Introduction
This article offers comprehensive information about load cells and their applications.
You will learn about:
- What a Load Cell is
- The Wheatstone Bridge
- Types of Elastic Elements or Spring Materials
- Load Cell Shapes and Profiles
- Air Tightness
- And much more...
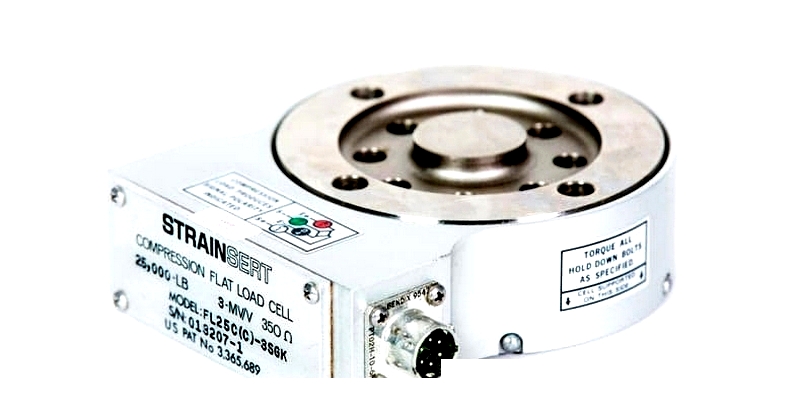 Compression Load Cell from Strainsert
Compression Load Cell from Strainsert
Chapter 1: What is a Load Cell?
A load cell is a transducer that converts tensile and compressive forces into measurable electrical signals. Typically constructed with a spring element and strain gauges, load cells are made from durable materials like steel or aluminum, providing strength with minimal elasticity.
The strain gauge load cell is the most common type, while other variants include pneumatic and hydraulic models. Pneumatic load cells suit hazardous environments, and hydraulic ones work well where power access is limited. All types transform mechanical force into digital data for easy monitoring and recording.
While internal structures vary by application, all load cells are designed to deliver precise measurements of mechanical forces or weights. They are categorized based on measurement accuracy and load capacity.
Different load cell types include:
- Strain gauge
- Capacitive force
- Piezoelectric
- Vibrating wire
- Magnetic
- Hydraulic
- Pneumatic

Chapter 2: The Principle Behind Load Cells
Load cells are essential force measurement devices used across industrial applications, from material testing to automation. Their operation relies on materials that deform predictably under force, with sensors detecting this deformation to generate proportional electrical signals. Most output millivolt-range signals that require amplification for accurate interpretation.
Common Transducers in Load Cells
Modern load cells employ various transducers, each using different physical principles to convert mechanical loads into electrical signals. Strain gauge load cells are the most prevalent due to their accuracy and versatility, though capacitive, piezoelectric, vibrating wire, and magnetic transducers also play important roles.
Strain gauge transducers work by measuring resistance changes in deformed conductors. These load cells excel at measuring static and dynamic forces like tension, compression, and bending with high precision.
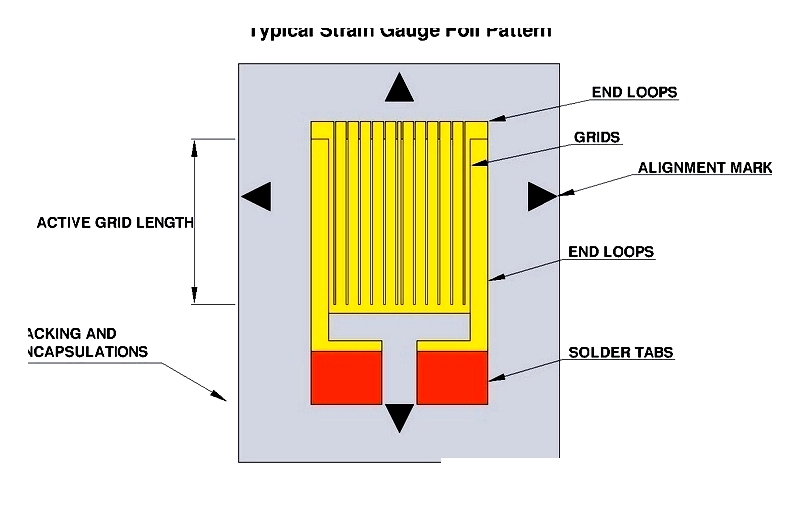
In these load cells, foil strain gauges bond to metal elements. When force is applied, the gauges deform with the material, changing resistance proportionally to the force. This change is measured using a Wheatstone bridge for accurate detection.
Capacitive force transducers measure changes in capacitance between plates separated by a dielectric material. These sensors are highly sensitive to small displacements, making them ideal for precise low-force measurements.
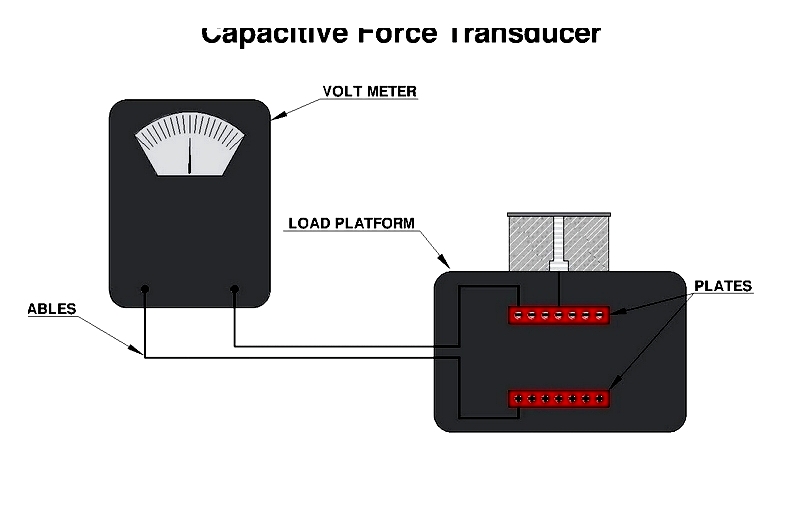
When force is applied, the dielectric compresses or expands, altering the capacitance between plates. This change provides a precise measurement of the applied force.
Piezoelectric transducers use materials that generate electrical charge when mechanically stressed. These load cells are ideal for dynamic measurements due to their fast response times.
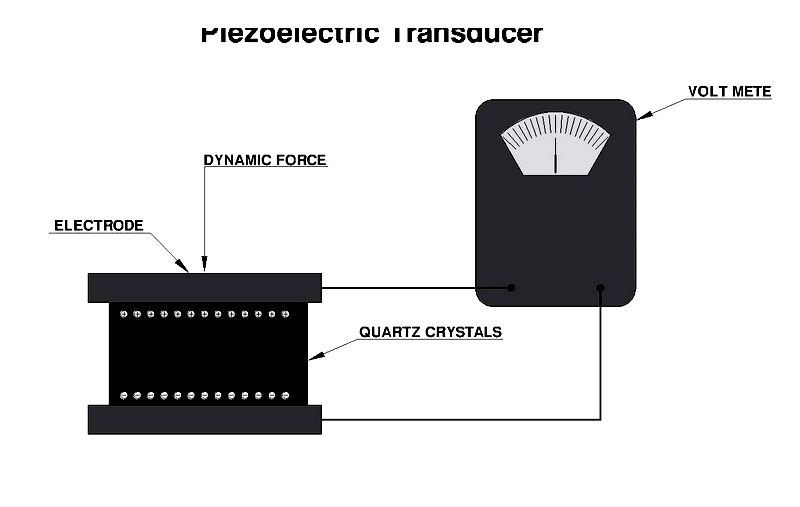
Common in vibration analysis and impact testing, piezoelectric load cells provide high-speed measurements with excellent sensitivity.
Vibrating wire transducers measure force by detecting changes in a wire's vibration frequency. Increased tension raises the frequency, while decreased tension lowers it.
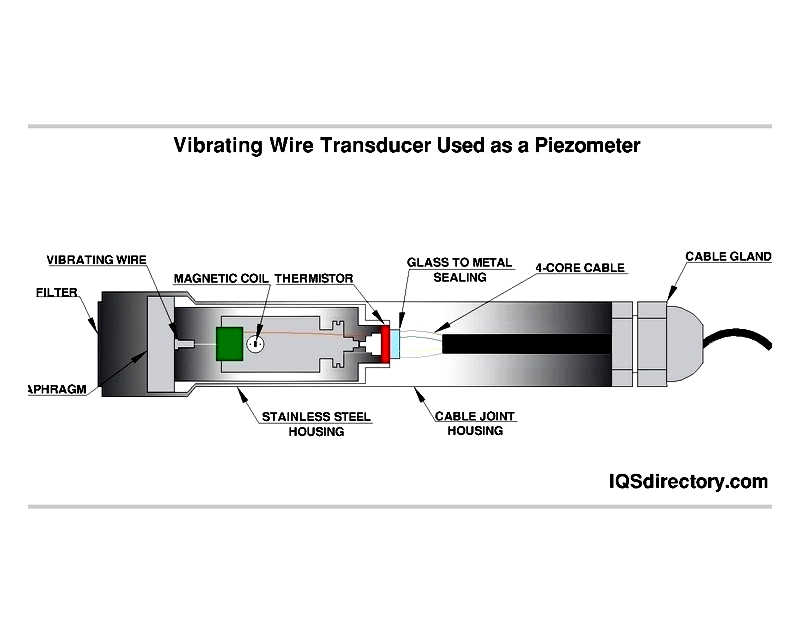
These transducers are valued in geotechnical applications for their stability and resistance to electromagnetic interference.
Magnetic Transducer (Pressductor Load Cell)
Magnetic transducers like the Pressductor use magneto-elastic effects to measure force. Changes in a ferromagnetic core's permeability under load produce measurable magnetic flux variations.
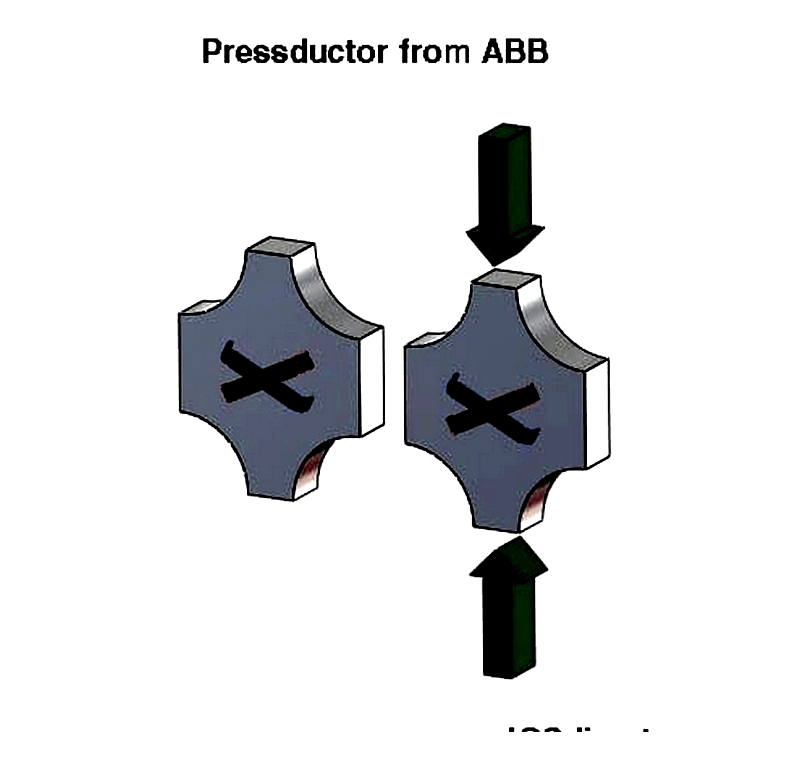
These load cells are particularly useful in harsh industrial environments due to their durability and interference resistance.
Hydrostatic Pressure Transducers
Hydraulic and pneumatic load cells measure force through fluid pressure changes. They're ideal for hazardous environments where electrical components are impractical.
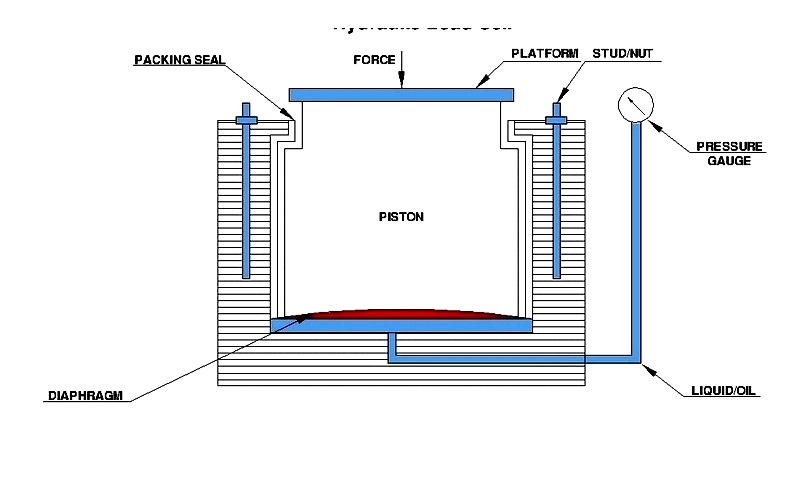
Common applications include silo weighing and tank monitoring where maintenance-free operation is required.
Selecting the right load cell involves considering force characteristics, accuracy needs, environmental conditions, and integration requirements. Modern load cells support digital calibration and industrial communication for seamless system integration.
Chapter 3: The Wheatstone Bridge
The Wheatstone bridge is an electrical circuit for precise resistance measurement. By balancing two bridge legs—one containing an unknown resistor—it accurately determines resistance values. The circuit consists of four resistors: two known, one unknown, and one variable, powered by a DC source with a galvanometer for balance detection.
In the bridge configuration, resistors connect at points A, B, C, and D. Voltage is applied between A and B, while the galvanometer connects C and D. When balanced, no current flows through the galvanometer, enabling precise measurements.
Modern applications often use the variable resistor as a strain gauge. In load cells, resistance changes from applied force are detected and converted to electrical signals, making the Wheatstone bridge essential for accurate sensor readings.
Strain gauge load cells typically use a full-bridge circuit with four gauges. When force is applied, all gauges deform, changing resistance proportionally. The bridge detects these changes, converting mechanical force to electrical signals.
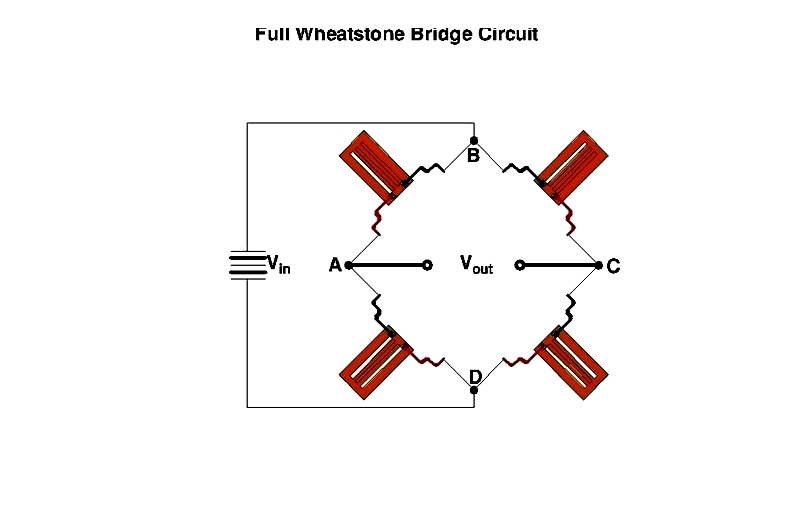
Alternative configurations like half-bridge or quarter-bridge circuits are used when higher sensitivity is needed. These arrangements amplify output voltage for better signal quality.
The Wheatstone bridge excels at detecting small resistance changes while rejecting noise and thermal drift. Its ratio-based measurement provides inherent stability, making it ideal for demanding environments.
Key advantages include:
- High sensitivity for small resistance changes
- Temperature compensation through matched components
- Noise rejection in electrically noisy environments
- Wide application in instrumentation and automation
Choosing the right bridge configuration depends on application requirements, sensor type, and environmental factors. Understanding the Wheatstone bridge is essential for accurate force measurement and signal conditioning.




