Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of closed cell foam.
It covers essential topics including:
- Principles of Closed Cell Foam
- Varieties of Closed Cell Foam
- Applications and Advantages of Closed Cell Foam
- And More...

Chapter 1: Understanding Closed Cell Foam Principles
This chapter introduces closed cell foam, explaining its definition and manufacturing process. You'll learn cutting techniques and key selection criteria for this material.
What is Closed Cell Foam?
Closed cell foam features tightly sealed, non-interconnected cells. Unlike open cell varieties like polyurethane, its structure contains gas-filled pockets that enhance durability for demanding applications.

The sealed cellular structure prevents water penetration, offering excellent pressure resistance. Available in various densities from rigid polyethylene to softer Flotex, this versatile material ensures stability and secure sealing. Its color and thickness options, combined with superior robustness, distinguish it from other foam types.
Closed Cell Foam Production
Manufacturing involves specific materials and processes:
Production Materials
Polyethylene Foam - This water-resistant material offers sound dampening, buoyancy, and shock absorption, making it suitable for packaging and crafts.
Polyethylene Rolls – Versatile rolls used across automotive, healthcare, and sports industries.

Cross-linked Polyethylene – Available in 0.063-0.700 inch thicknesses with 2-20 lb/cubic foot densities, this mildew-resistant material suits packaging, flotation devices, and industrial uses.
Polystyrene Foam – Ideal for projects requiring rigid blocks, commonly used in storage and packaging.
Neoprene Rubber – Used in sheet or roll form for insulation and clean environments like medical facilities and sports venues.
Gym Rubber – High-density material with shock resistance for gyms, daycares, and insulation.
Polypropylene Foam – Heavy-duty option for protective packaging requiring substantial rigidity.
Manufacturing Processes
Foam production involves gas entrapment in liquid, followed by solidification under pressure and heat. The resulting material provides impact cushioning, noise reduction, and waterproofing benefits.
Spray Foam Insulation
This highly efficient insulation method offers superior thermal properties for residential and commercial applications.
Cutting Techniques
Straight, non-serrated blades work best for closed-cell materials. Scissors may suffice for thinner foams, while thicker materials require multiple passes with a straight edge guide.
Scissor Cutting
Suitable for materials under 1/8" thickness, primarily for light hobby projects.
Single-Pass Method
Ideal for materials up to 1/2" thickness, producing clean edges with one steady cut.

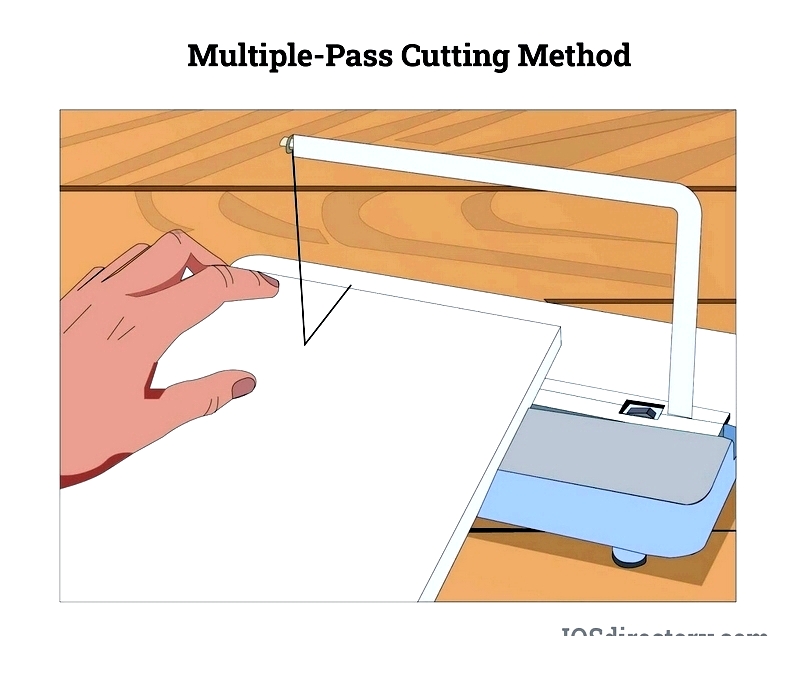
Multiple-Pass Method
Necessary for foams exceeding 1/2" thickness, involving progressive deepening cuts for clean results.
Selection Criteria
Closed cell foam excels when structural stability, energy efficiency, and water resistance are priorities. Its dense cellular structure improves air quality by blocking contaminants and preventing mold growth.
Chapter 2: Leading Closed Cell Foam Equipment Manufacturers
Industrial production requires specialized equipment to maintain quality and efficiency. Closed cell foam serves construction, automotive, marine, and packaging industries with its thermal insulation, water resistance, and structural benefits. Below are five prominent manufacturers of foam production machinery.
Cannon Viking Series
This series offers precision mixing and automated curing for rigid polyurethane and polyethylene foam production, minimizing waste through advanced process control.
Hennecke High-Pressure Metering Machines
Renowned for precision and flexible production capabilities, these machines handle various closed cell polyurethane formulations with consistent quality.
Linden Industries High-Pressure Machines
North American-made equipment ensuring accurate density control for building insulation and automotive applications.
Gusmer H-20/35 Pro
Reliable system for spray foam contractors, featuring precise chemical ratio control for commercial insulation and roofing.
Evonik High-Pressure Systems
Versatile solutions for insulation panels and specialty foams, with automated dosing technology for consistent production.
For optimal equipment selection, consult manufacturers for current specifications and technical support.
Chapter 3: Closed Cell Foam Varieties
Different types serve specific applications in packaging, construction, and other industries. Here are the main categories:
EVA Foam
Flexible material for sports padding and marine applications, offering shock absorption and water resistance.

FloTex Foam
Medium-firmness foam for marine and recreational products, featuring excellent water repellency.

Polyethylene Rolls
Versatile rolls for insulation, medical devices, and automotive applications, available in various thicknesses.

Cross-linked Polyethylene
Superior moisture and chemical resistance make this ideal for premium packaging and medical applications.





