Introduction
This article provides a comprehensive analysis of rotary latches and their applications.
You will learn about:
- The definition of a Rotary Latch
- Different types of Rotary Latches
- The manufacturing process of Rotary Latches
- Materials used in Rotary Latch production
- And additional important information
Chapter 1: What is a Rotary Latch?
A rotary latch is a locking mechanism designed to secure openings like doors, enclosures, cabinets, and panels, preventing accidental opening. Commonly called slam latches, these devices engage with a striker when pushed into position. The main components typically include a housing, jaw, lever, and spring, with the housing supporting the mechanism and enabling mounting. As part of the broader latch category, rotary latches are often referred to as slam latches due to the action required for secure closure.
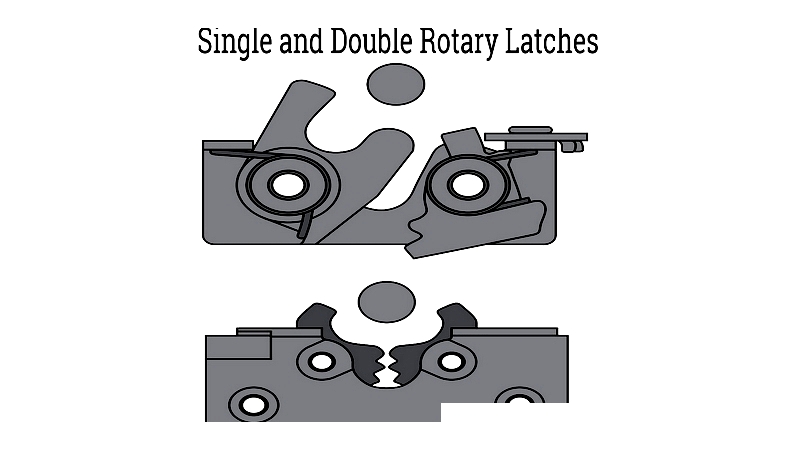
Rotary latches come in several types, primarily single, double, and two-stage versions. Single rotary latches have one rotating mechanism, while double versions feature two. Two-stage rotary latches operate in two segments for secure closure. An actuator, connected via rod or cable, releases the latch to open doors or panels.
Easy to install, rotary latches have long been used for securing vehicle doors, storage compartments, and industrial machinery. They offer reliable holding strength despite vibrations, stress, or harsh conditions. Their user-friendly design allows single-action disengagement, unlike other systems requiring multiple steps.
Chapter 2: Types of Rotary Latches
Rotary latches are crucial for securing access points in mechanical, industrial, and automotive applications. Selecting the right size, load rating, and strength ensures optimal performance, safety, and equipment longevity. Key considerations include mechanism type, actuator compatibility, material durability, and application environment.
Rotary latches are categorized into single-stage, double-stage, and specialized variants, each suited for specific needs. They vary by material (stainless steel or zinc-plated alloys for corrosion resistance), actuation style (manual, remote, or electronic), mounting configuration, and load capacity - suitable for applications ranging from light-duty panels to heavy-duty industrial enclosures.
The optimal rotary latch depends on your opening type (rigid or flexible), security needs, vibration resistance, and installation space. Advanced systems may require multi-point locking, remote release, or tamper-resistant features. Early assessment of these requirements enhances equipment integrity, user convenience, and compliance with standards.
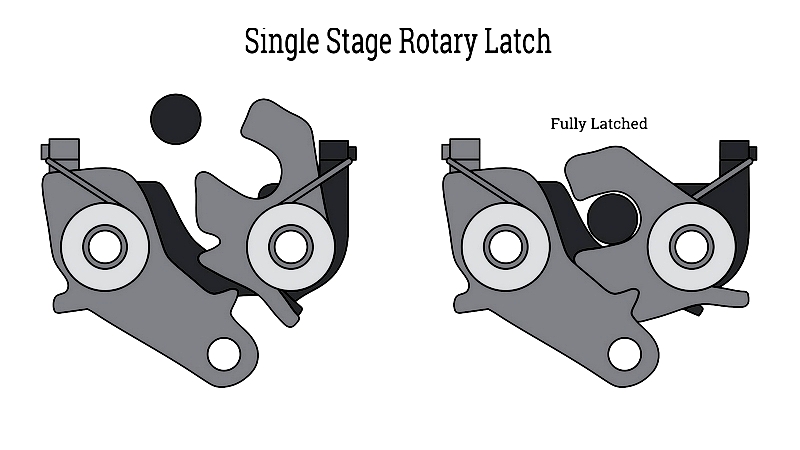
Single Stage Rotary Latches
Featuring a single rotor configurable for left- or right-hand closing, these latches engage directly with the striker pin. Ideal for light to medium-duty applications like panels and cabinet doors in commercial vehicles. Despite their simplicity, they offer various trip levers and mounting options. Ensure the latch matches the door's weight and usage frequency for optimal performance.
Their compact design makes them versatile for OEM and custom applications, with multiple actuation points and stacked levers. Commonly used in automotive glove boxes and machinery covers where easy installation and reliable operation are priorities.
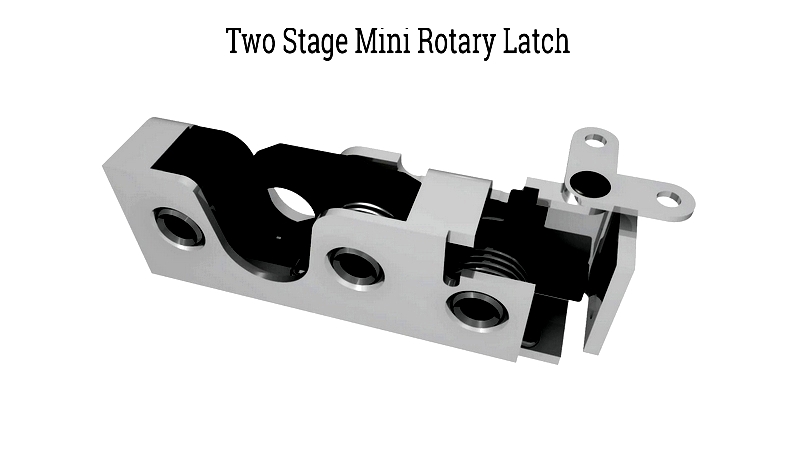
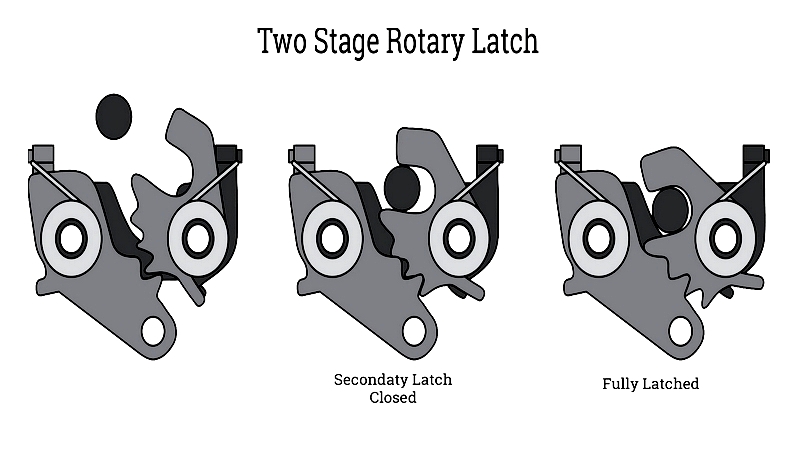
Two Stage Rotary Latches
Designed for heavy-duty use in automotive and industrial applications, these latches feature rubber bumpers to reduce noise and vibration. While similar in appearance to single-stage versions, they offer superior safety through their two-stage engagement process.
The secondary latching position prevents accidental opening and improves misalignment tolerance, making them ideal for transportation and automotive applications. Available with multiple actuators, remote release, or electronic options, they're used in vehicle doors, truck access panels, and marine hatches where vibration resistance and safety compliance are critical.
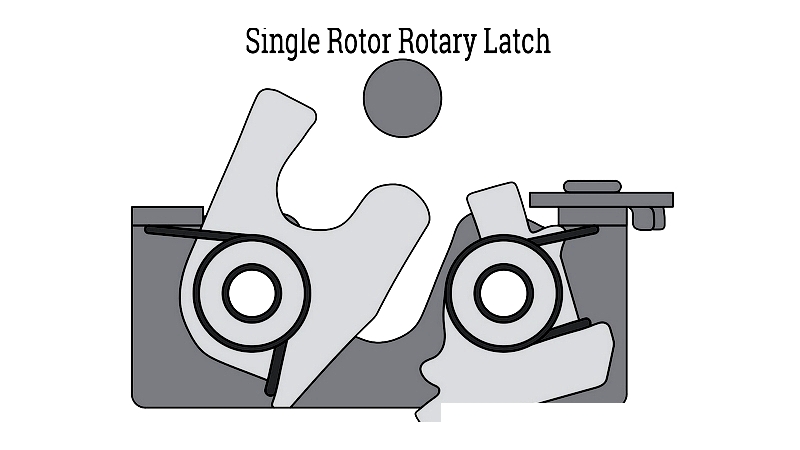
Single Rotor Rotary Latch
This subset features a robust single rotor engaging with the striker pin, suitable for light to medium loads with limited space requirements. Their application is often constrained by panel thickness and weight.
For harsh environments, choose corrosion-resistant materials like stainless steel. Commonly used in utility cabinets, machinery guards, and access panels requiring consistent operation.
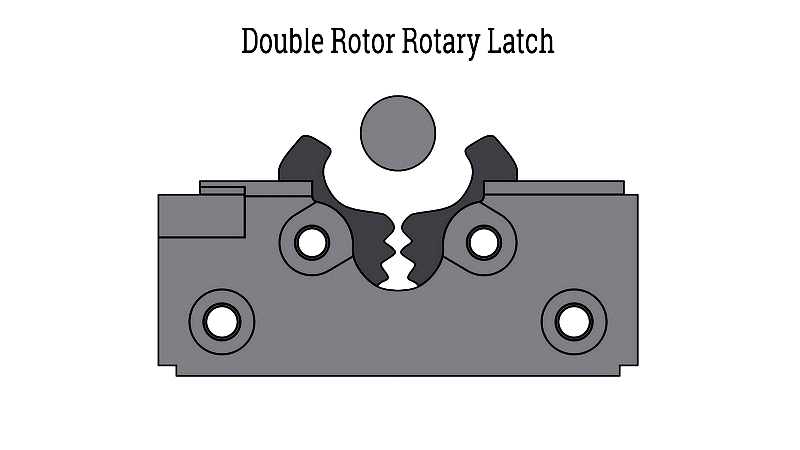
Double Rotor Rotary Latch
Offering enhanced strength and misalignment tolerance, these latches feature two rotors creating a wide catch opening. Ideal for applications with vibration or heavy use where panels may become misaligned.
Widely used in construction equipment, aerospace, and heavy transport where maximum reliability is required. Options include direct handle actuation, remote release, and electronic upgrades for added security.
Pawl Rotary Latch
Using a rotating cam mechanism, these latches provide secure closure through quarter-turn engagement. Their anti-backlash design makes them reliable for access doors and covers, often paired with ratchet wheels for better control.
Available in fixed or adjustable grip models, they're ideal for applications requiring tool-free operation and vibration resistance, such as electronics enclosures and industrial access doors.
Quarter Turn Spring Latches
These latches rotate 90° to lock/unlock, maintaining constant pressure via a spring mechanism. Ideal for vibration-prone or high-frequency access points, they prevent accidental disengagement while suppressing noise.
Their simple, fastener-free installation makes them cost-effective for OEM applications. Commonly found in HVAC equipment, electrical cabinets, and telecom enclosures, their combination of affordability and reliability has led to widespread adoption.
They also offer excellent tamper resistance while maintaining compliance with safety standards.

Rotary Draw Latch Opened with a Tool
Requiring a tool for operation, these latches provide enhanced tamper resistance in industrial settings. They're ideal for preventing unauthorized access to agricultural equipment, machinery guards, and safety enclosures.
Capable of withstanding hundreds of pounds of tension, they're available in various configurations to meet different security requirements. Their use improves equipment safety and helps comply with occupational regulations.

Understanding rotary latch types and their characteristics enables proper selection for mechanical assemblies and safety equipment. For more information or to find suppliers, visit our Rotary Latch Manufacturers Directory.
Chapter 3: Components of a Rotary Latch
Known for durability and reliable performance, rotary latches are widely used in industrial applications. These robust mechanisms enhance security while providing repeated operation in various environments. A complete assembly typically includes actuators, housing, rotors, lever, spring, and connectors working together for secure locking.
Latch
The central locking element determines the system's strength and reliability. Available in single or two-stage configurations, with two-stage versions offering enhanced security for high-vibration applications. The rotor engages with the striker, with double rotor designs providing extra strength for demanding applications.




