Introduction
This article provides comprehensive information about overhead conveyors and their applications.
You will learn about:
- Overhead Conveyor Basics
- Different Types of Overhead Conveyors
- Applications of Overhead Conveyors
- How Overhead Conveyors Operate
- And more...
Chapter 1: What is an Overhead Conveyor?
An overhead conveyor is an advanced material handling system designed to transport parts, products, and supplies through a motor-driven chain suspended in the air. By utilizing vertical space, this system efficiently moves loads of various shapes and sizes for processing, production, storage, or placement. Overhead conveyors are less intrusive than other transport methods and ideal for moving items in hazardous or inaccessible areas like ovens, paint booths, and chemical handling zones.

Overhead conveyors can be categorized by their movement systems, track configurations, and installation methods. They may operate manually or through motorized mechanisms. Track designs vary from simple I-beams to sophisticated enclosed formations.
Installing overhead conveyor systems requires careful planning and specialized skills. While adaptable to most settings, each location's unique features demand a tailored approach. Factors like building structures, work zones, and facility specifications must be considered before installation begins.
Chapter 2: Types of Overhead Conveyors
Overhead conveyors come in various shapes, sizes, and configurations to meet diverse manufacturing and distribution needs. These systems are widely used in automotive, food processing, warehousing, and aerospace industries for moving heavy or delicate items efficiently. They maximize throughput and optimize floor space while supporting transport of items undergoing various processes.
Manual Overhead Conveyors
Despite automation advances, manual overhead conveyors remain valuable for low-to-medium volume applications where cost-effectiveness and flexibility are priorities. These systems are commonly used in fabrication shops and light manufacturing for transferring workpieces between processing stages.
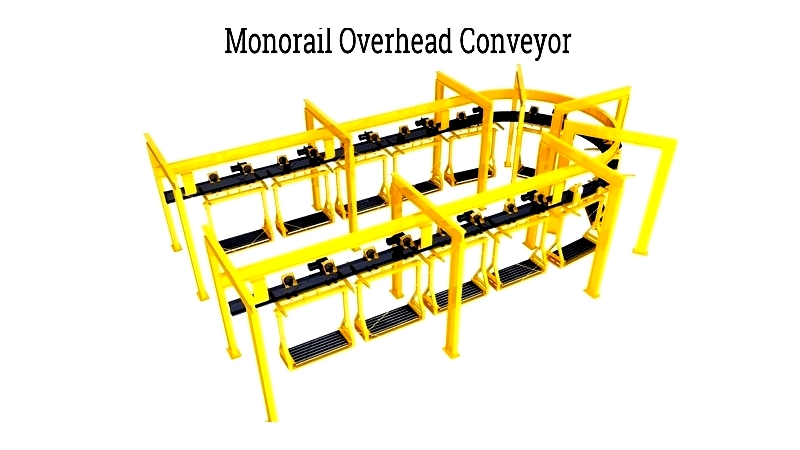
Monorail Overhead Conveyor
Monorail systems are designed for continuous material transport over extended distances. They use ceiling-mounted tracks with powered or manual carriages, making them ideal for automotive assembly and finishing applications.
Power and Free Overhead Conveyor
These advanced systems offer flexibility for complex manufacturing operations, featuring separate power and free-moving tracks with pusher mechanisms for controlled movement and accumulation.
Enclosed Track Overhead Conveyor
Engineered for reliability and cleanliness, enclosed track systems protect components from contaminants, making them ideal for paint shops and cleanroom environments.
I-Beam Overhead Conveyors
Known for durability and high load capacity, I-beam systems are workhorses in heavy industrial environments like foundries and metal fabrication.
Accumulating Electric Monorail Conveyor System (EMS)
These advanced systems feature independently controlled carriers for flexible, programmable material flow in smart factory environments.
Chapter 3: Trolley Overhead Conveyors
Overhead trolley conveyors efficiently transport materials while maximizing floor space. These versatile systems adapt to complex facility layouts with straight runs, curves, and inclines.
Friction Drive Trolley Conveyors
These chainless systems use motor-powered rotating tubes for quiet, energy-efficient operation with reduced maintenance needs.
Chapter 4: Overhead Conveyor Components
Overhead conveyors consist of carefully designed components including chains, drives, tracks, trolleys, and take-up units.
Overhead Conveyor Chains
Available in various designs, these chains are selected based on application requirements and durability.
Overhead Conveyor Drives
Drive systems include caterpillar, sprocket, and friction tube types, each offering different movement characteristics.
Overhead Conveyor Tracks
Tracks come in I-beam and enclosed designs, chosen based on application needs.
Overhead Conveyor Trolleys
Trolleys move along tracks to transport loads, with designs matching specific track types.
Overhead Conveyor Take-Ups
These units maintain proper chain tension for smooth operation.
Pendants for Overhead Conveyors
Pendants connect to chains and support transported loads in various configurations.
Chapter 5: Overhead Conveyor Applications
Overhead conveyors optimize material movement by utilizing vertical space in industrial facilities.
Finishing
Commonly used for painting and coating processes, preventing overspray and drips.
Automotive Industry
Essential for assembly lines, particularly for painting and transporting vehicle frames.




