Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of agitators.
Continue reading to learn about:
- What Agitators Are
- Agitators vs. Mixers
- Agitator Components
- Flow Patterns of Agitator Impellers
- Agitator Types
- Agitator Configurations
- And More...
Chapter 1: Understanding Agitators
Agitators are devices that uniformly blend media within tanks. They operate by rotating submerged impellers at specific RPMs (revolutions per minute). The impeller movement generates flow and turbulence, ensuring consistent mixing of single or multiple components throughout the tank.
In industrial applications, agitators serve several key functions:
- Creating uniform textures in solutions and suspensions
- Maintaining mixture homogeneity to prevent concentration variations
- Dispersing gases into liquid solvents
- Accelerating chemical reactions in reactors
- Regulating solution temperatures within vessels
- Enhancing heat transfer to external jackets
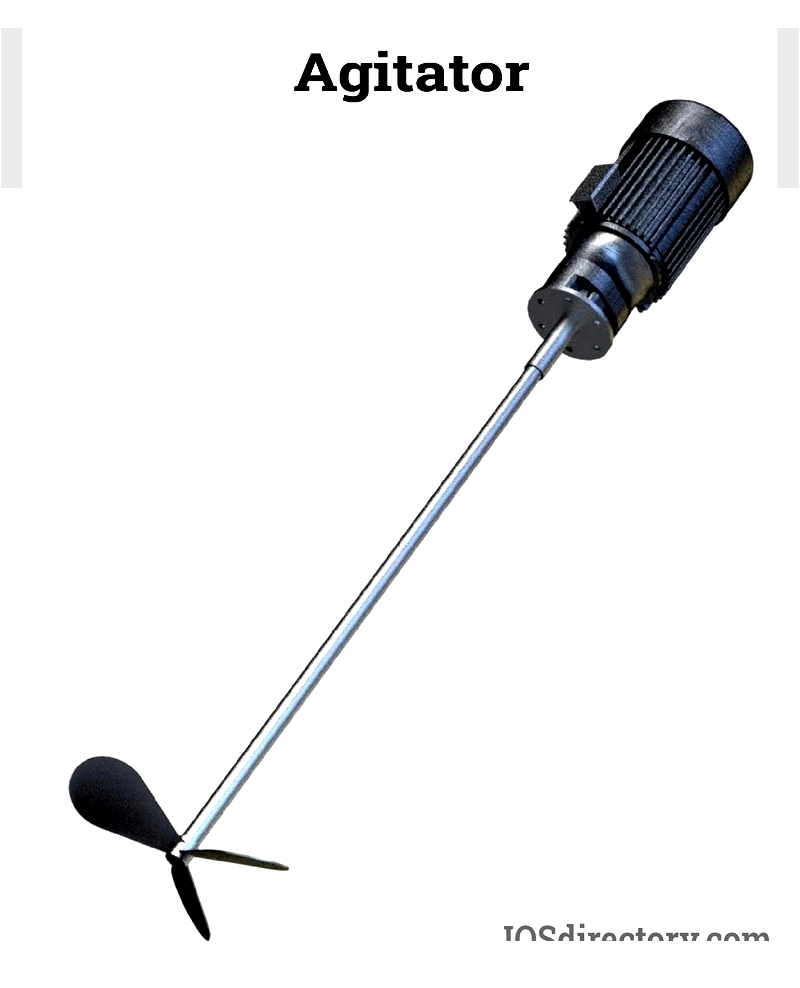

Agitators handle diverse media types, including liquids, gases, solids (granules and powders), slurries, suspensions, and viscous liquids. Proper selection of agitator type, size, and design is crucial and depends on media characteristics like viscosity and shear sensitivity. These devices find applications across industries such as food and beverage, pharmaceuticals, agriculture, biotechnology, paint production, and water treatment.
Agitators vs. Mixers: Key Differences
Though often used interchangeably, agitators and mixers serve different purposes. Mixers rapidly combine multiple components, regardless of phase (solid-liquid, liquid-liquid, gas-liquid), typically processing pure inputs into mixed outputs. Agitators, conversely, maintain uniformity in existing mixtures, preventing concentration and temperature variations to ensure consistency.
Chapter 2: Agitator Components
Industrial agitators are vital mechanical devices used in chemical processing, pharmaceuticals, wastewater treatment, food and beverage, and paints and coatings. Understanding their main components—motor, shaft, and impeller—helps optimize mixing performance, maintenance, and efficiency.
Motor Component
The motor powers the agitator by converting electrical energy into mechanical rotation. It provides the torque needed to turn the shaft and impeller, creating the mixing action. Motor power requirements depend on:
- Media viscosity, specific gravity, and solid content
- Impeller speed (RPM)
- Impeller diameter and blade design
- Impeller power number (energy transfer efficiency)
- Number of impellers per shaft
Proper motor selection ensures blend uniformity, reduces power consumption, and enhances reliability. Common options include electric motors, pneumatic motors, and variable speed drives, chosen based on process needs and environmental conditions.
Shaft Component
The shaft transmits rotational torque from the motor to the impeller. Industrial mixer shafts often incorporate couplings, end caps, and bushings for stability and alignment. Proper shaft design prevents vibration, deflection, and failure, especially in high-viscosity or large-volume applications. Mechanical seals and gland packing systems prevent leaks and contamination at vessel entry points.
Impeller Component
The impeller is the agitator's most critical part, as its design determines flow patterns, mixing efficiency, shear rates, and dispersion. It directly affects blend time, particle suspension, gas dispersion, and overall uniformity.
Impellers consist of a hub (attached to the shaft via a key and screw) and blades (welded or screwed to the hub). Welded connections are preferred in sanitary applications like food and pharmaceuticals for easier cleaning. Multiple impellers on a single shaft can enhance mixing in tall tanks, with optimal spacing depending on vessel dimensions, liquid height, media properties, and desired results.
Two primary impeller types exist:
- Open-blade impellers: Blades connect directly to the shaft, promoting turbulence and easy cleaning.
- Disc-type impellers: Feature a central disc with attached blades, ideal for uniform radial flow in gas-liquid dispersions (e.g., aeration tanks).
Correct impeller selection ensures performance in homogenization, emulsification, heat transfer, and solid suspension. Advanced designs include hydrofoil, anchor, turbine, and propeller types, each suited to specific needs.
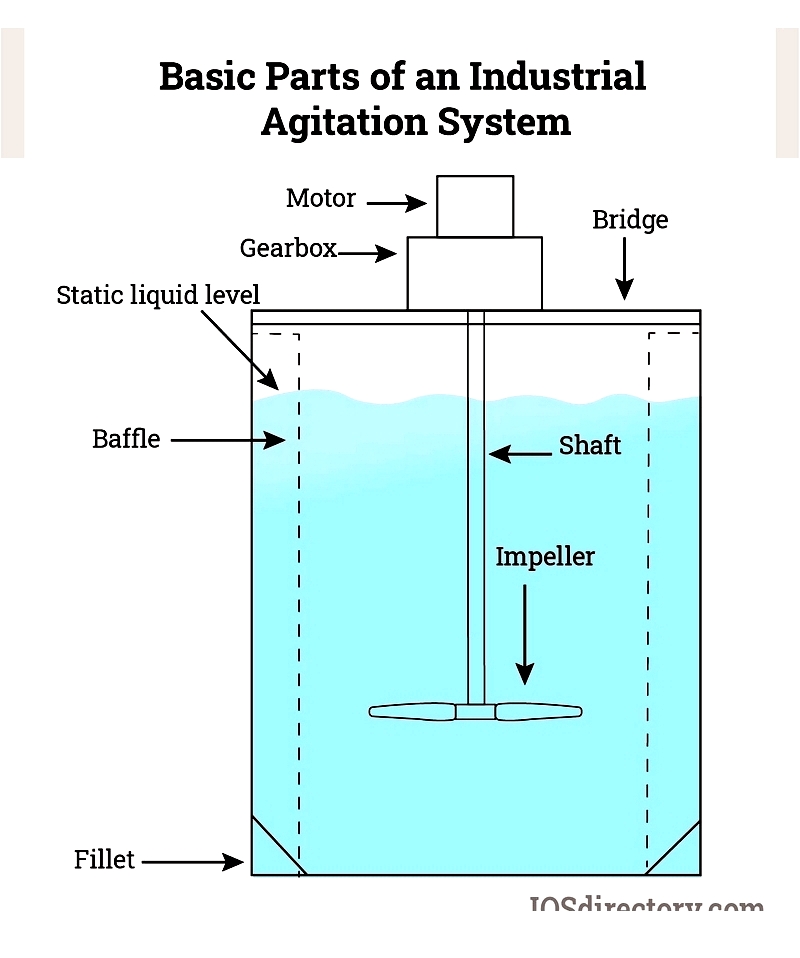
Selecting Agitator Components
When choosing agitator parts, consider tank geometry, process goals (blending, solids suspension, heat exchange), product viscosity, and chemical compatibility. Consulting agitator manufacturers and mixer suppliers improves efficiency and ensures optimal component selection. Regular maintenance of motors, shafts, and impellers minimizes downtime and extends equipment life.




