Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of metal moulding, also referred to as metal Moulding.
It covers detailed information on various topics including:
- Principle of metal Moulding
- Architectural metal Mouldings
- Decorative metal Mouldings
- Types of Roll Formed & metal Moulded Parts
- Applications of Roll Formed metal Mouldings
- And much more…
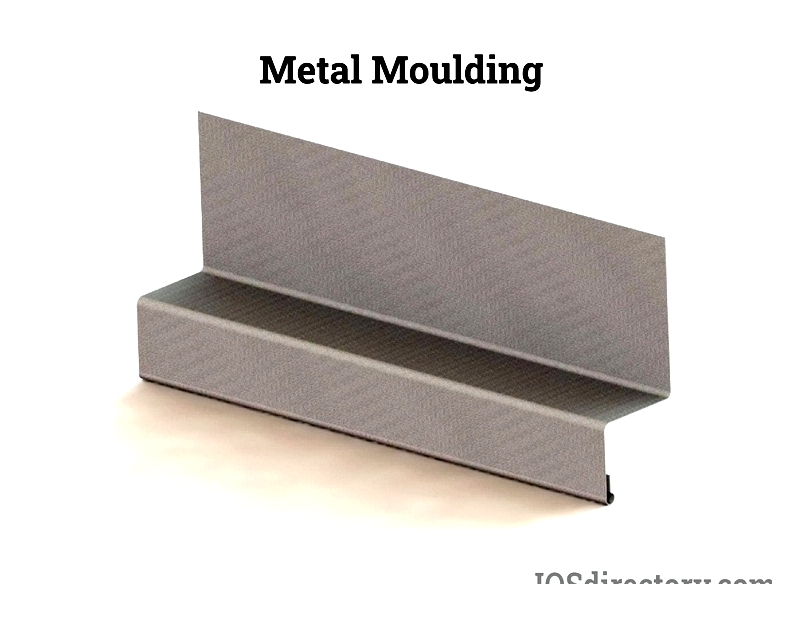
Chapter 1: What is the Principle of metal Moulding?
This section explores the principles of metal moulding and roll forming, with a focus on mouldings created through roll forming methods. It also provides a detailed explanation of the metal moulding process.
Understanding metal Mouldings and Roll Forming
Roll forming is a process where a flat metal sheet is progressively bent using sequentially arranged tool dies to create a consistent profile, continuing until the desired shape is achieved.
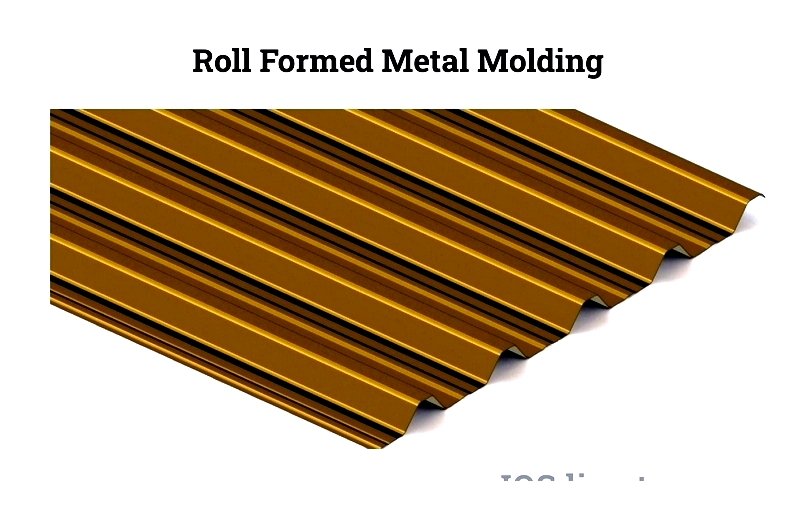
This method enables the production of metal mouldings by systematically bending sheet metal with matched dies, resulting in long, uniform profiles.
While roll forming may require higher initial tooling investments compared to other methods, it offers advantages such as continuous production, suitability for medium to large volume runs, and improved output. The technique achieves fine tolerances and superior finish quality. Additional tooling allows for intricate designs without length restrictions, as the material is continuously fed through the setup. In high-volume manufacturing, roll forming becomes cost-effective, capable of producing high-strength steels with excellent ductility while reducing labor costs through integrated fabrication.
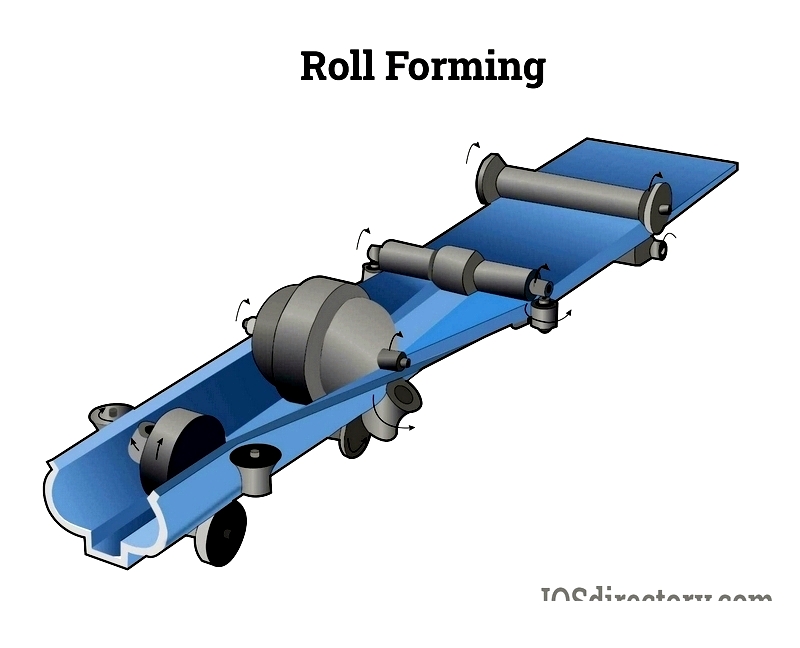
Roll forming has few drawbacks. For example, smaller production orders can be more expensive compared to other forming processes like press brake forming. Despite higher tooling costs, labor savings over time can offset these on a per-piece basis. A skilled operator is required to set up the roll forming line. End flare, where one component end flares outward due to linear stresses, can be minimized through design adjustments. Roll forming is ideal for projects requiring medium to high volume, precise tolerances, and attractive aesthetics.
Difference between metal Moulding and metal Injection Molding
Process
metal Moulding
metal moulding encompasses various methods for shaping metal components, including casting (such as sand and die casting), forging, and machining. The chosen method depends on specific manufacturing needs.
metal Injection Molding
metal Injection Molding is a specialized, relatively new manufacturing technique that combines fine metal powder with a polymer binder to form a feedstock. This is then injected into a mold, similar to plastic injection molding, and shaped through heat and pressure, removing the binder and sintering metal particles.
Materials
metal Moulding
metal moulding processes can use various metals like aluminum, steel, and copper, selected based on the required properties of the finished part.
metal Injection Molding
metal Injection Molding (MIM) typically uses powdered metals and alloys such as stainless steel, tungsten, titanium, and other high-performance materials.
Tolerance and Complexity
metal Moulding
metal moulding techniques allow for varying levels of precision and complexity, depending on the method used. Precision machining, for example, can achieve tight tolerances and intricate designs.
metal Injection Molding
metal Injection Molding (MIM) excels in producing small to medium-sized components with intricate designs and precise tolerances, making it ideal for complex parts with near-net shapes.
Cost and Production Volume
metal Moulding
The cost and production scale vary widely across metal moulding methods, with some being more economical for mass production and others suited for lower volumes or customized components.
metal Injection Molding
Due to its efficiency in producing parts with minimal waste and post-processing, metal Injection Molding (MIM) is cost-effective for mid-to-high-volume operations, although initial tooling costs may be higher than other metal moulding techniques.
Post-Processing
metal Moulding
Depending on the technique used, metal moulding may require post-processing steps like machining, heat treatment, or surface finishing to meet specified requirements.
metal Injection Molding
metal Injection Molding (MIM) typically requires less post-processing since parts are formed close to final specifications during molding.
Chapter 2: What are Architectural metal Mouldings?
This chapter offers a comprehensive overview of architectural metal mouldings, focusing on their definition and the precise roll forming process used in their manufacture. Architectural metal mouldings—also known as metal trim, architectural profiles, or decorative metal edging—are specialized components used in commercial and residential construction to enhance durability, aesthetics, and structural integrity.
How Roll Formed metal Mouldings are Made
As previously described, roll forming is a highly efficient and cost-effective process that produces custom metal mouldings by gradually shaping flat sheet metal into long, consistent profiles. Using state-of-the-art machinery and precision-matched tool dies, manufacturers can create complex and repeatable architectural profiles tailored for specific building applications, such as wall trims, ceiling edges, door frames, curtain wall components, and more. The roll forming process begins with uncoiling a metal substrate—typically steel, aluminum, stainless steel, or other high-strength alloys—and feeding it through a sequence of roll dies. Each die set is powered by its own gear system to ensure synchronized movement, allowing even delicate architectural details to be formed with accuracy and consistency.

Think of these paired dies like a railway wheel and track. They are designed to fit together precisely, providing optimal clearance to allow the metal coil to pass through smoothly without distortion.
Throughout the roll forming process, each set of dies incrementally bends the metal toward its final shape. For intricate or custom-designed moulding profiles, additional die sets are required to accommodate complex angles and decorative features. A typical roll forming mill may contain between 10 and 30 or more pairs of roller die supports, depending on the moulding’s architectural complexity and specifications.
Bending metal in just one direction often isn't sufficient because it relies on force to alter the metal's flat structure. This force creates stress, which needs to be managed and relieved throughout the entire workpiece. To achieve this, additional techniques such as twisting or curling are used. The force must be applied gradually and controlled to "massage" the metal into its final shape during roll forming. This careful process allows the metal to adapt almost perfectly to its new form by managing the direction in which stresses are released.
Depending on project requirements, architectural metal mouldings can be further enhanced during the roll forming process with additional steps such as punching, perforating, notching, or coating (e.g., powder coating or anodizing) for improved corrosion resistance, aesthetics, or functional performance. Roll formed mouldings offer exceptional versatility and can be customized in terms of profile, gauge, length, surface finish, and color to meet a wide range of commercial and architectural demands.
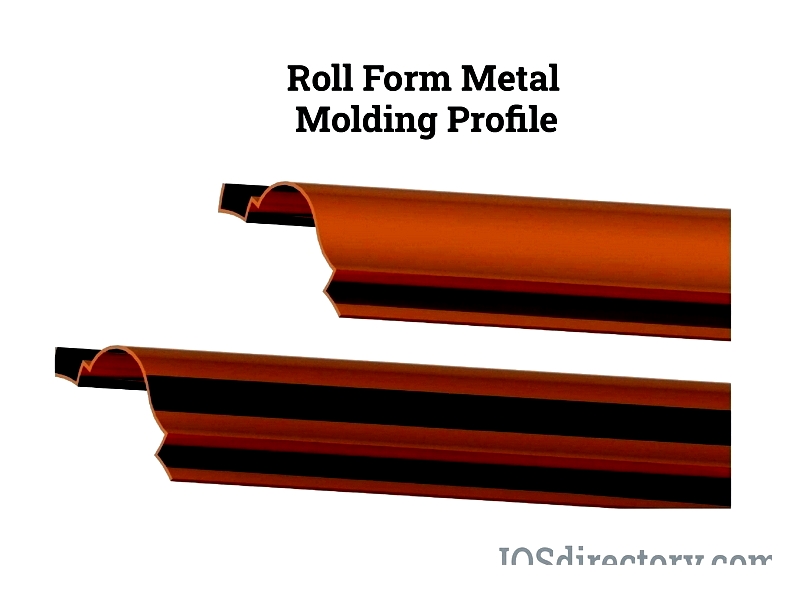
After forming, the metal strip is cut into distinct profiles using one of two methods: either a dedicated cutoff mechanism, which ensures precise measurements and clean ends ideal for ready installation, or rough-cut methods when such precision is not required. Advanced roll forming lines typically utilize flying cutoff presses to maintain




