Introduction
This article provides a comprehensive guide to high shear mixers, covering the following topics:
- What is a high shear mixer?
- Operating principles of high shear mixers
- Achieving equilibrium mixing
- Comparison with high pressure homogenizers
- Applications of high-shear mixers
- And more...
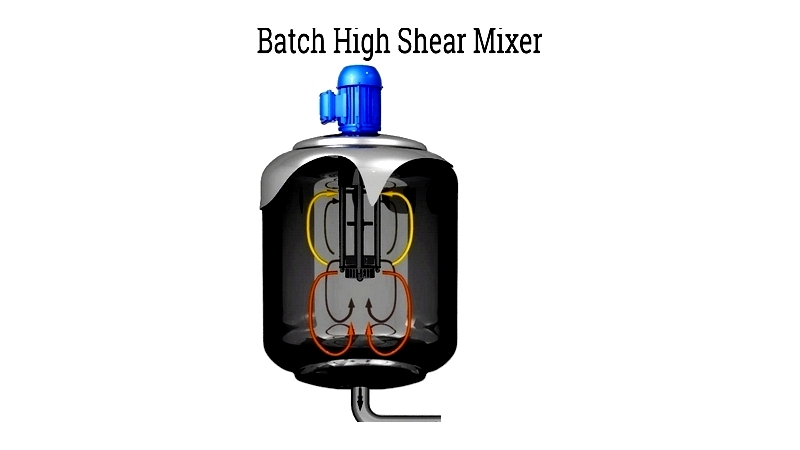

Chapter 1: What is a High Shear Mixer?
High shear mixers, also called high shear reactors, rotor-stator mixers, or high shear homogenizers, are specialized devices designed for emulsifying, homogenizing, dispersing, grinding, and dissolving immiscible mixtures. These devices operate at high rotor tip speeds and shear rates, delivering concentrated energy dissipation while consuming more energy than standard industrial mixers.
Shearing forces refer to the stresses that mixing blades or impellers exert on processed liquids, solids, and other materials. In high-speed mixing applications, a rotating rotor forces material against a stationary stator, creating shear by moving different portions of the material in opposite directions within the same plane. This unique method enables the blending of liquids, solids, or gases that conventional mixing techniques cannot effectively combine.
High shear mixers are essential for producing consumer goods with immiscible components, such as salad dressings, paints, cosmetics, detergents, shampoos, and ointments. They perform multiple functions including emulsifying liquids, blending liquids of different viscosities, incorporating solids into liquids, dispersing powders, and reducing particle size. These mixers play a vital role in industrial operations, particularly in manufacturing pharmaceuticals, chemicals, healthcare products, and cosmetics.
Chapter 2: Operating Principle of High Shear Mixers
A fluid is any substance in liquid or gaseous state that can flow freely without being constrained by surface effects. Fluid mechanics studies the behavior and properties of fluids, including viscosity, density, and flow patterns. Like solids, fluids can experience force, stress, or pressure—factors crucial to industrial mixing applications. When a fluid flows, it encounters shear stress, which forms the fundamental principle behind high shear mixer operation in process engineering.
Shear stress in fluids primarily results from friction between fluid molecules due to viscosity. Additional shear stress occurs from friction between the fluid and any moving body within it, such as the fast-rotating elements in industrial mixers. The relationship between viscosity, shear forces, and friction is essential for achieving specific mixing results like homogenization, emulsification, dispersion, and particle size reduction.
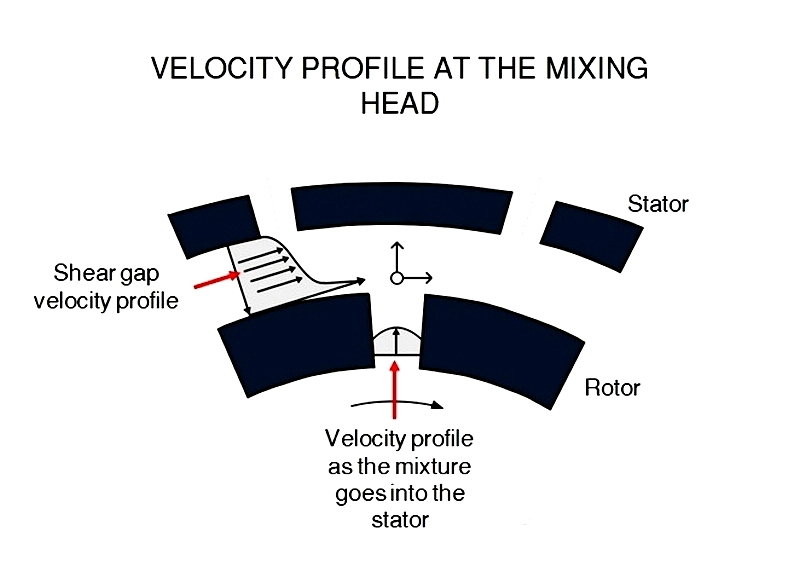
The moving body and adjacent fluid molecules share the same velocity—a phenomenon called the no-slip condition. Intermolecular forces between fluid molecules and the body's surface (the boundary layer) create an attractive force. once steady state is reached, the velocity profile across these layers becomes linear. At this stage, no additional acceleration or force is needed to deform the fluid. Motion transfers across each fluid layer while being opposed by viscosity, directly affecting mixing efficiency and energy transfer in food processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, and cosmetics production.
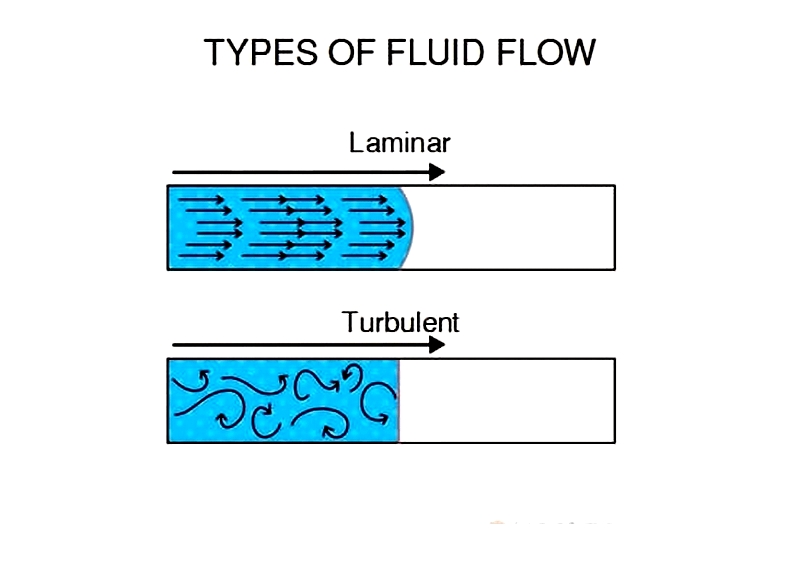
Laminar flow occurs when fluid moves smoothly and evenly across layers without disturbances. Introducing bodies that create shearing forces in different directions disrupts this flow, causing turbulent flow. Turbulent flow features random, chaotic motion that enhances mass transfer and blending across fluid layers. This accelerated, uneven flow is crucial for breaking up suspended droplets or particles, resulting in emulsion, dispersion, and homogenization—key steps in formulating creams, suspensions, and emulsions for various industries.
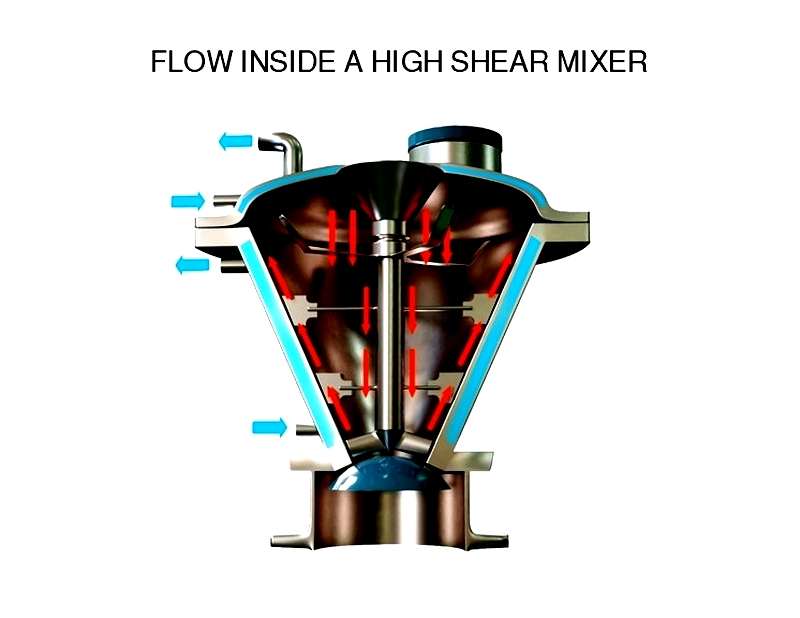
High shear mixers primarily consist of two components: the rotor and stator—collectively called the mixing head or generator. These form the core of high shear mixer design. The rotor accelerates fluid tangentially, creating intense inertia that prevents the fluid from matching the rotor's speed. Consequently, fluid is forced into the narrow gap between rotor tip and stator—the shear gap. Within this precisely engineered gap, high velocity differentials and turbulent flow generate intense shear rates. The resulting mechanical energy ensures rapid, uniform mixing of diverse materials.
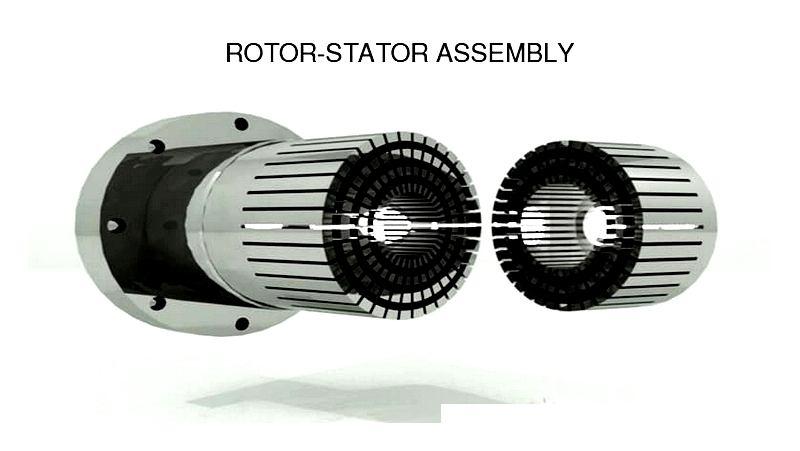
The rotor and stator's profile and configuration—including holes, slots, and vane shapes—significantly influence fluid flow and determine mixing intensity for specific applications, whether high-viscosity pastes, powders, or liquids. Below are key mixing processes facilitated by high shear mixers, each addressing unique production challenges in chemical manufacturing, pharmaceuticals, food processing, cosmetics, and adhesives.
Emulsion Homogenization
Creating a uniform mixture with a single continuous phase requires evenly sized and distributed liquid droplets—fundamental to emulsion manufacturing. Here, droplets represent the dispersed phase, while the surrounding liquid is the continuous phase. Emulsions often naturally separate, especially with immiscible liquids like oil and water. Since oil is nonpolar and less dense than water, it tends to float and separate. High shear mixers prevent this separation by continually breaking down droplets through intense shear energy.
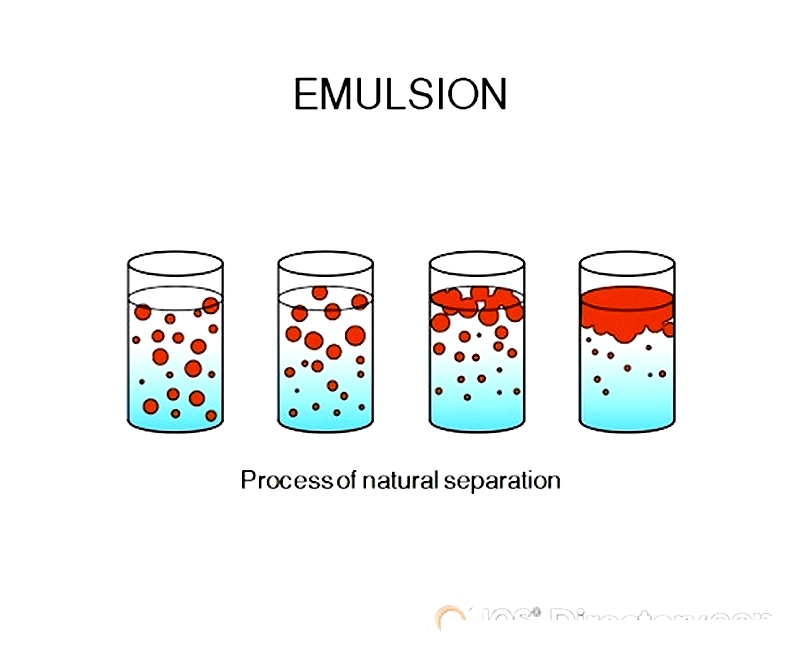
Another emulsion type involves mixing miscible liquids with different viscosities. When adding low-viscosity droplets to high-viscosity solvents, careful control of mixing time and addition rates is necessary. High shear mixers enhance emulsification by reducing droplet size, increasing surface area, and ensuring long-term physical stability—critical for quality control in products like lotions, creams, sauces, and pharmaceuticals.
- Common emulsion applications: Mayonnaise production, vaccine adjuvant formulation, paint mixing, cosmetic lotions, and industrial detergents.
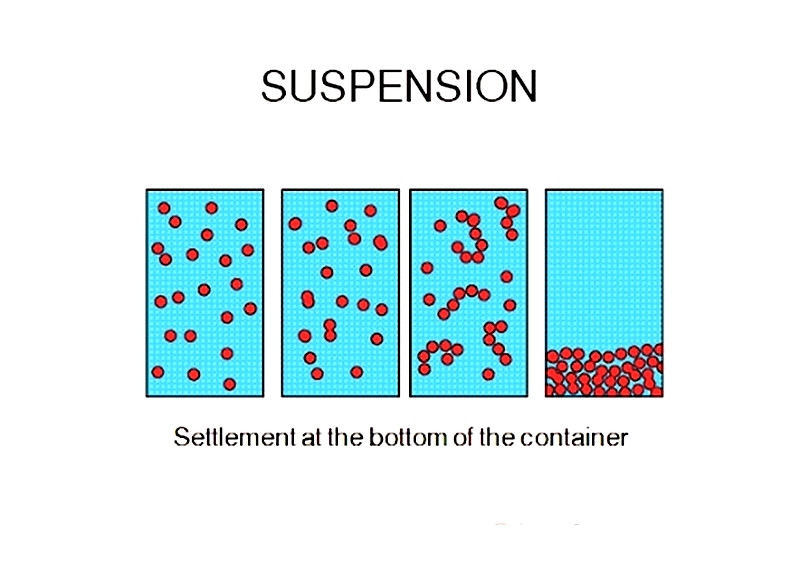
Suspension Homogenization
Suspension mixtures contain solid particles large enough to settle out without dissolving in the liquid. The goal, similar to emulsion homogenization, is to break these particles into smaller sizes and disperse them evenly throughout the medium. This process creates stable suspensions and prevents sedimentation, ensuring product consistency.
A key challenge is effectively wetting solid particles that often float due to liquid surface tension and particle hydrophobicity. Advanced high shear mixers use optimized rotor-stator geometries and precise control over mixing parameters—such as tip speed and residence time—to achieve complete particle dispersion. This topic will be explored further in the section on in-line high shear mixers.
- Common suspension applications: Pharmaceutical suspensions, pigment dispersion in inks, nanoparticle production, ceramic slurries, and beverage stabilization.
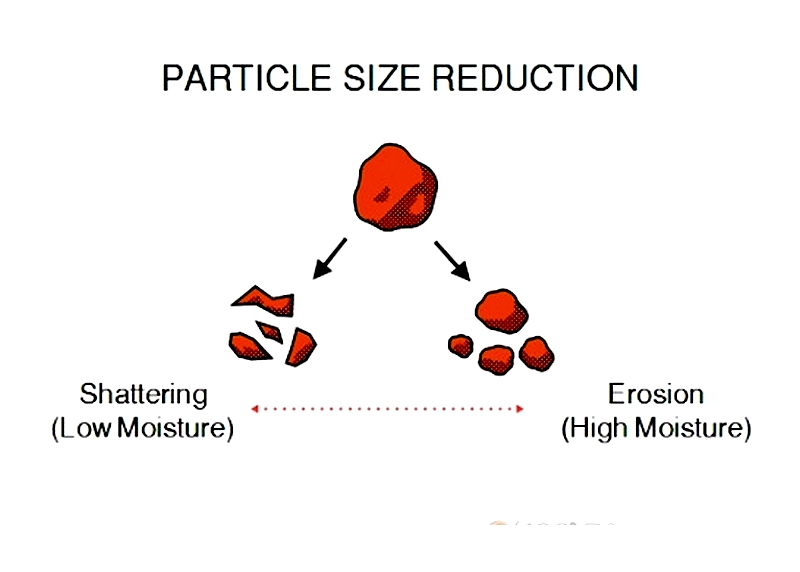
Particle Size Reduction
This application involves grinding solid or semi-solid materials into finer particles within a solution or fine suspension. The extent of size reduction depends on material hardness, brittleness, and applied mixing energy. High shear mixing achieves precise particle size reduction by exposing particles to repeated high-stress cycles, resulting in uniform distribution and improved product performance. This method is vital for micro-emulsions, drug delivery systems, food sauces, and specialty chemicals requiring consistent particle distribution.
Granulation
This process combines solid products with a binder or granulating liquid. As powder and binder mix, they form high-density granules—improving flow properties, reducing dust, and enhancing compressibility. High shear granulation is widely used in pharmaceuticals for tablet manufacturing, in food




