Introduction
This article provides an in-depth examination of Linear Bearings.
Continue reading to explore topics including:
- What are Linear Bearings?
- Types and design aspects of Linear Bearings
- Rolling Linear Bearings
- Plain Linear Bearings
- Materials used in Linear Bearing construction
- And much more...
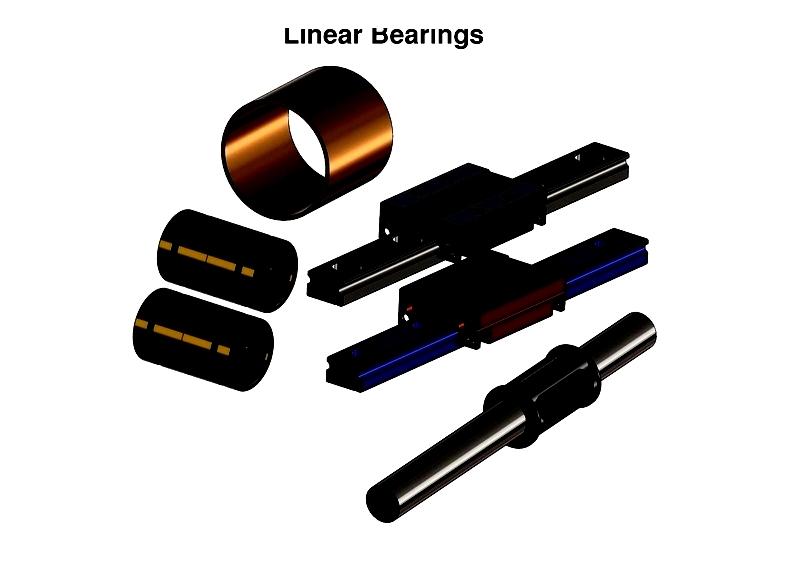

Chapter 1: What are Linear Bearings?
Linear bearings are designed to support carriage loads while moving along a single axis, providing a low-friction interface for smooth sliding on guide rails. In a linear guide system, the carriage moves along either straight or curved paths on the embedded guide rail.
Available in various forms including rolling elements and fluid-based devices, these bearings minimize friction while ensuring high precision, stable mounting, and smooth motion. They are widely used in 3D printers, sliding doors, and other automated systems requiring precise rail movement.
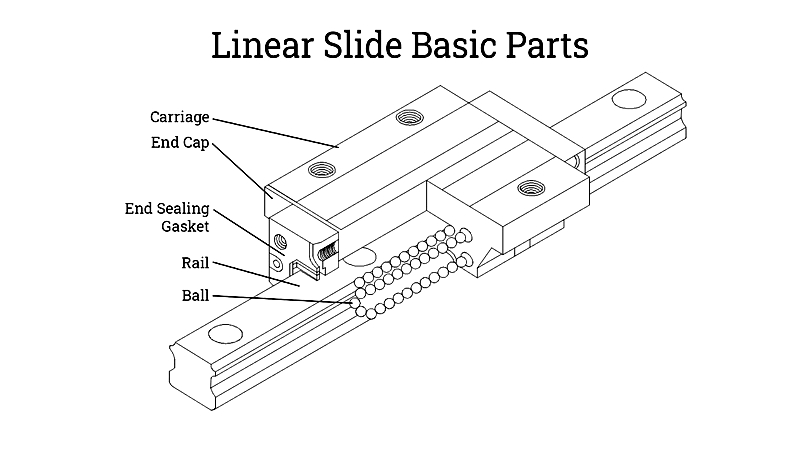
As a crucial component of linear guide assemblies, linear bearings find applications in cutting machinery, XY positioning tables, machine slides, industrial robots, and instrumentation systems. Movement can be powered by motor-driven ball screws, lead screws, pneumatic or hydraulic cylinders, or manual force, with motion restricted to a single axis in the X-Y plane. Hydraulic and pneumatic cylinders are fundamental components in CNC milling machine XY beds.
Linear bearings are primarily classified into two types: rolling linear bearings and plain linear bearings. The following sections will examine each type's components, operational principles, and design considerations in detail.
Chapter 2: Rolling Linear Bearings
Rolling linear bearings play a vital role in industrial automation and precision machinery by enabling smooth, accurate linear motion along guide rails or shafts. These linear bearings are valued for their low friction and efficient movement, utilizing rolling elements—either balls or rollers—positioned between matching grooves on the bearing and guide rails. This design reduces friction compared to plain bearings, ensuring wear resistance and reliable performance in applications ranging from CNC machines to medical devices and automated manufacturing equipment.
When selecting an optimal linear bearing system, key considerations include the diameter of balls or rollers—which affects maximum travel speed and system stability—and the contact angle that determines force management capabilities. A 45° contact angle, for instance, balances performance across radial, reverse radial, and lateral loads, enhancing flexibility for multi-directional force applications while slightly reducing lateral load capacity.
Available in specialized designs and configurations, rolling linear bearings feature structural and material characteristics tailored to specific operational environments. Understanding these engineering differences is crucial for achieving optimal motion control, extended service life, and minimal maintenance in demanding industrial applications.
Geometry of the Rolling Elements
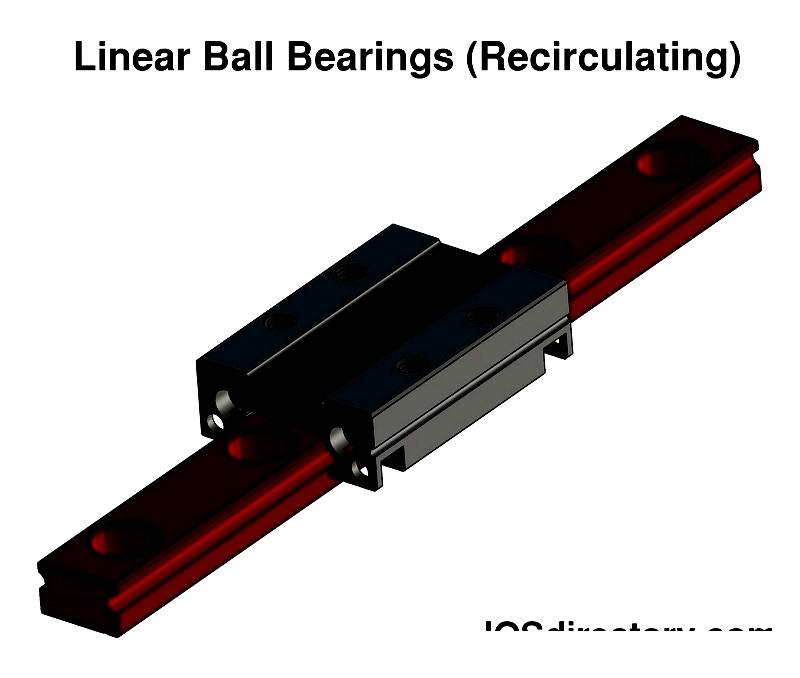
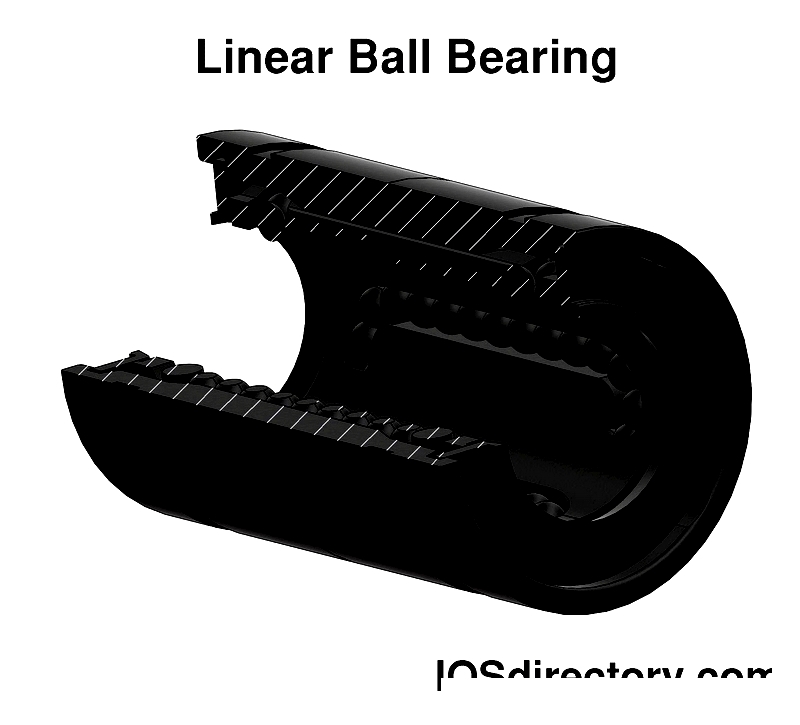
Linear Ball Bearings
Linear ball bearings use spherical rolling elements made from hardened steel or advanced ceramics, offering low rolling resistance, precision guidance, and repeatable accuracy. These qualities make them ideal for automation systems, robotics, and medical diagnostics equipment. Their adaptability supports various linear motion applications requiring high efficiency, reliable positioning, and minimal friction. Popular for their accuracy, quiet operation, and speed capabilities, they are preferred where performance and longevity are critical.
Linear Bearings with Cylindrical Rolling Elements
Featuring cylindrical rollers, these linear roller bearings provide higher load capacity, rigidity, and shock resistance compared to ball designs. Their elongated contact surface distributes force more effectively, making them suitable for heavy-duty linear motion in material handling, packaging machinery, and construction automation. The trade-off for enhanced durability is slightly increased operational friction due to the expanded contact area and need for precise alignment.

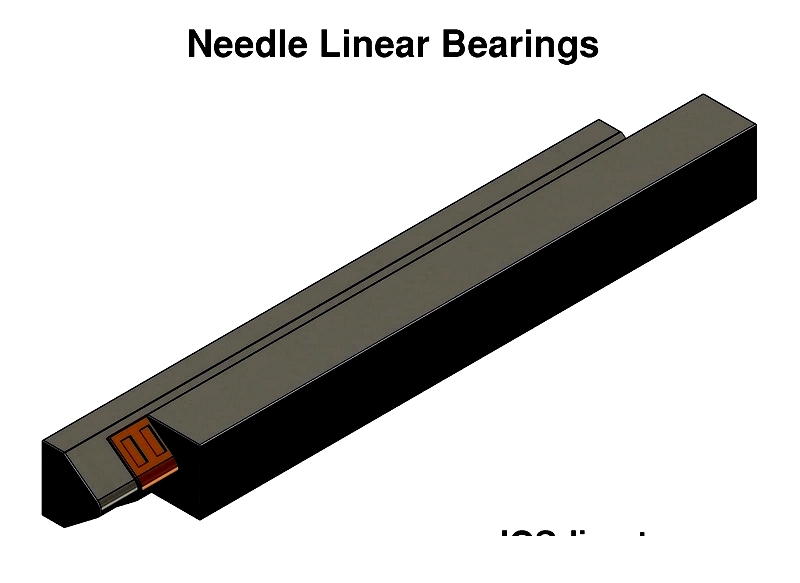
Needle Linear Bearings
Needle linear bearings utilize slender cylindrical rollers with high length-to-diameter ratios (3:1 to 10:1), maximizing contact area for improved load distribution, rigidity, and deflection resistance. Their compact design makes them ideal for space-constrained installations in high-precision industrial equipment, automated assembly lines, and transportation machinery where extreme load capacity and durability are essential.
Track Geometry
The track profile geometry significantly influences the interaction between rolling elements and raceways, affecting contact points, load-bearing potential, and friction coefficients. Proper track geometry selection is vital for optimizing performance in high-speed automation, material transfer systems, and motion control applications.
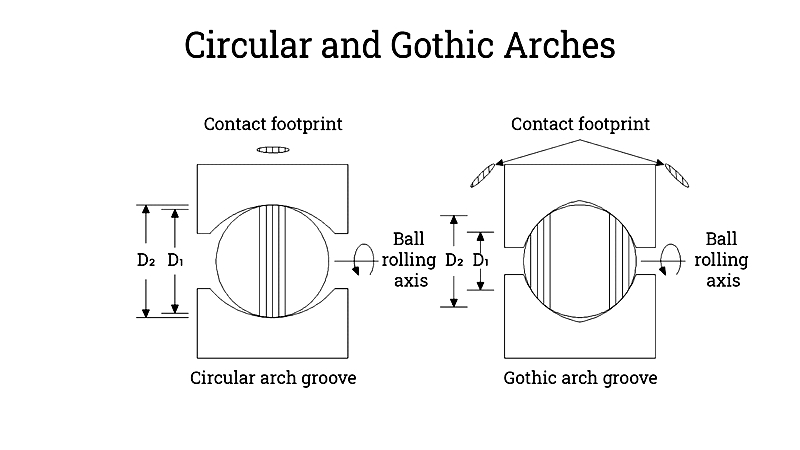
Gothic Arc Profile
A gothic arch track profile creates four contact points per ball, improving moment load capability and enabling compact installations. While this design enhances rigidity and shock absorption, it introduces greater differential slip and friction. It's favored in CNC machinery and semiconductor automation where moment load resistance is crucial.
Circular Arc Profile
The circular arc profile reduces contact to two points per ball, minimizing differential slip and friction for smoother, quieter motion. Although load capacity is somewhat reduced, this profile is preferred in laboratory automation and precision instruments where smooth travel is prioritized.
Linear Guide Profile Shapes
The linear guide rail profile determines system rigidity, support, and installation suitability. Matching bearing and rail geometries ensures long-term reliability and precise motion control for specific automation or production environments.
Round Rail
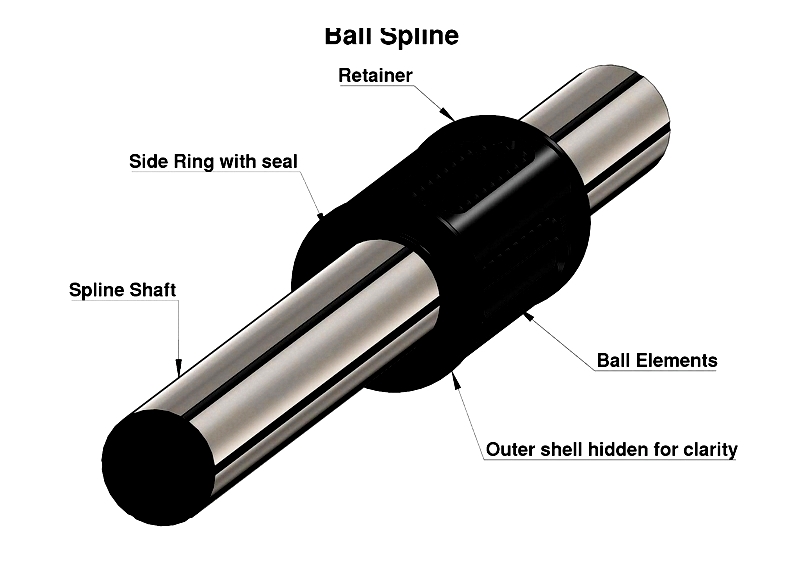
Round rail profile linear guides use cylindrical shafts with linear ball bushings for frictionless movement. These versatile systems accommodate shaft misalignment and offer simple installation, making them popular in 3D printers, laboratory instruments, and electronics production. Ball splines—a specialized variant with axial grooves—prevent shaft rotation while transmitting torque, making them ideal for robotic arms and automation tooling requiring combined linear and rotational movement.

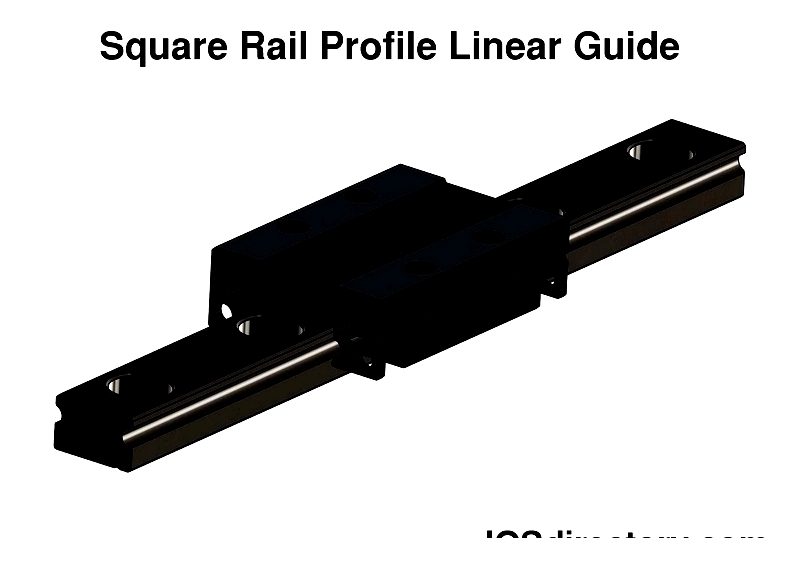
Square Rail
Square rail profile linear guides feature rolling elements on flat, square-edged rails for exceptional rigidity, high load capacity, and vibration damping. These systems outperform round rails in applications demanding maximum accuracy and stiffness, such as CNC machines and industrial motion platforms, particularly where space constraints and lateral stability are concerns.

Vee Linear Guides
V-guide rail systems use precision rollers with ball bearings running along V-shaped steel tracks, offering misalignment tolerance and debris displacement. The V-guide rail system provides low friction, quiet operation, and contaminant protection, making it suitable for industrial automation, food processing, and dusty environments. DualVee guides excel in harsh conditions where minimal




