Introduction
This comprehensive guide covers everything you need to know about hinges.
- What is a Hinge?
- Types of Hinges
- Hinge Components and Characteristics
- Design Considerations
- Common Manufacturing Processes
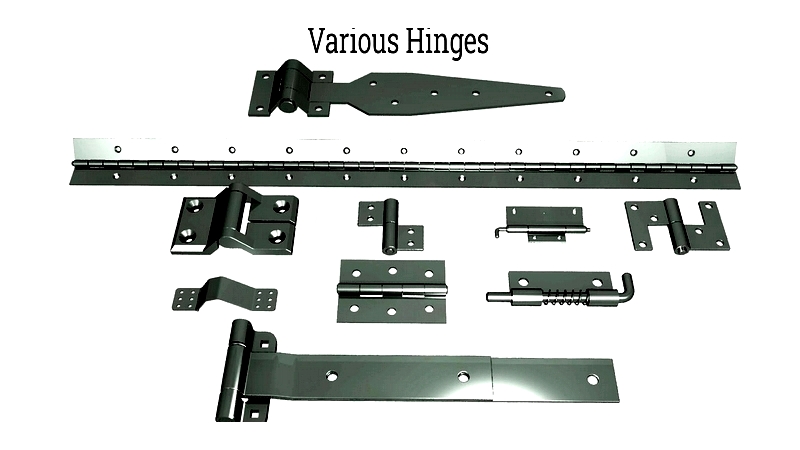
Chapter 1: Understanding Hinges
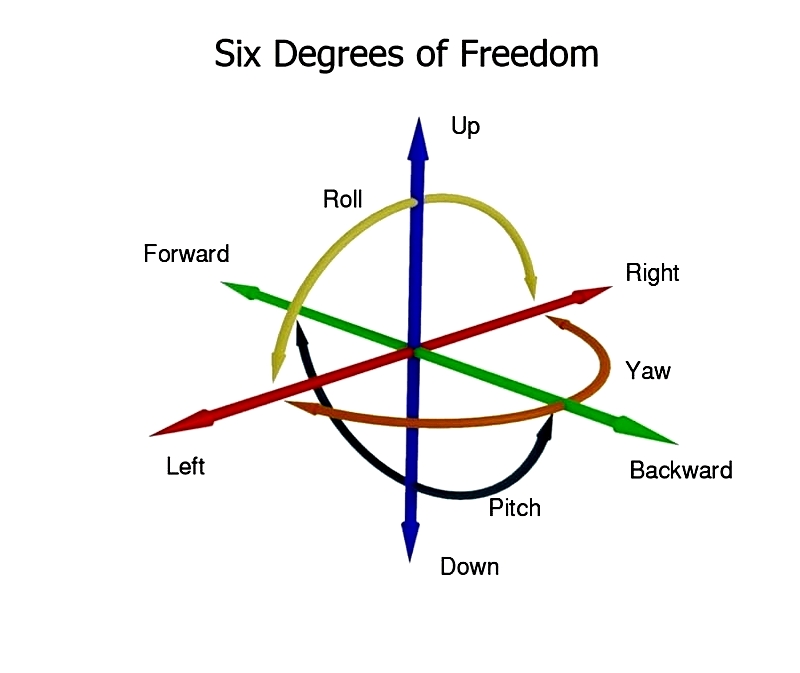
A hinge is a mechanical device that connects two components, enabling them to pivot around a fixed axis while restricting movement in other directions. Essentially functioning as a journal bearing with a single degree of freedom, hinges allow rotation while limiting motion to specific planes. They typically facilitate movement in one primary direction, usually yaw, though some designs accommodate pitch or roll.
These flexible, jointed mechanisms serve as mechanical bearings that link moving parts at designated points. By constraining relative motion between connected objects to a single angle, hinges ensure movement occurs only within a defined plane.
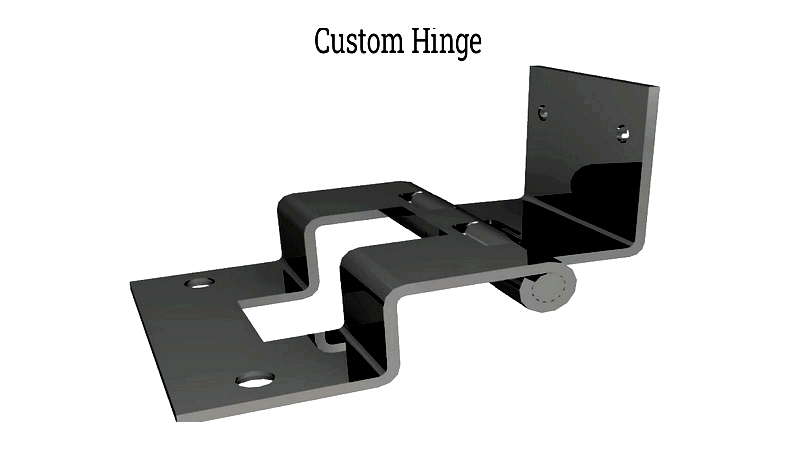
Hinges have widespread applications across various industries, including doors, enclosures, containers, furniture, jewelry, construction, and electronics. For specialized requirements, custom hinges can be designed and manufactured cost-effectively to meet specific needs.
Chapter 2: Types of Hinges
Selecting the appropriate hinge requires understanding the diverse range available for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. Different hinge types—including door hinges, cabinet hinges, and industrial hinges—are engineered to meet specific installation requirements, weight capacities, and environmental conditions.
The following comprehensive list details popular hinge types and their applications to assist in making informed selections:
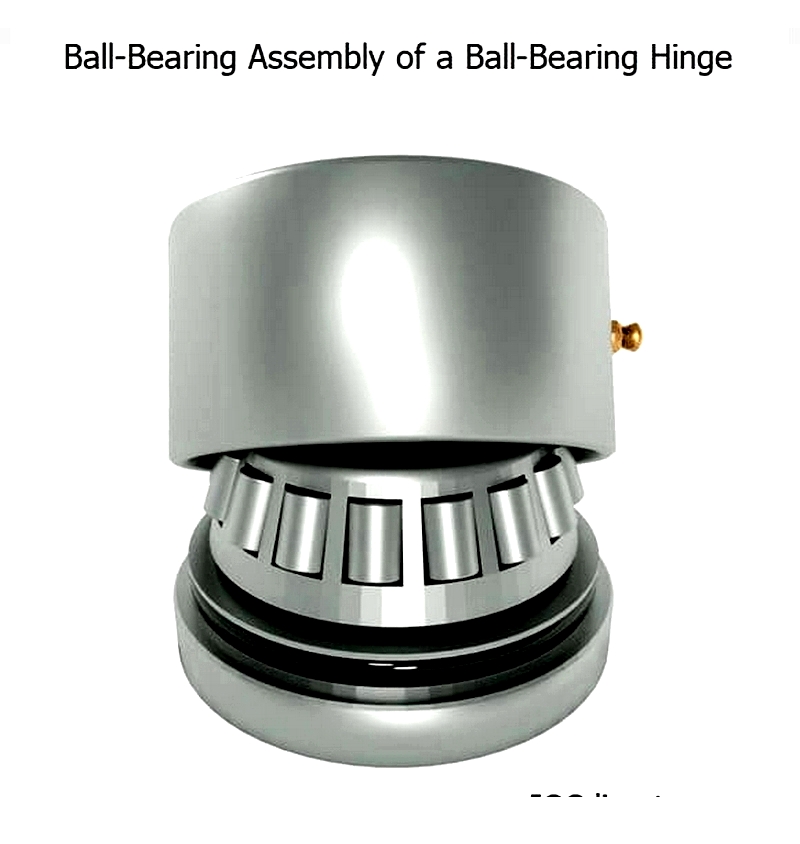
Ball-bearing Hinges
These hinges utilize ball bearings instead of traditional knuckle-and-pin assemblies, reducing friction through minimized contact surfaces. Ideal for high-traffic commercial doors and heavy exterior applications, they provide smooth operation and exceptional durability.

Block Hinges
Characterized by their robust, square profile, these heavy-duty hinges feature galvanized steel barrels with stainless steel pins for corrosion resistance. Commonly used in security doors and warehouse gates, they excel in high-load applications requiring maximum strength.





