Introduction
This article provides comprehensive insights into urethane casting and its applications.
You will learn about:
- The definition of urethane casting
- Its working principle
- The urethane casting process
- Polyurethane's mechanical properties
- Materials used in urethane casting
- Advantages of urethane casting
- Practical applications of cast urethanes
Chapter 1: Understanding Urethane Casting
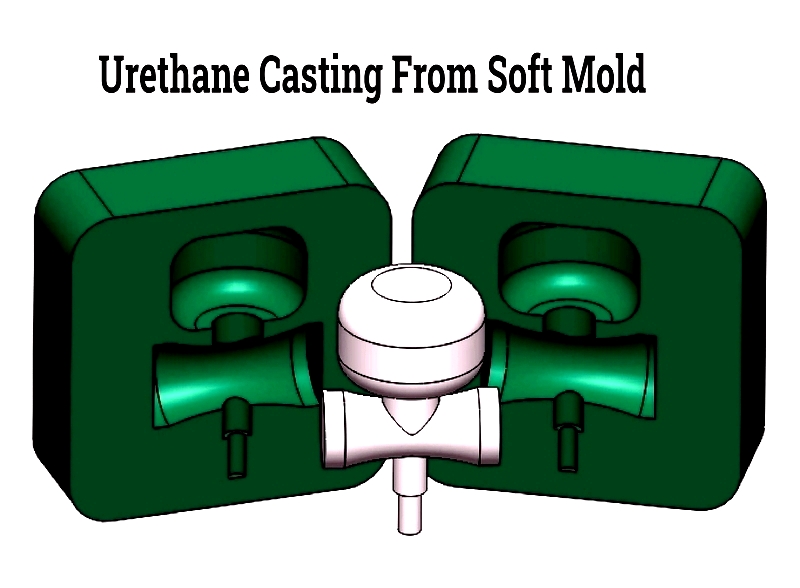
Urethane casting is a manufacturing process that involves injecting polyurethane and other additive resins into flexible silicone elastomer molds. Unlike injection molding, this method doesn't require rigid metal molds. Since silicone molds wear out relatively quickly, urethane casting is ideal for short runs and low-to-medium volume production. It offers a cost-effective and faster alternative to metal molds while maintaining high-quality output.
Castable polyurethane, a specific type of polyurethane, can be engineered into advanced, high-performance products. Its mechanical properties range from soft and flexible to hard and rigid, depending on the formulation.
Key Differences Between Urethane Casting and Injection Molding
While both urethane casting and injection molding produce plastic and polymer products, they differ significantly in materials, production methods, and cost-effectiveness.
Injection molding is primarily used for high-volume production of thermoplastics. The process involves melting plastic pellets and injecting them under high pressure into mold cavities, making it perfect for mass-producing identical items like automotive components or consumer products.
Urethane casting, however, is better suited for low-to-medium volume production, particularly for prototypes, small batches, or custom parts with complex geometries. This method uses liquid polyurethane or silicone that's poured into molds and cured at room temperature, offering an economical solution for small production runs requiring design flexibility.
Injection molding excels in large-scale production with minimal design variations, while urethane casting is ideal for smaller quantities and intricate, customized components. Both processes serve distinct production needs effectively.
Chapter 2: The Urethane Casting Process
Urethane casting, or polyurethane casting, is a versatile rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing technique for producing high-quality plastic parts. The process involves four key chemical components: polyol compounds, diisocyanate compounds, chain extenders or curatives, and performance-enhancing additives. The prepolymer resin formulation—a blend of polyol and diisocyanate compounds—along with curatives, determines the mechanical properties and durability of the final product. Additives improve various characteristics including curing time, machinability, appearance, surface finish, color, flexibility, abrasion resistance, dimensional stability, and UV protection. However, precise measurement of additives is crucial as excessive amounts can weaken structural integrity.
Managing the coefficient of friction (COF) is essential in urethane molding, as it affects how plastic materials interact. High COF can cause manufacturing problems and impact part performance. Manufacturers often use slip additives like acid amides, erucamide, and oleamide to reduce friction during demolding and improve part ejection. Erucamide provides long-lasting lubrication, while oleamide offers immediate slip properties.
The polyurethane reaction creates strong, flexible polymer chains by combining polyol (with terminal alcohol groups) and diisocyanate (with reactive isocyanate end groups). This reaction produces molecules that can further extend polymer chains when combined with chain extenders containing hydroxyl or amine groups. The exothermic nature of this reaction requires careful temperature control to prevent defects like bubbles or warping.

Urethane casting employs three main processing methods: single shot, prepolymer, and quasi-prepolymer techniques. The single shot method mixes all components separately before combining them and injecting into the mold. The prepolymer method partially reacts polyols and diisocyanates beforehand for better heat management and surface finish. The quasi-prepolymer technique reduces mixture viscosity and processing temperatures, making it suitable for complex or large parts.
Modern urethane casting is widely used for rapid prototyping, low-volume production, and bridge manufacturing across industries like automotive, aerospace, consumer goods, medical devices, and electronics. It allows production of custom parts with properties similar to injection-molded components without the high costs or long lead times of traditional tooling.
For optimal results, manufacturers use advanced design software to refine part geometry, select appropriate materials, and control processing conditions. Factors like shrinkage rate, mold release agents, and post-curing processes significantly impact the quality and performance of urethane cast products.




