Introduction
This is the most comprehensive online resource about metal channels.
You will discover:
- What metal channels are
- Different shapes of metal channels
- Common applications of metal channels
- Materials used in metal channel production
- And much more...
Chapter 1 – Understanding metal Channels
Wire brushes are tools with sturdy bristles made from durable materials, designed for cleaning and preparing metal surfaces. Their densely packed filaments effectively handle demanding cleaning tasks. These brushes can be manually operated or used with machinery, depending on their design and purpose.
A specialized wire drawn brush offers enhanced durability and strength, with filaments securely fastened through precise manufacturing.
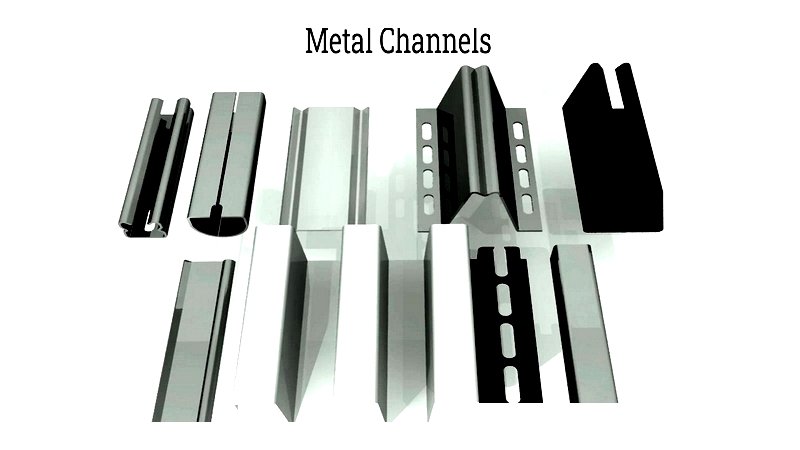
metal channels are roll-formed metal strips shaped into various profiles like tubes, and U, J, or C shapes, widely utilized in industrial settings. Material selection—steel, aluminum, zinc, or brass—depends on specific application requirements. Aluminum is often preferred for its strength, versatility, and corrosion resistance.
In construction, metal channels reduce sound transmission between plasterboard layers, improving acoustic insulation by minimizing vibrations. This demonstrates just one of their many practical applications, valued for their strength and durability.
Chapter 2 – Types of metal Channels
metal channels are crucial structural elements manufactured through high-speed roll forming. This precise process shapes metals into linear channel profiles, allowing custom designs for specific engineering and architectural needs. Their superior load-bearing capacity and design flexibility make them ideal for commercial construction, industrial framing, and product assembly.
The design process starts with a web section flanked by flanges. Roll forming converts metal coils into various channel shapes for specific applications. While C channels are most common, the category includes U channels, hat channels, and J channels—each with versatile configurations suitable for framing, cable management, and architectural facades.
Types of metal Channels
C Channel
C channels, or structural channels, are extensively used in construction and manufacturing. They provide support for buildings, roofs, and ceilings in steel structures, bridges, and shelving systems. Their strength-to-weight ratio, easy installation, and compatibility with various alloys make them popular. The name reflects their C-shaped cross-section.
Manufacturers produce C channels by adding flanges to a U-shaped web, sometimes crimping them for extra rigidity. Available in hot-rolled steel, cold-formed steel, stainless steel, and aluminum, these channels meet diverse load and corrosion resistance requirements. Selection depends on gauge thickness, leg length, web width, and load capacity.

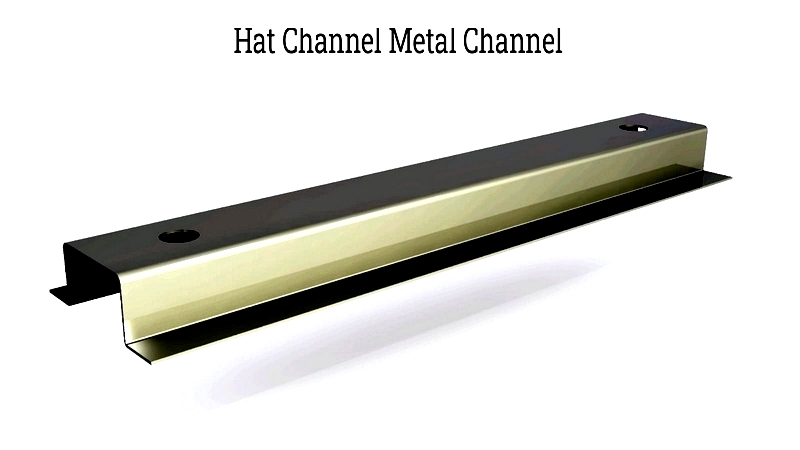
Hat Channels
Named for their hat-like shape, these channels feature a broad base with outward-flaring edges. They're used in wall assemblies, ceiling systems, and masonry facings, offering excellent horizontal support and thermal breaks. Particularly effective in roofing and concrete reinforcement, hat channels come in standard 20-foot lengths or custom sizes, made from galvanized steel, stainless steel, or aluminum.

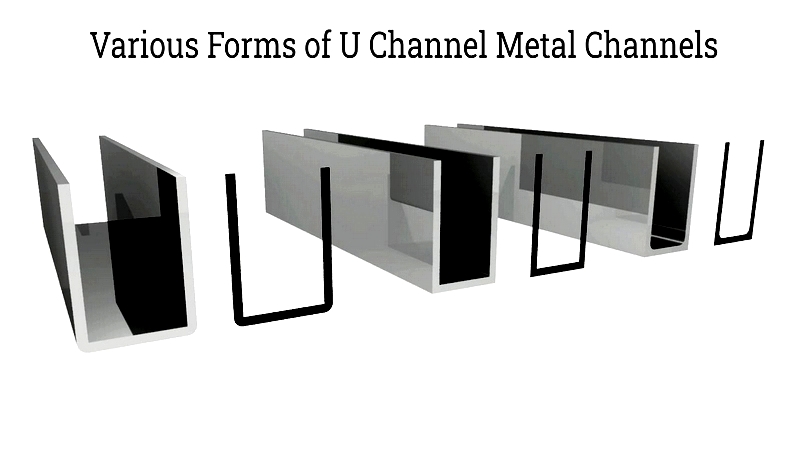
U Channel
U channels have a simple symmetric design with variations including flat-bottom and round-bottom profiles. Their sizes range from under an inch to several feet, tailored to structural needs. Commonly used for edge protection and cable raceways, they're available in galvanized steel, aluminum, and stainless steel, with options for custom features like punch-outs and notches.
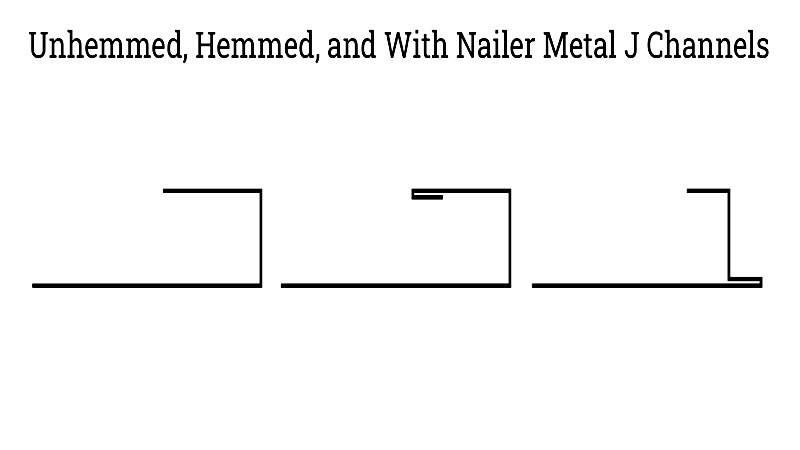
J Channels
J channels feature one longer leg, creating an asymmetrical J-shaped profile. They're ideal for trim work, siding terminations, and framing openings in commercial buildings. Available in hemmed and unhemmed versions, they come in various lengths and finishes to match architectural designs while directing water away from critical joints.
Choosing the Right metal Channel
Selecting the appropriate channel requires considering load requirements, material, corrosion resistance, and environmental factors. Whether you need a steel C channel for heavy framing or an aluminum hat channel for coastal projects, consulting manufacturers ensures optimal performance. Look for suppliers offering value-added services like powder coating and custom fabrication, prioritizing those with ISO certification and proven quality standards.




