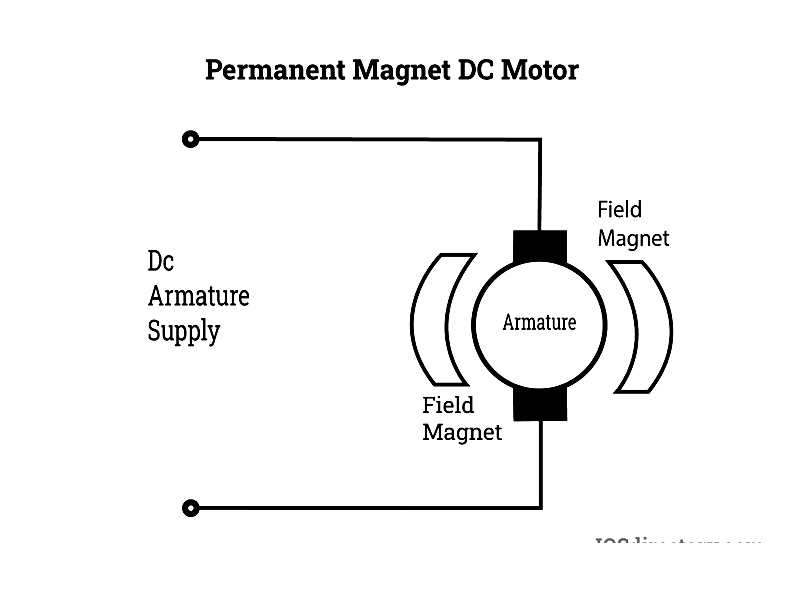
Permanent Magnet DC Motor
PMDC motors use powerful magnets (neodymium, ferrite, or samarium cobalt) in the stator, eliminating field windings. This design offers compact size, light weight, and high efficiency, making them ideal for small appliances, automotive starters, and actuators.
Modern PMDC motors with rare earth magnets deliver strong fields and high torque density, improving energy efficiency for continuous operation in robotics and electric vehicles.
Self Excited DC Motor
Powered by a single source, these motors include shunt-wound, series-wound, and compound-wound types. They're widely used in electric propulsion, lifting equipment, and braking systems where torque and speed regulation matter.
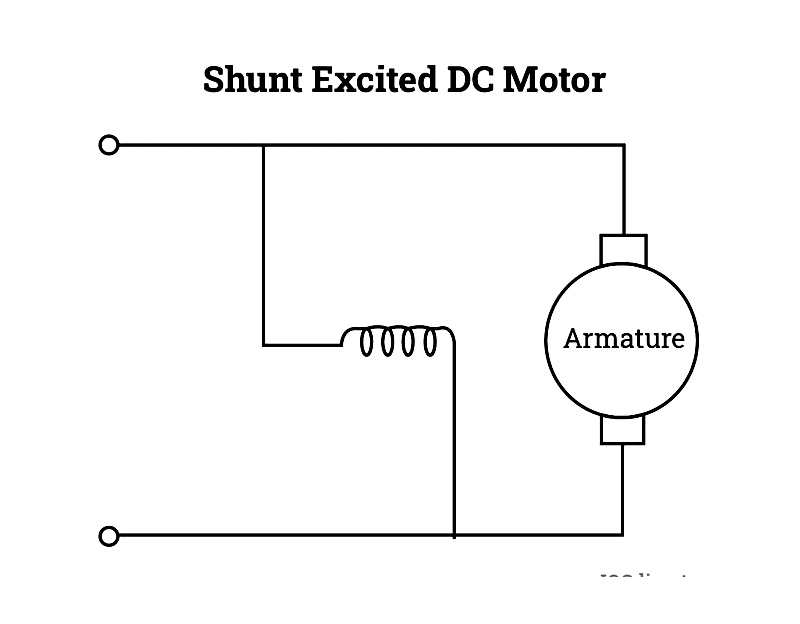
Shunt
Shunt-wound motors connect field and armature windings in parallel, maintaining stable speed under varying loads. Ideal for machine tools and conveyors requiring constant speed.
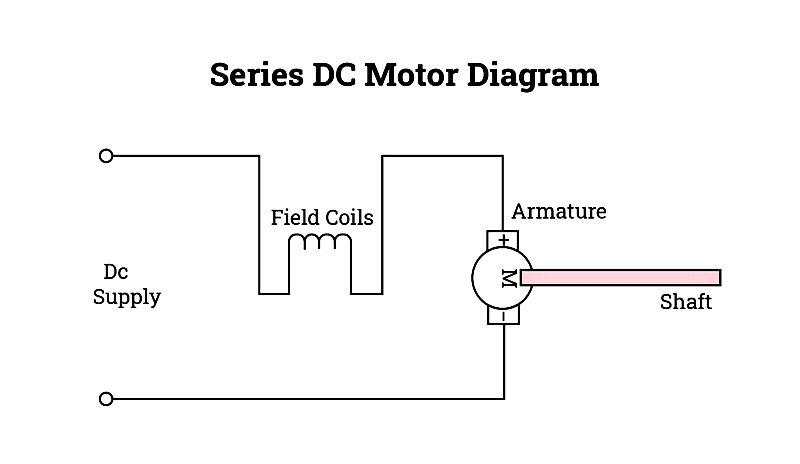
Series
Series-wound motors connect windings in series, delivering high starting torque for cranes and locomotives. Their speed varies significantly with load changes.
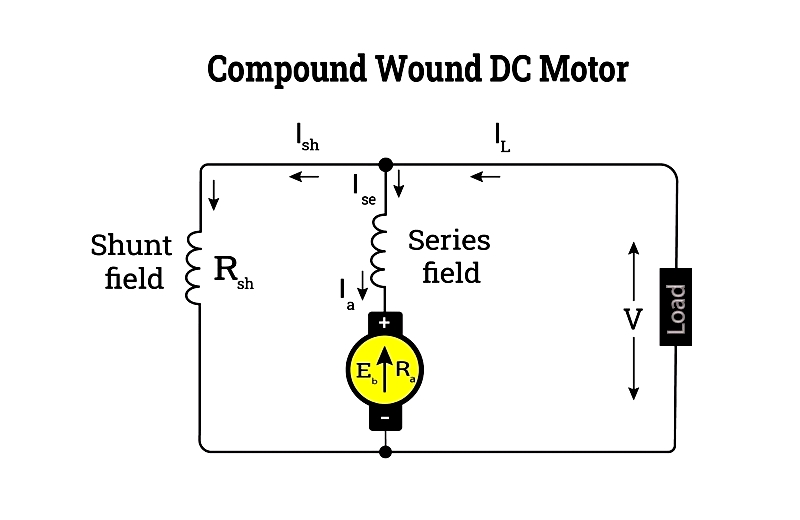
Compound
Combining series and shunt windings, compound motors offer both strong starting torque and stable speed. Used in elevators and heavy-duty conveyors, they come in cumulative and differential types with various shunt configurations.
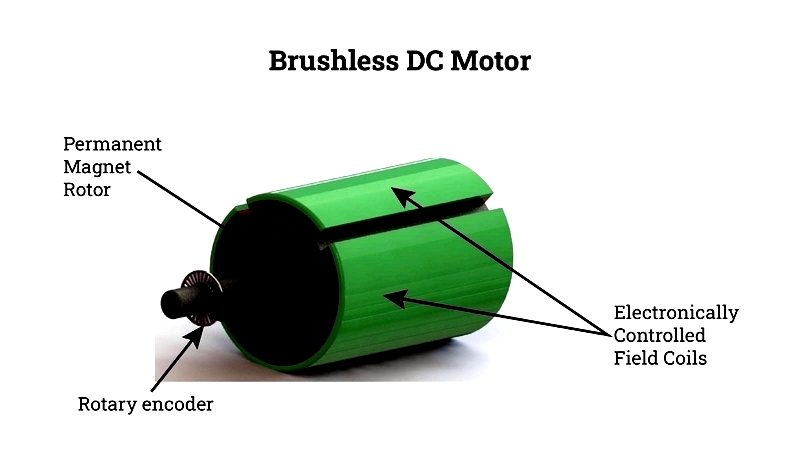
Brushless DC Motor (BLDC)
BLDC motors combine permanent magnet efficiency with electronic commutation, eliminating brushes for longer life and lower maintenance. Used in drones, medical devices, and electric vehicles, they feature three-phase stators and permanent magnet rotors with precise electronic control.
Offering 85-90% efficiency, BLDC motors provide high power density and reliability for demanding applications.
Brushless DC Motor Construction
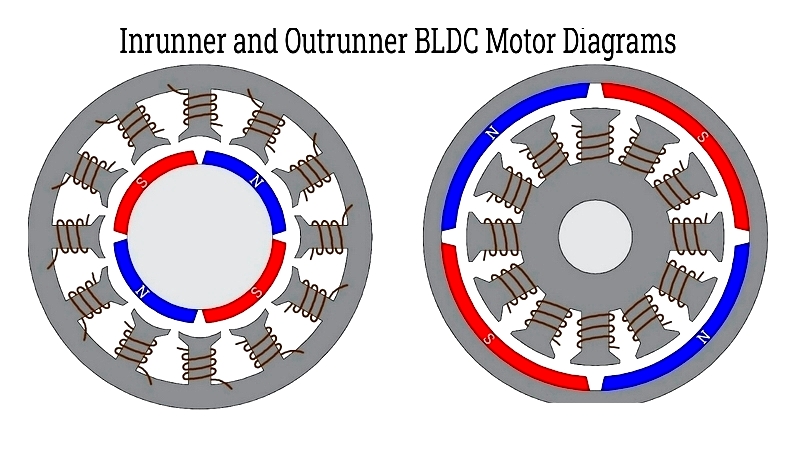
BLDC motors feature three-phase stators and permanent magnet rotors in inrunner or outrunner configurations, optimized for power density and cooling.
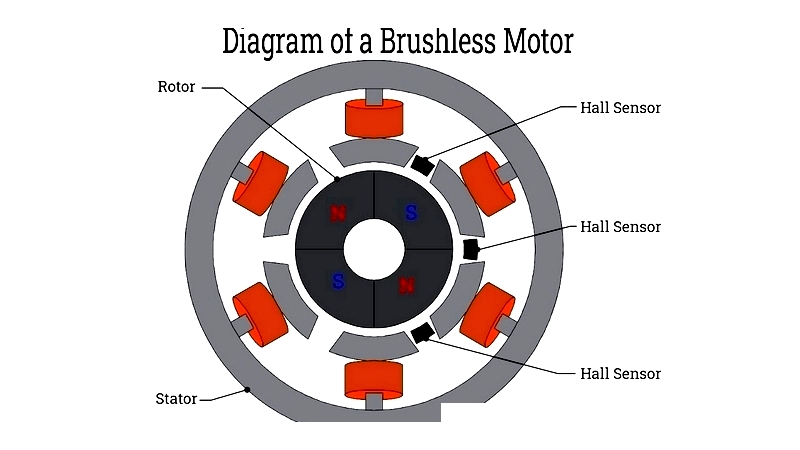
Stator
BLDC stators use laminated steel with slot or slotless windings, determining electrical characteristics for high-speed applications.
Rotor
BLDC rotors incorporate high-strength magnets in various geometries to maximize torque and minimize cogging.
Hall Sensor
Hall sensors provide rotor position feedback for precise commutation, enhancing performance in variable-speed drives.
Benefits of BLDC Motor
- No brushes reduce maintenance
- High efficiency operation
- Compact, lightweight design
- Long service life
- Fast response
- Low electromagnetic interference
- Quiet operation
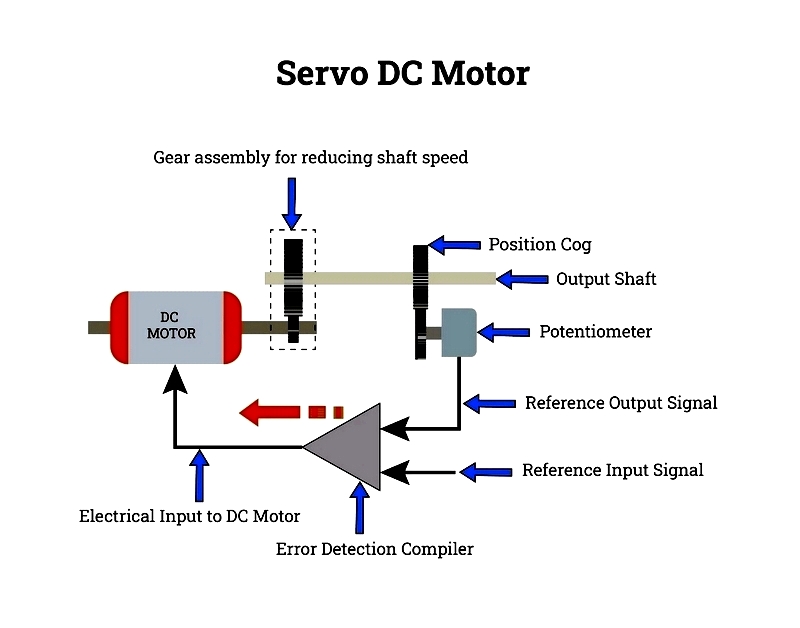
Servo DC Motor
Servo DC motors integrate a DC motor, gearbox, control circuit, and position sensor for precise motion control. Used in robotics and CNC machinery, they offer accurate positioning, variable speed, and responsive feedback.
Featuring rapid acceleration and high torque-to-inertia ratios, servo motors suit both consumer electronics and industrial automation.