Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of belt conveyors.
It covers essential topics including:
- Belt Conveyors and their Components
- Types of Belt Conveyors
- Design and Selection of Belt Conveyors
- Applications and Benefits of Belt Conveyors
- And Much More...
Chapter 1: Understanding Belt Conveyors and Their Components
This chapter explores the fundamentals of belt conveyors and their key components.
What is a Belt Conveyor?
A belt conveyor is an efficient system for transporting materials, goods, or people between locations. Unlike traditional conveying systems that use chains or hydraulics, belt conveyors employ a continuous belt loop supported by rollers and powered by an electric motor.
The belt material varies depending on application requirements, typically made from polymers or rubber to suit specific operational needs.
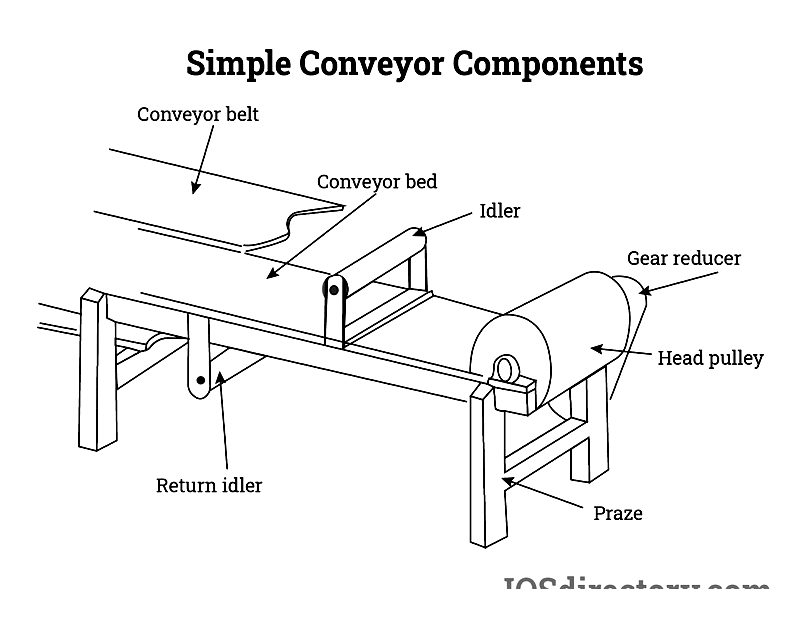
Components of a Belt Conveyor
A standard belt conveyor includes essential parts such as head pulleys, tail pulleys, idler rollers, the conveyor belt, and supporting frame.
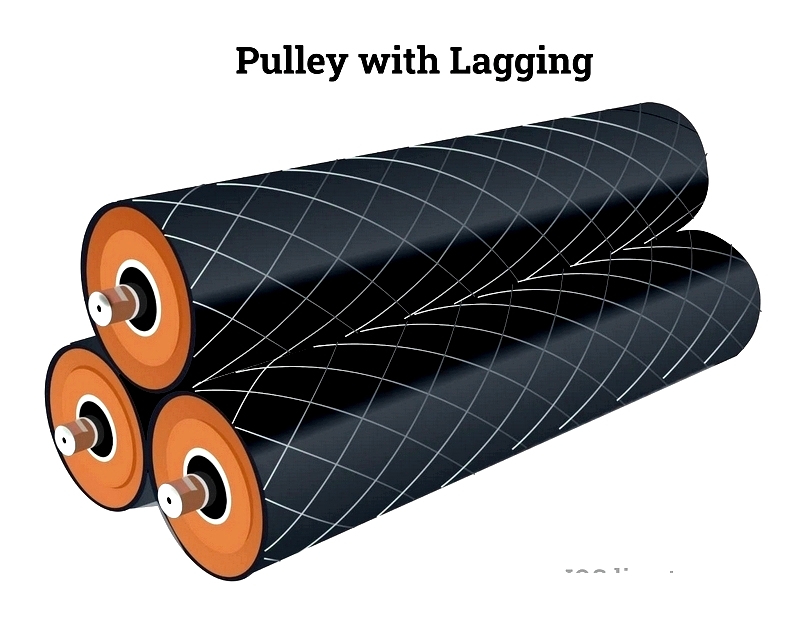
Head Pulley
The head pulley connects to the drive motor and generates the pulling force for conveyor operation. Positioned at the discharge end, it often features lagging for improved traction and typically has the largest diameter among all pulleys.
Return or Tail Pulley
Located at the loading end, tail pulleys often incorporate wing designs to remove debris from the belt. Simple systems use adjustable guides for tensioning, while advanced systems employ dedicated take-up mechanisms.
Idler Roller
Idler rollers support the belt along its length, preventing sagging and maintaining proper alignment while clearing residual material.
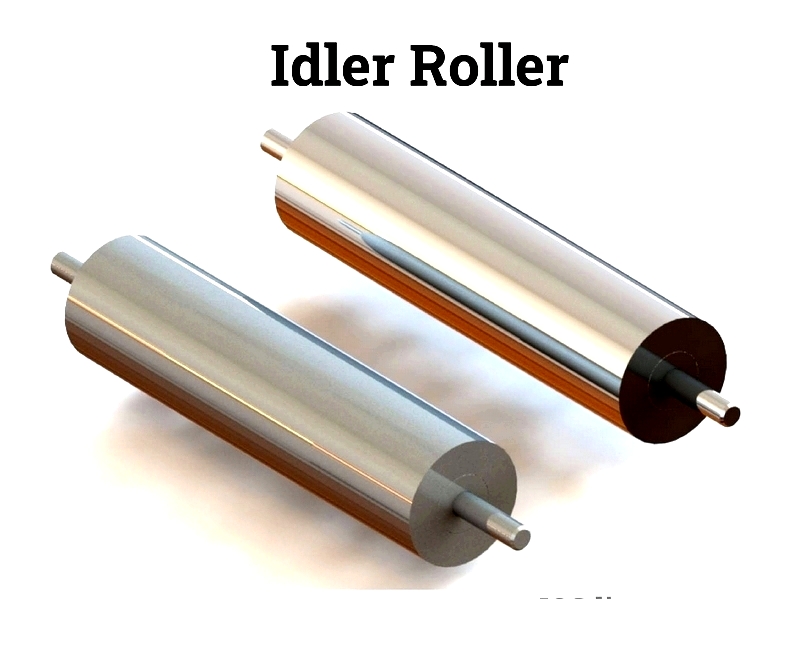
Various idler types serve specific functions:
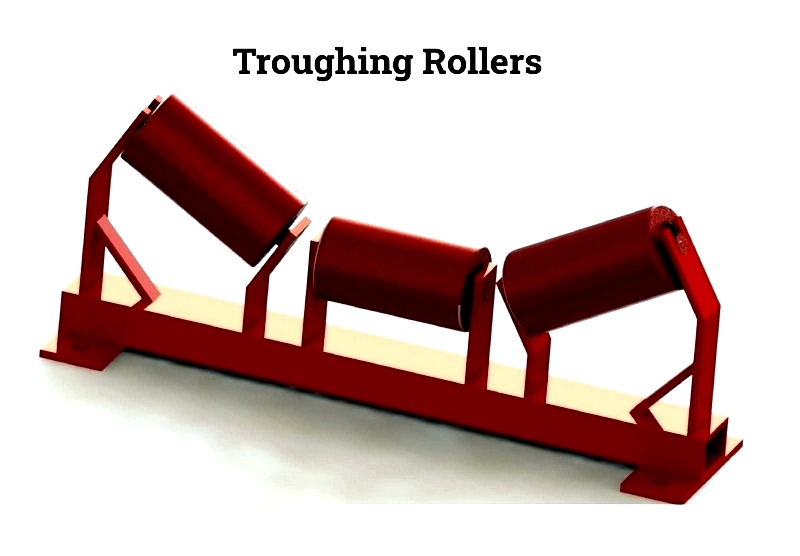
Troughing Idlers
These feature three rollers forming a trough to support the loaded belt, maintaining stability and minimizing spillage.
Rubber Disk Idler
Equipped with spaced rubber disks, these idlers clean the belt and prevent material buildup that could cause misalignment.

Screw Idler Roller
With helically arranged disks, these idlers offer effective cleaning where scrapers aren't practical.

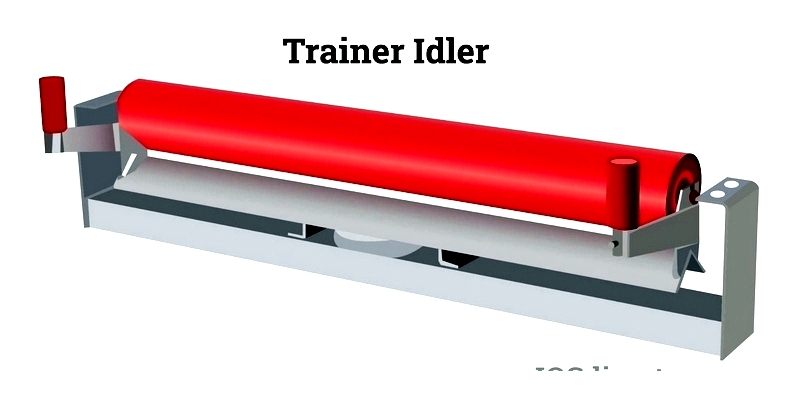
Trainer Idler
These self-aligning idlers feature guide rollers to correct belt tracking issues.
Conveyor Belt
The belt itself represents the most sophisticated component, requiring careful material selection to balance strength, cost, and application requirements.

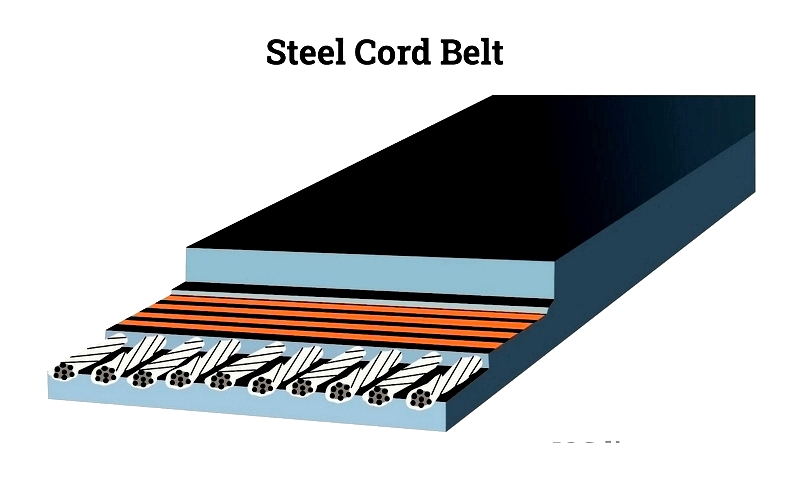
Conveyor Carcass
The carcass provides structural support, typically constructed from steel cords or textile plies with various reinforcement materials.
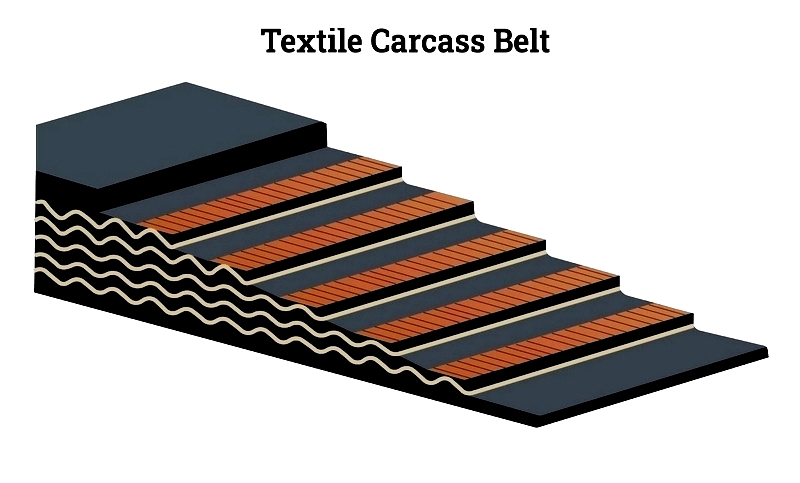
Conveyor Covers
Top and bottom covers protect the carcass, with material selection based on operational requirements like temperature resistance or food safety compliance.
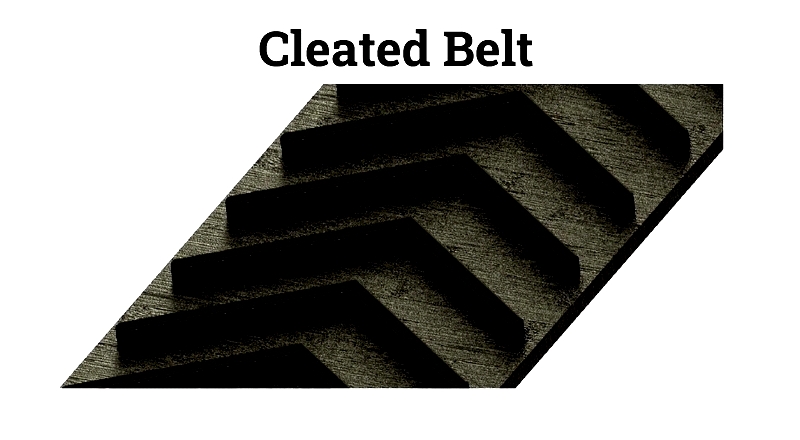
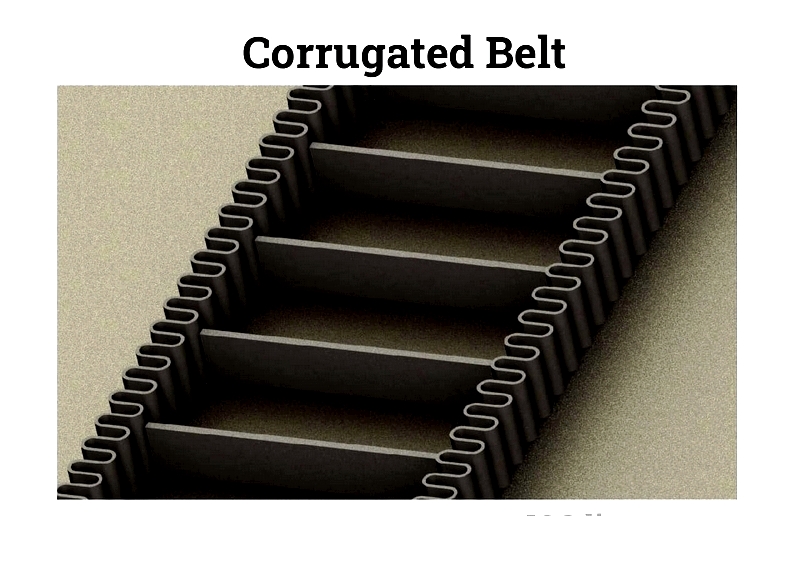
Specialized belt surfaces include cleated or corrugated designs for specific applications.
Conveyor frame
The frame design must accommodate load requirements and operational conditions, ranging from simple aluminum extrusions to heavy-duty truss structures.

Poor frame design can lead to operational issues including:
- Belt misalignment
- Structural failures causing:
- Production delays
- Safety hazards
- Material spillage
- Increased installation costs

Chapter 2: Types of Belt Conveyors | Industrial Conveyor Systems Guide
This chapter examines various belt conveyor types used across industries, highlighting their unique features and applications.
Roller Bed Belt Conveyor
Featuring closely spaced rollers, these conveyors minimize friction and support heavy loads efficiently.
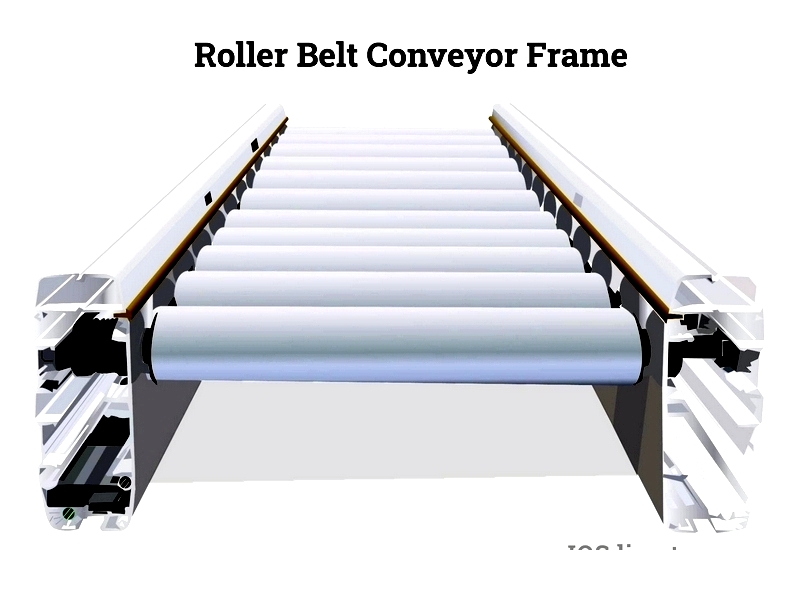

Common applications include:
- Airport baggage handling
- Parcel sorting systems
Flat Belt Conveyor
Versatile and widely used, flat belt conveyors handle diverse products in manufacturing and distribution.

Ideal




