Introduction
This article provides comprehensive information about Marking Machinery.
Continue reading to learn more about:
- Overview of Marking Machinery
- Marking Methods and Their Applications
- Advantages of Marking Processes and Machinery
- And Much More...

Chapter 1: Overview of Marking Machinery
Marking machinery includes industrial tools designed to inscribe texts, images, labels, and codes on various parts and products. Different machines use distinct methods to modify material properties, creating the desired marks. Common processes include stamping, engraving, inking, and etching.

Marking is essential for product identification, traceability, and decoration, making items recognizable by humans and machines like scanners. This reliable process enhances supply chain efficiency and supports marketing efforts.
Upcoming chapters will explore various marking techniques, detailing their machinery, principles, and applications. Choosing the right method depends on material properties, cost, and product value.
Chapter 2: Physical Marking Methods
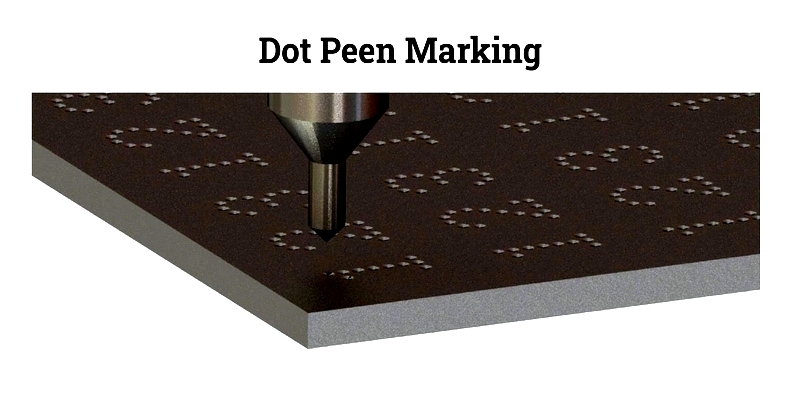
Dot Peen Marking
Dot peen marking uses a carbide pin to engrave small dots that form lines. This low-stress method is ideal for metals and stainless steel, creating permanent, readable marks for traceability. The process uses a coordinate system for precise dot placement, with adjustable parameters for depth and visibility.
This fast, accurate method works on various materials and shapes, producing logos, text, and barcodes. It's widely used in aerospace, automotive, and metal fabrication industries.
Scribe Marking
Scribe marking uses a hardened stylus to create continuous lines. Compared to dot peen, it operates more quietly and offers higher resolution. Guided by CNC systems, it works on various surfaces, including irregular geometries.
This robust method is common in transportation, construction, and aerospace industries for marking metal parts.

Die Marking
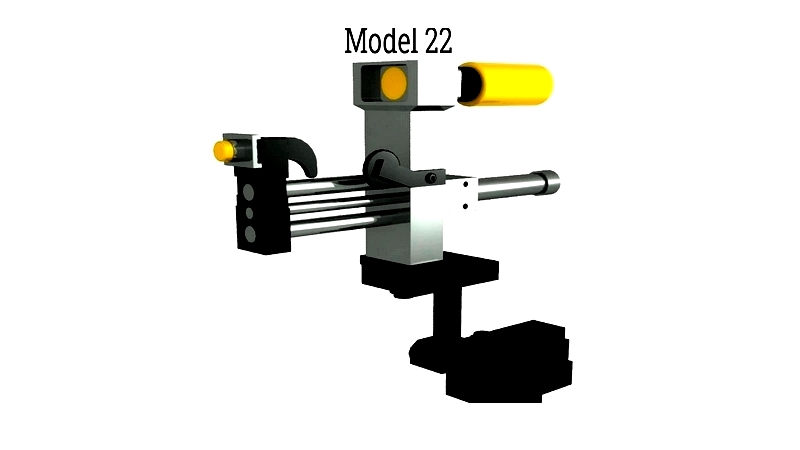
Die marking uses engraved dies to create patterns. It can be ink-based or high-pressure, depending on the application.
Ink-based Die Marking
This method uses specialized inks transferred via flexible dies. It's suitable for fragile materials like glass and ceramics, commonly used for batch coding and labeling.

Examples include:
Reciprocating Coders
These devices print details like expiration dates and batch numbers, used in packaging and pharmaceutical industries.
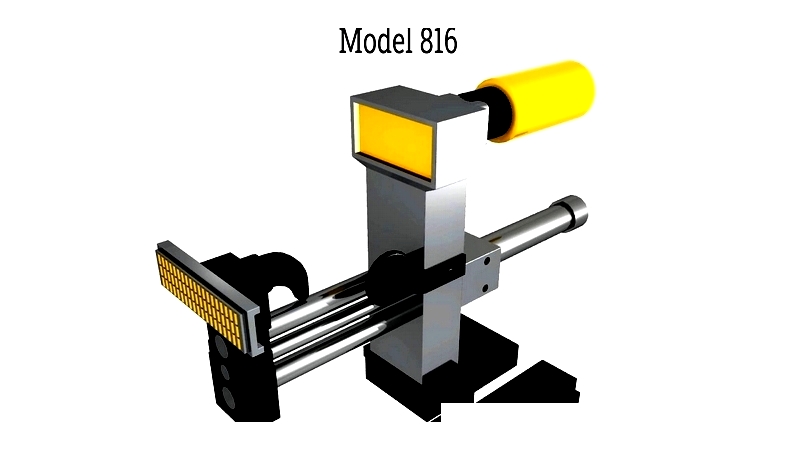

Pad Printers
These machines use silicone pads to transfer ink onto complex surfaces, ideal for electronics and medical devices.

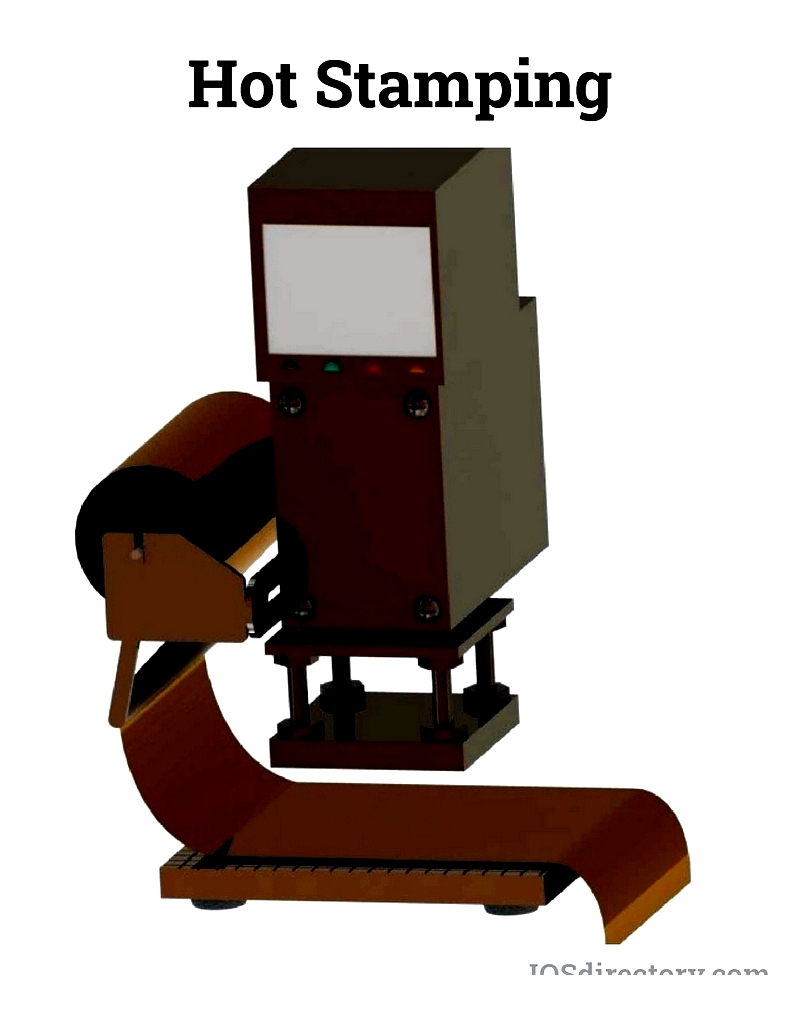
Hot Stamping Machines
Hot stamping transfers foil using heated dies, creating glossy marks for decorative applications.

High Pressure Marking
This method uses force to imprint substrates, creating permanent marks. Equipment includes:
Stamping Machines
These create raised or recessed marks, used for tamper-resistant identification in automotive and defense industries.
Roll Die Marking Machines
These use cylindrical dies for high-throughput marking on metal sheets and bars.

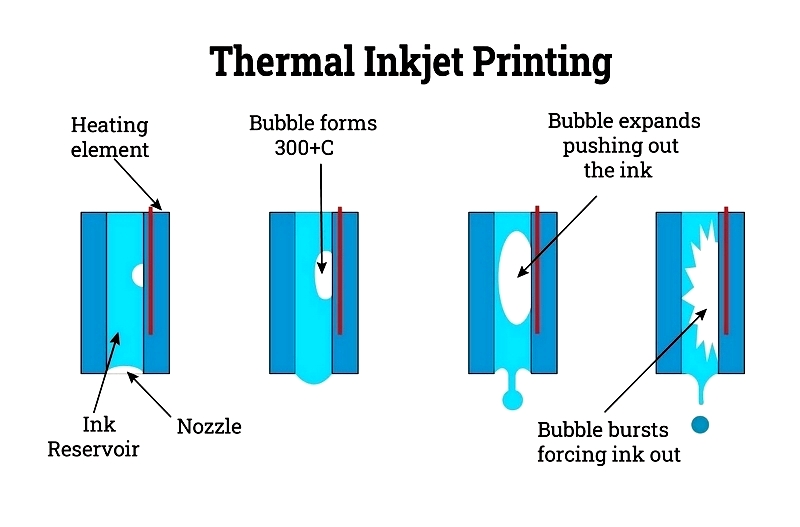
Thermal Inkjet Printing
This non-contact method prints variable data quickly. While cost-effective, the marks are less durable than engraved ones.
Contact and Non-Contact Marking
Marking helps distinguish parts during manufacturing. Invisible UV marks are used for anti-tampering in electronics and aerospace.
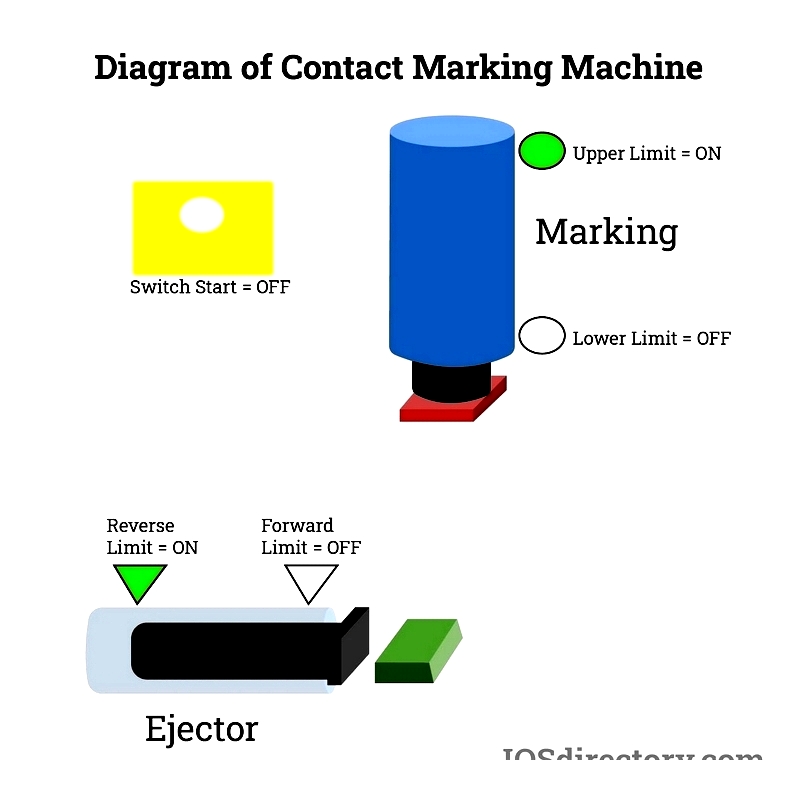
Contact Marking Systems
These use ink reservoirs to mark parts, suitable for metal and plastic components.
Non-Contact Marking System
These spray marks without touching the surface, ideal for textiles and automotive assembly.

Marking Stains
Stains vary by substrate and requirements. Transparent stains dry quickly, while opaque ones offer high contrast.
Chapter 3: Electrochemical Etching
This method permanently marks conductive materials using electrolysis. It preserves material integrity and is approved for aerospace components.
The process uses stencils and electrolytes to create durable marks without mechanical stress.
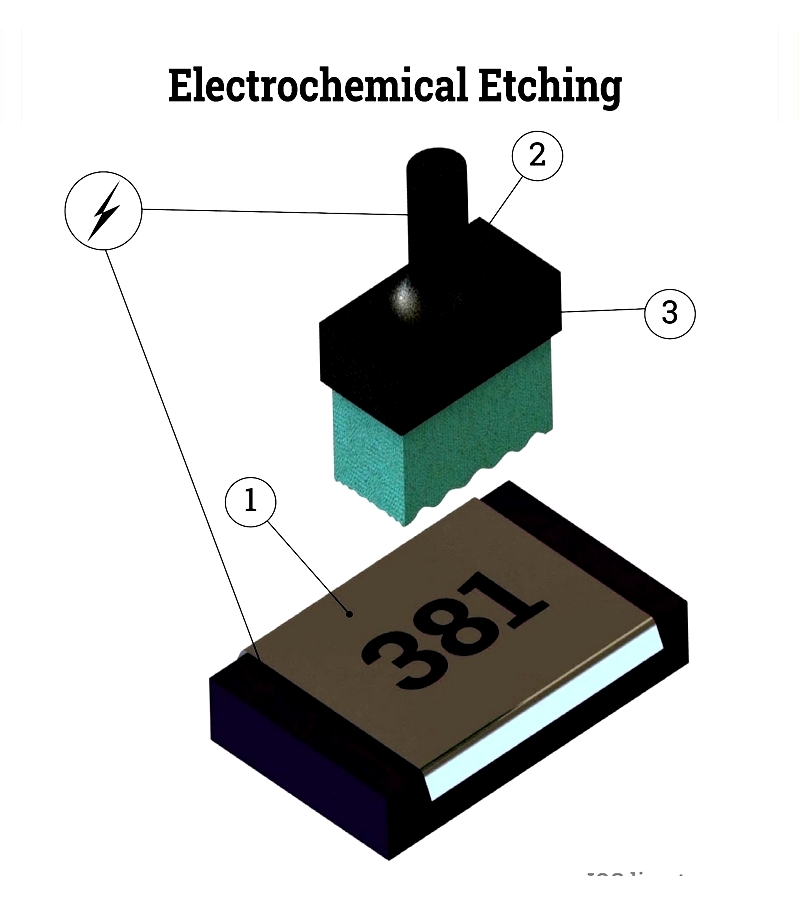
It's versatile, cost-effective, and works on various metals.
Chapter 4: Laser Marking
Laser marking uses beams to create permanent marks without contact. It's precise and works on various materials.
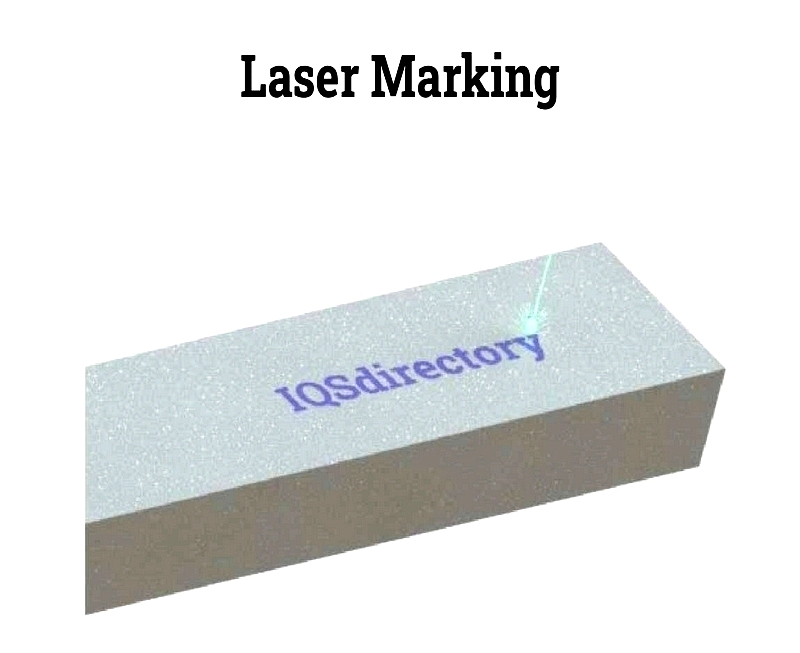
Laser Marking Processes
Different methods include:
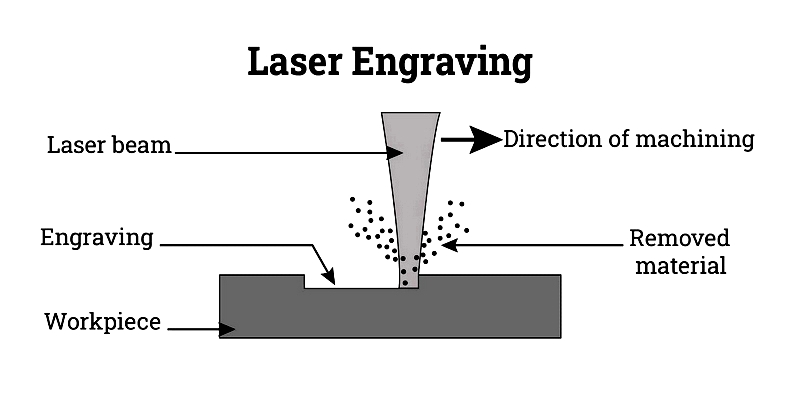
Laser Engraving
Vaporizes material to create deep, durable marks.
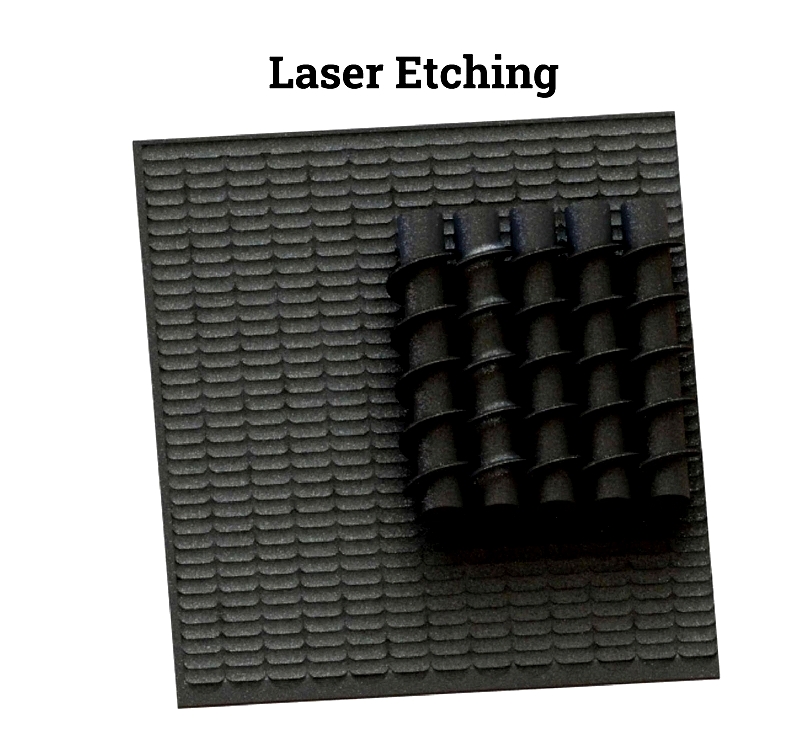
Laser Etching
Melts material to form raised marks quickly.
Laser Annealing
Creates color changes through oxidation, preserving material strength.




