Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of eyelets.
Key topics covered include:
- Principle of Eyelets
- Types of Eyelets and Installation
- Applications and Benefits of Eyelets
- And Much More...
Chapter 1: Understanding the Principle of Eyelets
This chapter examines the definition of eyelets, their manufacturing processes, and the deep drawn stamping technique essential for their production.
Defining an Eyelet
An eyelet is a small circular component typically made of metal, rubber, or plastic, designed to reinforce holes in thin materials. Similar to grommets but smaller, eyelets are used in less demanding applications.
Eyelets protect materials from wear caused by rough hole edges, commonly used in textiles, sheet metals, and fibrous materials. They prevent tearing and reduce damage in thin fabrics.
How Eyelets Are Manufactured
Eyelets are simple components typically produced through metal stamping. This process transforms flat metal sheets into specific shapes using techniques like blanking, punching, bending, and piercing. A punch applies significant force to mold or cut the metal.
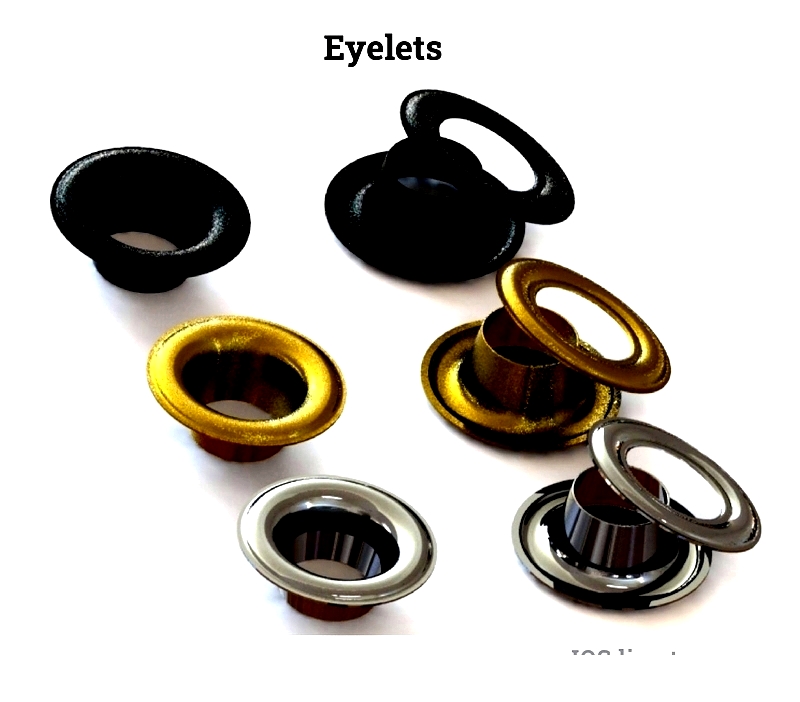

An eyelet consists of a metal ring with a flange around its hole. The ring extends into a barrel inserted into the material's hole. Tools expand the barrel to secure the material between the flange and barrel.
The design includes a short metal tube through the hole, reinforced by a metal ring. This reinforcement minimizes tearing risk, with strength proportional to size—larger flanges provide greater strength.
Deep drawing, explained below, is the primary manufacturing method for eyelets.
Deep Drawn Stamping Methodology
Deep drawn stamping creates three-dimensional shapes from metal sheets for precise cylindrical components. Certain standards must be met for a part to qualify as deep drawn.
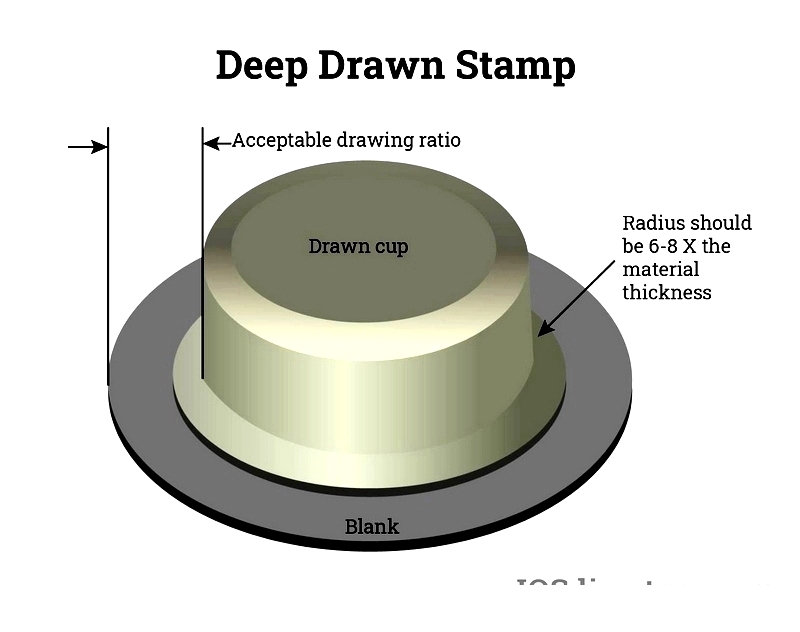
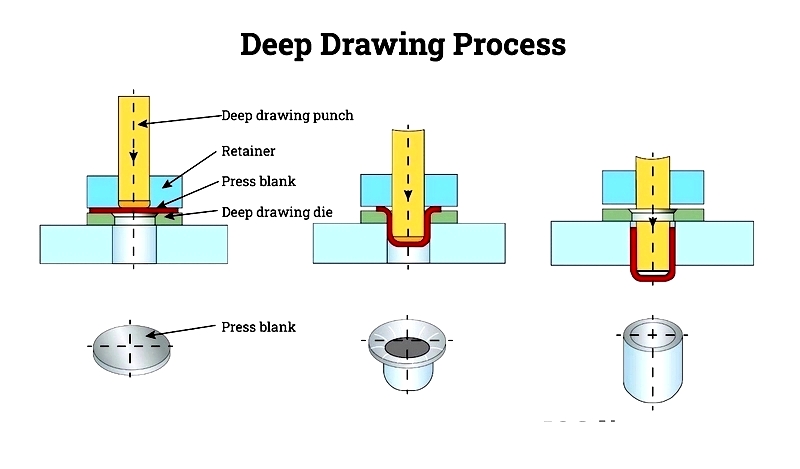
The process involves feeding a metal coil into a press with tooling stations. The depth and length must exceed half the diameter of the intended shape.
Design Considerations in Deep Drawn Stamping
Multiple forming processes can be used, including piercing, extruding, or conventional punching. Notches can be added for connections or attachments.

Threads are crafted using dies or taps. Trim lines remove excess material. Features like beads, ribs, and flanges strengthen flexible parts, potentially halving material thickness due to increased rigidity.
The Deep Drawn Stamping Production Process
The process shapes metal into forms like shells, cups, squares, rectangles, or cylinders. It begins with placing a metal blank onto the die.
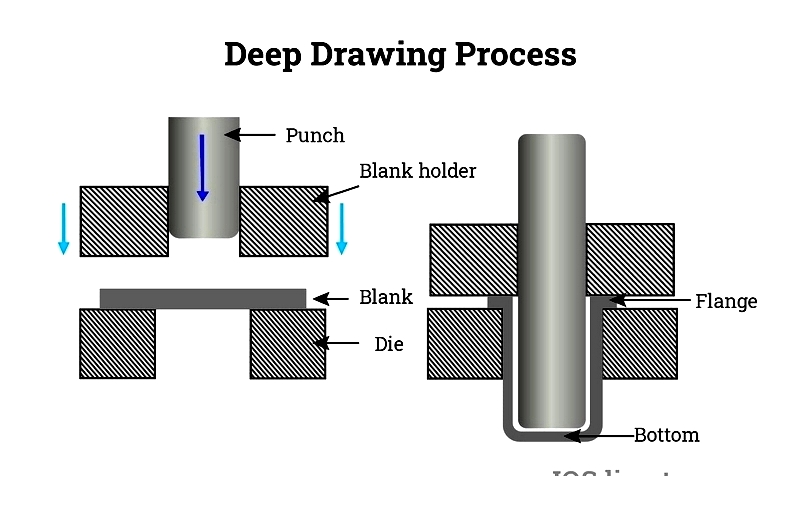
Blankholders secure the blank, preventing movement. A punch presses the blank into the desired shape within the die cavity.
Materials Utilized in Deep Drawn Stamping
Common materials include nickel, zinc, titanium, aluminum, and steel. Softer materials allow greater stamping thicknesses.
Applications for Deep Drawn Stamping
This technique produces components for industries like electronics (connection shells) and automotive (oil pans, motor housings).

It's also used in food and beverage packaging (cups, cans), fasteners, washers, enclosures, and kitchen sinks.
Materials for Crafting Eyelets
Eyelets are made from aluminum, steel, and brass sheets.
Aluminum Sheets
Aluminum (Al) is lightweight, with a density about one-third of steel. It forms a protective oxide layer when exposed to air.
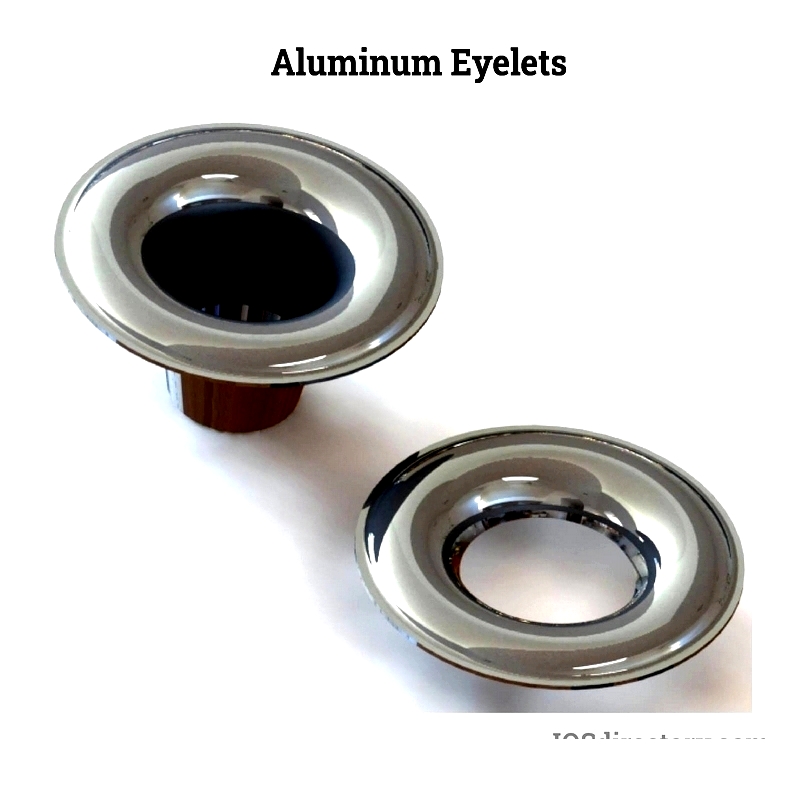

Aluminum sheets are pressed and rolled into panels. They are thin yet strong, flexible, and easy to install. Coatings enhance durability for outdoor use.
Key factors include surface dimensions and thickness. Finishes like anodizing improve corrosion resistance and appearance.
Aluminum thickness ranges from 1mm to 2mm. Grade 3003-H14 is preferred for its strength, formability, and weldability.
Advantages of aluminum:
- Versatile - Durable, strong, and lightweight, ideal for stamping.
- Lightweight - Weighs about one-third of steel by volume.
- Malleable - Easily formed into thin sheets.
- Corrosion Resistant - Forms a protective oxide layer.
- Odorless and Impermeable
- Recyclable - Retains properties after recycling, cost-effective, and eco-friendly.
Disadvantages of aluminum:
- Higher cost than steel.
- More prone to dents and scratches.
Steel Utilization in Eyelets
Steel is an iron alloy often enhanced with carbon for strength. Stainless steel contains chromium for corrosion resistance.

Stainless steel is eco-friendly and durable. Grades 304, 410, and 430 are suitable for eyelets.
Benefits of steel:
- Corrosion Resistance - Chromium oxide layer protects against rust.
- Easy Cleaning - Maintains appearance with common cleaners.
- Recyclable - Eco-friendly and inert in water contact.
- Mechanical Properties - Combines elasticity, ductility, and hardness.
- Aesthetic Appeal - Available in various finishes.
Disadvantages of steel:
- Challenging to stamp.
Brass Application in Eyelets
Brass, a copper-zinc alloy, offers corrosion resistance, durability, and aesthetics.

Typically 66% copper and 34% zinc, brass is vulnerable to water but more resistant than pure copper.
Benefits of brass:
- Strong - Zinc-copper synergy enhances strength.
- Durable - Long-lasting and corrosion-resistant.
- Decorative - Offers diverse finishes.




