Introduction
This article provides an in-depth exploration of AC motors and their applications.
You will learn about various topics including:
- What an AC Motor is
- How AC Motors Work
- Different Types of AC Motors
- Common Applications of AC Motors
- And more...
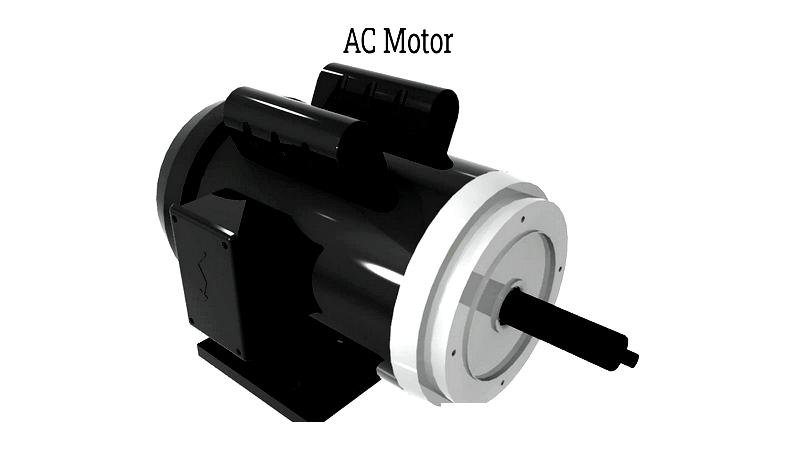

Chapter One – What is an AC Motor?
An AC motor, or alternating current motor, is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical motion. It consists of a stationary stator with a coil powered by alternating current and a rotating rotor. AC motors are classified as either single-phase or three-phase, with three-phase motors typically used for industrial power applications and single-phase motors for smaller tasks.
There are two main types of AC motors: synchronous and induction. Synchronous motors rotate at the same speed as the current frequency, using multiphase AC electromagnets to create a moving magnetic field. Induction motors, also called asynchronous motors, only require stator excitation. The stator's magnetic flux induces current in the rotor's shorted coil, producing torque and rotation.
AC motors are versatile and efficient, operating quietly in various applications. They power devices like pumps, water heaters, garden tools, ovens, off-road vehicles, and many other appliances and machines. Their adaptability makes them ideal for diverse uses.
AC motors feature a simple design with copper-wound stators that generate rotating magnetic fields. Induction motors meet IE3 and IE4 standards, which define global efficiency and performance requirements.
Chapter Two – How AC Motors Work
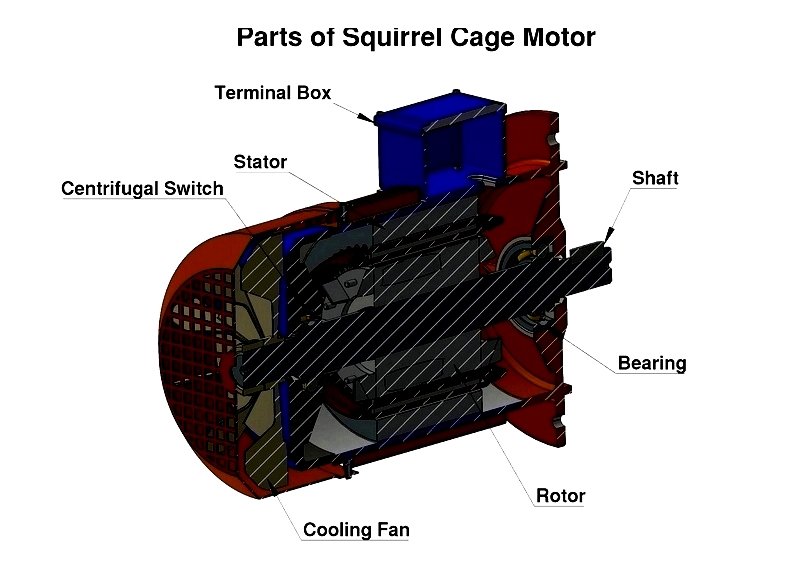
An AC motor has two main components: the stationary stator and the rotating rotor attached to the motor shaft. Together they create rotating magnetic fields essential for operation. The stator produces these fields when alternating current flows through its windings.
In AC motors, the windings serve as both armature and field winding. When AC voltage is applied to the stator, it generates a magnetic field rotating at synchronous speed. This field induces voltage in both stator and rotor windings, creating electromagnetic induction that converts electrical energy into mechanical rotation.
How AC Motors Work
AC motors come in various designs including single-phase, three-phase, brake, synchronous, and asynchronous models. Their differences often relate to intended applications, from household appliances to industrial machinery. Single-phase motors power devices like fans and small pumps, while three-phase motors drive commercial equipment such as conveyors and HVAC systems.
The electrical supply's phase configuration is a key differentiator. Residential settings typically use single-phase power for low-voltage needs, while industrial operations rely on three-phase power for high-torque applications. This affects both performance and motor selection.
Most AC motors are induction motors that use electromagnetic induction to generate torque. The stator's rotating field induces current in the rotor without direct electrical connection. Advanced options like servo motors and VFD-compatible motors offer greater speed and torque control.
Key Benefits and Applications of AC Motors
AC motors are valued for their simplicity, durability, and energy efficiency. They require minimal maintenance, operate quietly, and work well with automated controls. These motors are widely used in manufacturing, transportation, HVAC systems, water treatment, and renewable energy applications.
Start Up
AC motor starting methods impact performance and longevity. Basic methods include contactors and manual starters. Contactors allow remote startup, while manual starters connect motors directly to full voltage, causing high initial current draw.
Star-delta starters reduce inrush current in large three-phase motors. They begin in star configuration for reduced voltage, then switch to delta for full power operation. This method improves performance and extends equipment life.
Auto transformer starters apply reduced voltage during startup, limiting torque. Their adjustable taps enable customized current control, making them suitable for large industrial motors.
Rotor impedance starters work with wound rotor motors, using external resistors for precise speed control. They provide high starting torque but require more space and cost more than other options.
Single-phase motors need auxiliary windings and capacitors to start, as their pulsating fields can't self-start. Shaded pole motors offer simple, low-cost starting for small devices.
Modern soft starters and VFDs provide electronic control over acceleration, reducing electrical surges and mechanical wear. By adjusting voltage and frequency, they optimize efficiency and integrate with automation systems.
important Startup Considerations
- Motor size and application: Large loads benefit from reduced-voltage starting to prevent power issues.
- Energy savings: VFDs can significantly reduce energy use in variable load situations.
- Safety and protection: Modern starters include overload and thermal protection.
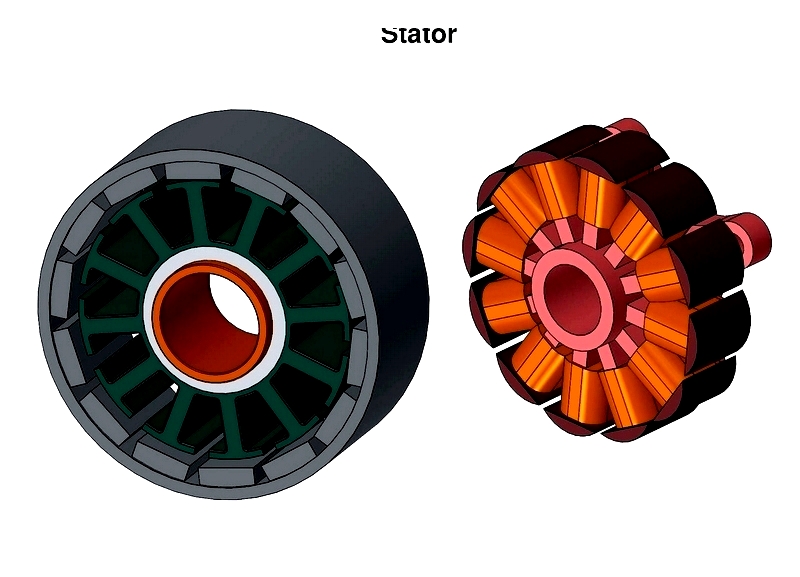
Stator
The stator forms the foundation for AC motor operation. Its laminated steel core minimizes energy loss, while copper windings generate the rotating field. Three-phase motors space windings 120° apart for balanced fields. The housing dissipates heat through cooling fins or fans, ensuring reliable operation under heavy loads.
Industrial stators often include temperature sensors and protection devices for harsh environments. Their robust design handles both dynamic and static loads efficiently.

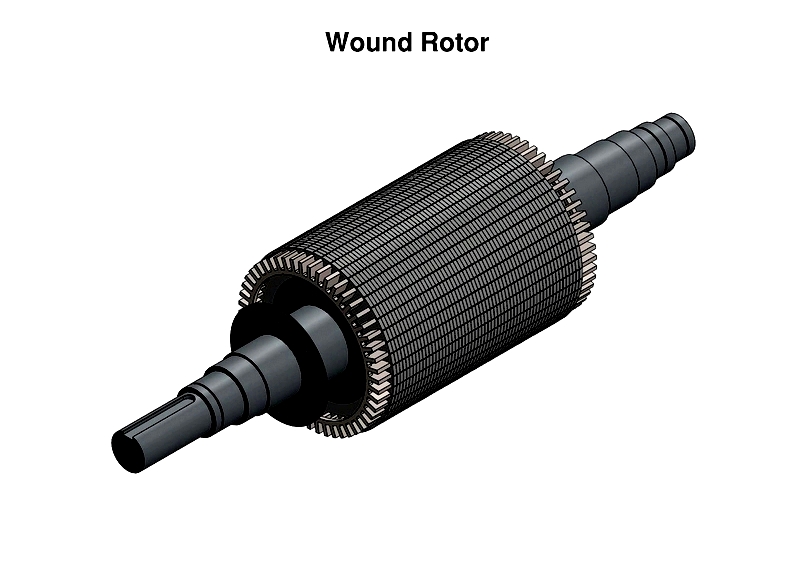
Rotor
AC motor rotors are energized by induction without direct power connection. The two main types are squirrel cage and wound rotors.
Squirrel cage rotors are simple, durable, and low-maintenance. They contain conductive bars in an iron core, short-circuited by end rings. This design suits various applications from pumps to compressors.
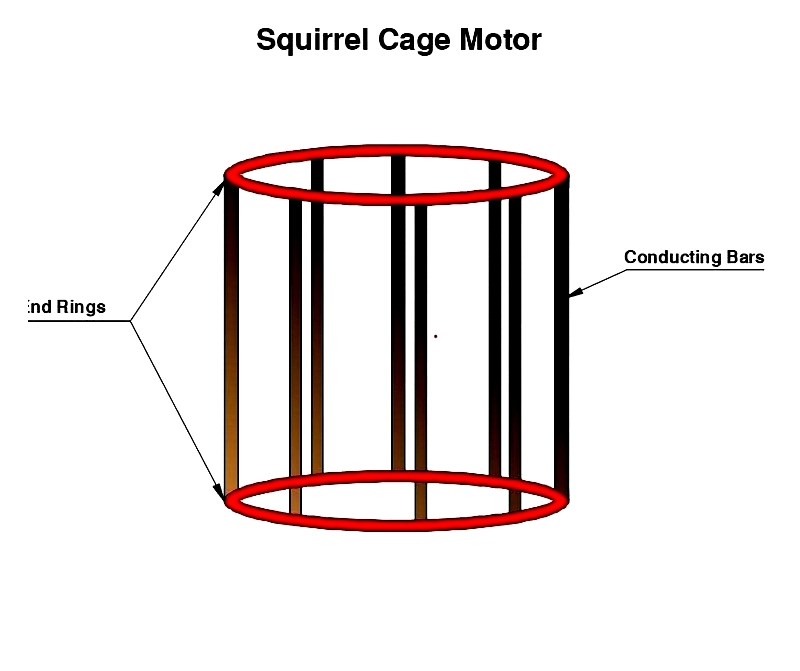
The stator's field induces current in the rotor bars, creating rotation. The rotor always lags slightly behind the stator's speed - a phenomenon called slip that enables torque production.
Wound rotors feature wire windings connected via slip rings. They provide precise speed and torque control for demanding applications like cranes and mills. External resistance adjustment enables smooth starts and energy efficiency.
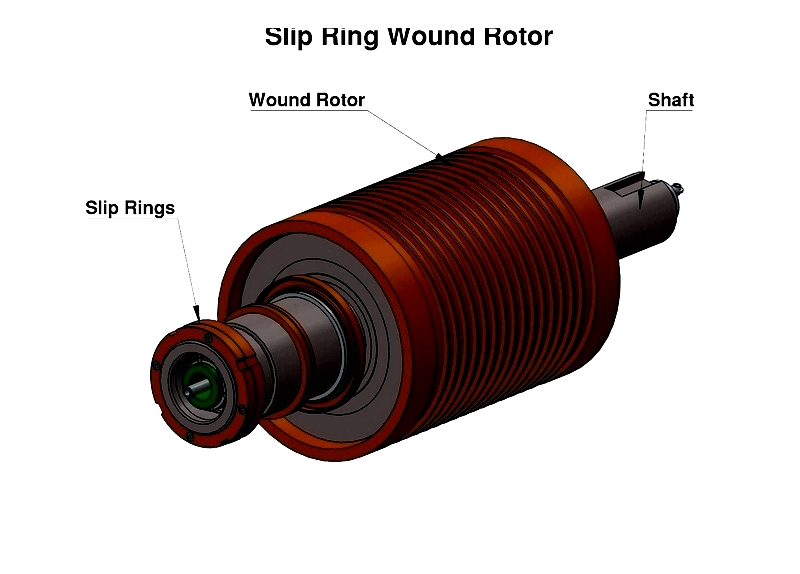
Wound rotor motors work asynchronously, with speed differences between rotor and stator fields enabling advanced control. Their slip ring design integrates with automation systems for optimized performance.

AC Motor Selection Tips
- Application type: Choose single-phase or three-phase based on power needs.
- Efficiency rating: Select IE3/IE4 motors for energy savings.
- Speed control: Consider VFD-compatible motors for variable speed applications.
- Environmental protection: Match motor enclosures to operating conditions.
Understanding AC motor construction, operation, and selection criteria helps ensure optimal performance for both residential and industrial applications. For specialized needs, consult manufacturers for guidance on installation and maintenance.




