Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of force sensors.
It covers detailed information on various topics including:
- Working Principles of Force Sensors
- Manufacturing Processes for Force Sensors
- Different Types of Force Sensors
- Applications, Benefits, and Limitations of Force Sensors
- And More...
Chapter 1: Understanding the Principle Behind Force Sensors
This chapter examines the mechanics of force sensors, explaining their operation and key selection criteria.
What are Force Sensors?
Force sensors are devices that convert mechanical forces—including weight, tension, compression, torque, strain, stress, or pressure—into measurable electrical signals. These signals quantify force magnitude and can serve as operational indicators or control inputs for machinery. They typically transmit data to displays, controllers, or computer systems.
Although technically distinct from force transducers, the terms are often used interchangeably. Force sensors play crucial roles in power equipment, engineering machinery, industrial automation, and various operational systems. They come in different sizes, capable of measuring forces ranging from grams to tons.

Applications span diverse fields, from household scales and musical instruments to medical devices, automotive systems, and industrial process controls. We'll explore various force sensor types and their working principles.
Principle of Operation of Force Sensors
Force sensors detect applied forces and convert them into measurable outputs. Different sensor types employ unique mechanisms. For example, force-sensing resistors change resistance when force is applied.
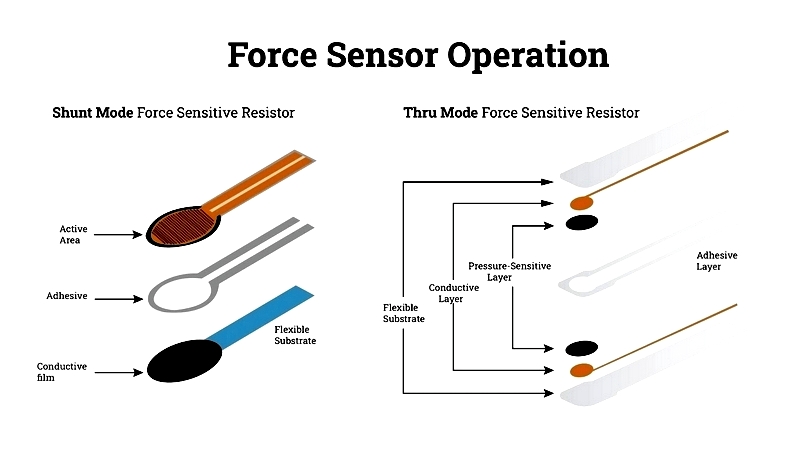
Typically consisting of electrodes and sensing materials, these sensors measure force by detecting resistance changes in force-sensing resistors, which form the basis of most designs.
Force-sensing resistors operate on contact resistance principles. A conductive polymer sheet alters its resistance under force, containing a matrix of conductive and non-conductive particles.
Applied force causes particles to contact sensor electrodes, changing the film's resistance. This change indicates force magnitude, where mechanical pressure modifies electrical resistance to provide measurable data.
Factors to Consider When Choosing a Force Sensor
Force sensors vary in design and application. While Chapter 3 details different types, this section highlights key selection factors to help make informed decisions.
Cost
Cost is a crucial factor in sensor selection, as expensive options may impact project feasibility.
Repeatability
Consider whether measurements can consistently produce identical results under the same conditions. Repeatability indicates a sensor's ability to deliver consistent outputs, even if not perfectly accurate.
Accuracy and Precision
These are critical specifications. Though often confused, they represent different concepts. Understanding the distinction helps determine which is more relevant for your needs.
Environmental Conditions
Select sensors based on operating environments. Temperature and humidity can affect performance in industrial, medical, or automotive applications, potentially impacting accuracy.
Temperature variations may significantly influence sensor outputs, though some models are designed to withstand such changes. Choosing resilient sensors ensures reliable performance.
Durability
Assess a sensor's robustness, lifespan, and resistance to harsh conditions. All sensors have finite lifespans, determined by performance over time or during storage.
Design, materials, manufacturing processes, and environmental factors affect longevity. Durable sensors maintain cost-effectiveness and accuracy under challenging conditions.
Response Time
Select sensors with appropriate response times. Rapid force changes require fast response times, while steady forces may tolerate slower responses.
Sensitivity
Understand your project's specific requirements when selecting sensors. Open load sensors offer high precision and can be customized for various applications.
Form Factor
The required size and shape will significantly influence force-sensing technology selection.
Chapter 2: How Force Sensors Are Manufactured
This chapter details the construction, engineering design, and production of force sensors, essential components in industrial automation, robotics, medical devices, automotive systems, and precision manufacturing. Understanding manufacturing processes helps select optimal products for specific measurement, testing, or control applications.
Construction and Design of Force Sensors
Force sensors, also called load cells or pressure transducers, come in various sizes and configurations for different measurement environments. Each sensor comprises three main components: the sensing element, conversion element, and output circuit. The sensing element, usually made from durable materials like aluminum alloy or stainless steel, translates mechanical force into measurable strain or electrical signals. Material selection affects accuracy, corrosion resistance, and environmental suitability.
The conversion element typically consists of high-precision strain gauges or piezoelectric crystals. Strain gauges, often made from conductive foil, form the core of resistive force measurement. Piezoelectric sensors use crystals like quartz that generate charge when deformed, offering high dynamic response for variable forces.
The circuit section uses enameled wire or advanced PCB layouts. Strain gauge arrays connect in configurations like Wheatstone bridges for high accuracy and linearity. Complex sensors may include up to thirty gauges, improving signal fidelity and supporting multi-axis measurements.
Force sensors provide various standardized outputs for different systems, including analog voltage, current (e.g., 4-20 mA for PLCs), frequency, discrete switches, and digital data. Selection depends on measurement range, sensitivity, linearity, environment, and output compatibility.
For precise, repeatable measurements, sensor circuits use principles like the Wheatstone bridge equation to balance potential differences and compensate for thermal drift. Calibration, temperature compensation, and electromagnetic shielding enhance reliability in real-world conditions.
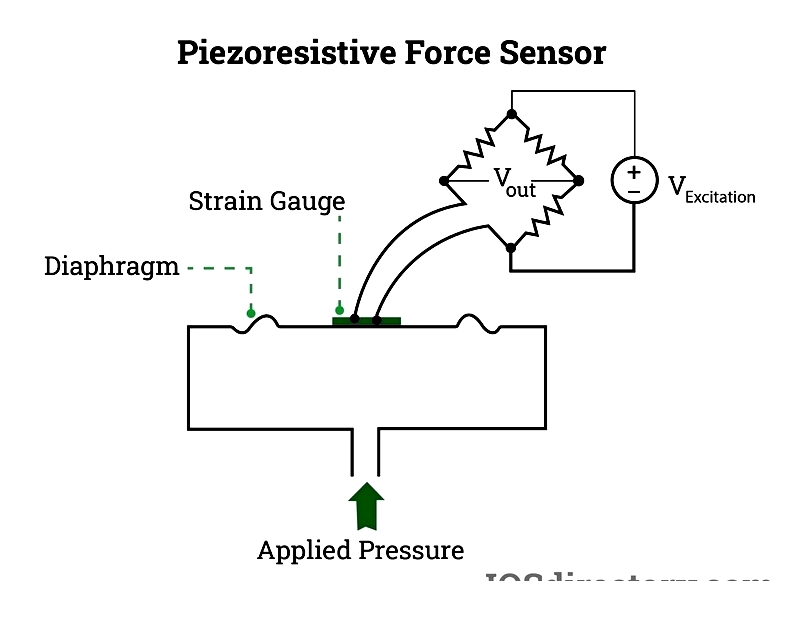
Wheatstone Bridge Circuit
The Wheatstone bridge is fundamental for force and pressure sensor signal processing. Its balanced resistor configuration precisely measures resistance changes corresponding to strain gauge deformations, converting mechanical loads into accurate electrical signals.
Modern operational amplifiers and digital filtering integrate with advanced sensors, including piezoelectric and MEMS-based designs, enabling precise measurement of small force variations for laboratories, industrial systems, and medical instrumentation.
The Wheatstone bridge design includes:
- Two input terminals connected to a stable voltage source
- Two output terminals for differential signal measurement
- Four matched resistors (or strain gauges) in a diamond pattern for maximum sensitivity
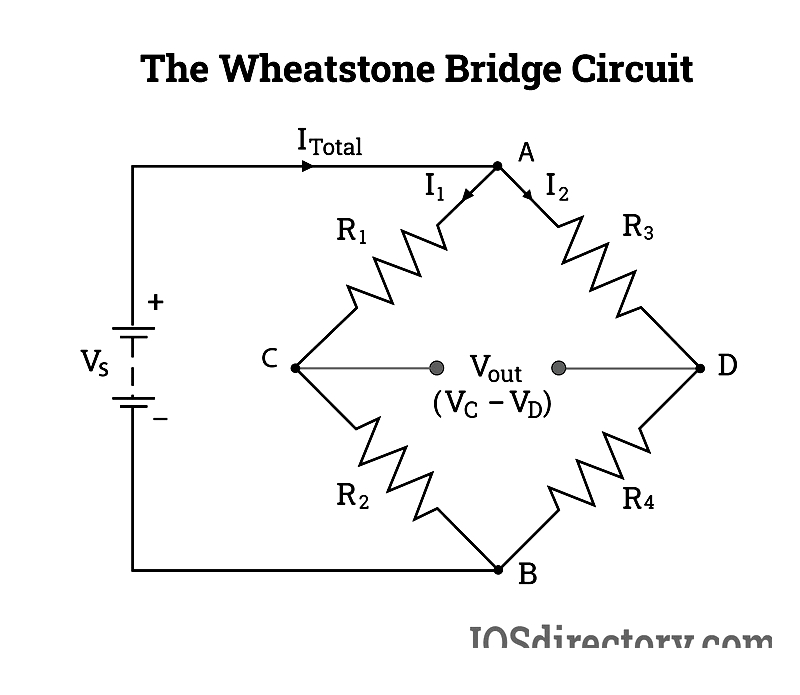
Precise calibration and temperature-compensated resistors maintain accuracy in challenging environments, from material testing to automated production.
Micro-electromechanical Systems (MEMS) Fabrication
MEMS technology has transformed force sensor miniaturization, durability, and cost-efficiency, particularly in consumer electronics, biomedical sensors, and automotive safety. MEMS fabrication uses silicon micromachining and thin-film deposition to create compact, high-precision sensor arrays.
The process begins with silicon nitride deposition on a silicon wafer, followed by front-side etching to define sensor diaphragms. Photolithography and reactive-ion etching pattern nitride for membrane isolation, improving mechanical performance. Silicon oxide deposition protects the substrate, while back-side etching shapes diaphragm regions for pressure sensing.
Anisotropic etching with potassium




