Introduction
This article covers everything you need to know about boiler rentals and their significance.
You'll discover:
- What a Boiler Rental is
- Reasons to Rent a Boiler
- Types of Boiler Rentals
- How to Select the Right Rental Boiler
- And much more...
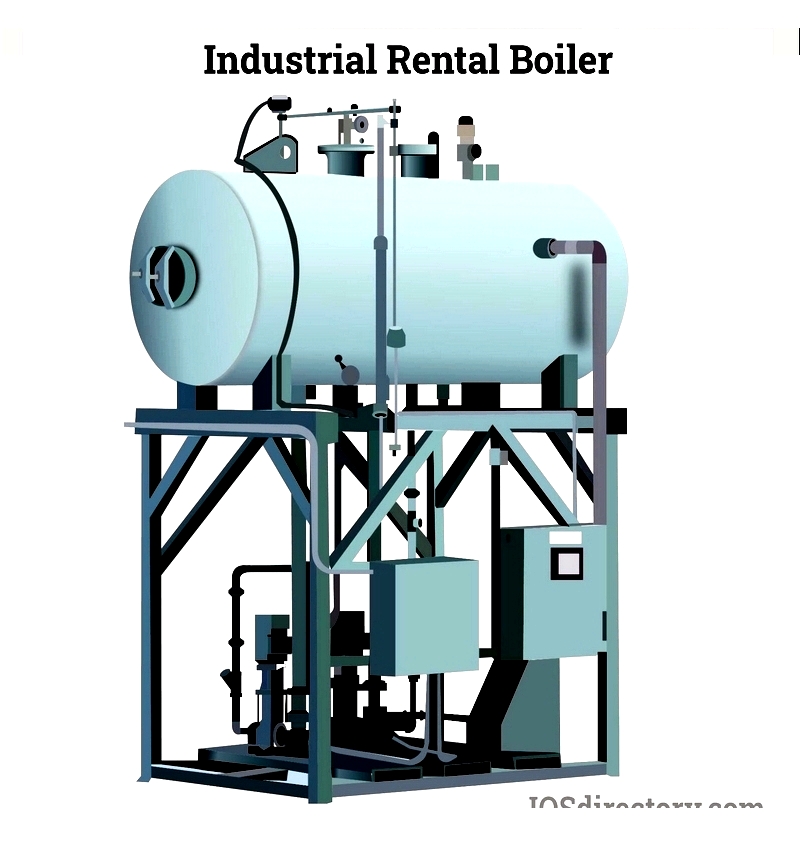
Chapter One: Understanding Boiler Rentals
Manufacturers provide boiler rental services to help industrial clients during emergencies, peak demand periods, or as a cost-efficient long-term solution. Available rental boilers range from small, forklift-movable units to large-scale systems. Rental companies streamline the process, enabling boiler operation within 48 hours.
Industries rent boilers for various needs, including replacing outdated equipment, temporary solutions during upgrades, or meeting increased production demands. For over fifty years, manufacturers have expanded offerings to assist clients with urgent repairs, unexpected breakdowns, or rapid expansion. Renting an industrial boiler provides practical access to high-quality equipment tailored to specific applications.
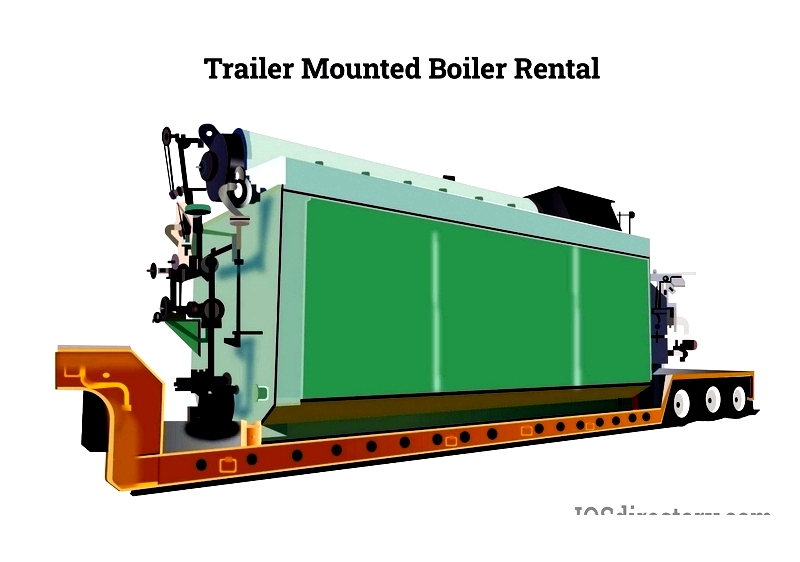
When industrial boilers fail or underperform, companies explore alternatives. While purchasing new equipment is an option, renting allows businesses to evaluate all possibilities while gaining immediate access to efficient boilers.
Chapter Two: Reasons to Rent an Industrial Boiler
Four primary factors drive boiler rentals: supplemental capacity, emergencies, planned outages, and budget considerations. Manufacturers address these needs through specialized rental services, offering solutions for temporary or long-term requirements across various industrial scenarios.
Supplemental Capacity
During peak demand, companies may require additional boiler capacity. Rental boilers provide quick, reliable solutions, often becoming operational within 48 hours. Many facilities keep rental boilers on standby to prevent production interruptions and maintain steam supply.
Emergency Situations
Emergencies like natural disasters or equipment failures create urgent boiler needs. Rental providers offer rapid response, expert assessment, and customized solutions to restore steam generation quickly, particularly in critical industries like healthcare and food processing.
Despite maintenance efforts, all facilities experience downtime. When unexpected failures occur, certified boiler manufacturers can quickly provide rental units to minimize operational impact.
Reduced Downtime
Renting boilers during maintenance or repairs prevents production halts. Mobile or trailer-mounted systems integrate seamlessly, reducing financial losses and ensuring customer satisfaction through continuous operations.
Cost-Effectiveness
Renting avoids large capital investments and maintenance costs, offering financial flexibility. Rental agreements accommodate short-term needs or long-term projects, with predictable rates and access to efficient technology.
Reputable providers ensure regulatory compliance, energy optimization, and 24/7 support, helping businesses adapt to changing demands while maintaining production.
Additional Considerations
Key rental factors include fuel type, capacity requirements, emissions compliance, and installation logistics. Expert guidance ensures proper system selection and integration with existing infrastructure for business continuity.
Chapter Three: What is a Boiler?
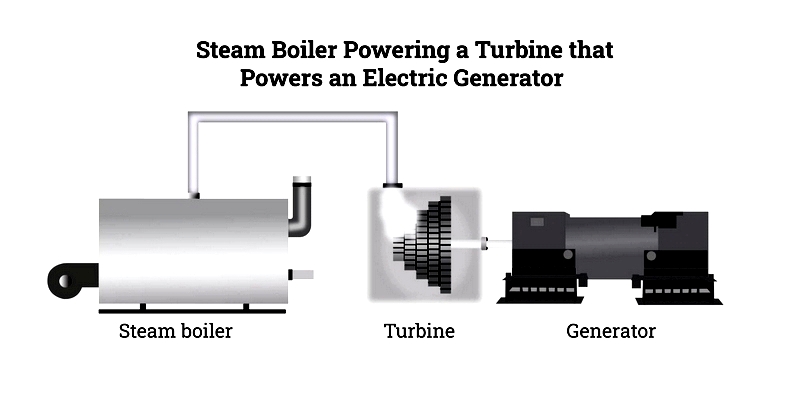
An industrial boiler is engineered equipment that heats fluids to produce steam or vapors for manufacturing, processing, and power generation across various industries. Unlike residential models, industrial boilers meet rigorous production demands.
How industrial boilers work: They heat fluids to generate steam for heating, sterilization, or power generation. Rental boilers support operations during maintenance or outages, offering efficient, rapidly deployable solutions with environmental benefits.
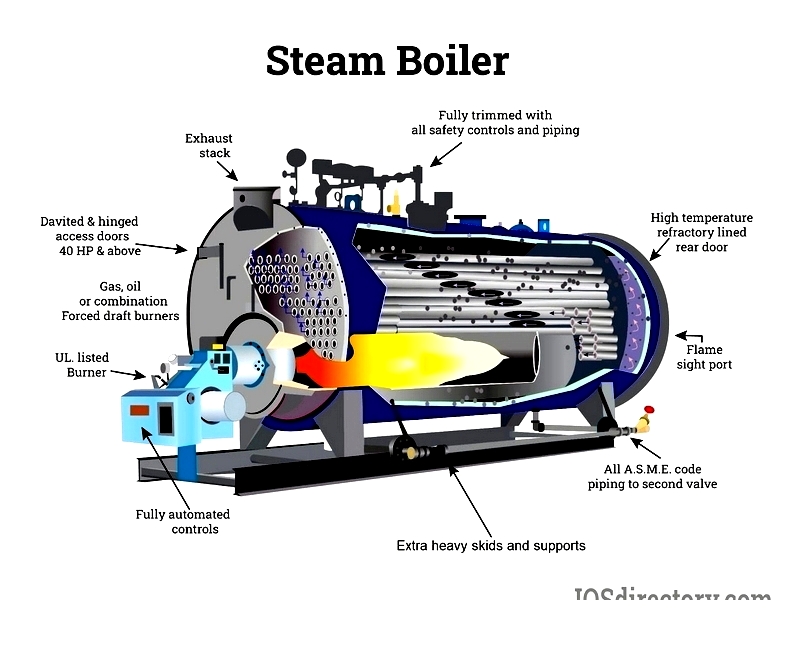
While electricity serves commercial needs, industrial-scale operations benefit from rental boilers' cost efficiency. Modern high-efficiency models minimize fuel use and energy loss, supporting sustainable operations and preventing costly downtime.
Parts of an Industrial Boiler
Though designs vary by application, industrial boilers share core components that ensure safe, efficient operation while meeting regulations.
Key elements include the burner, combustion chamber, heat exchanger, steam drum, and mud drum, each contributing to performance and compliance.
Burner
The burner mixes fuel and air for controlled combustion, with technologies varying by fuel type and emissions requirements.
Combustion Chamber
This steel or cast iron component withstands extreme temperatures where fuel burns to produce heat.
Heat Exchanger
Transfers heat efficiently, with economizers improving performance by preheating water with waste heat.
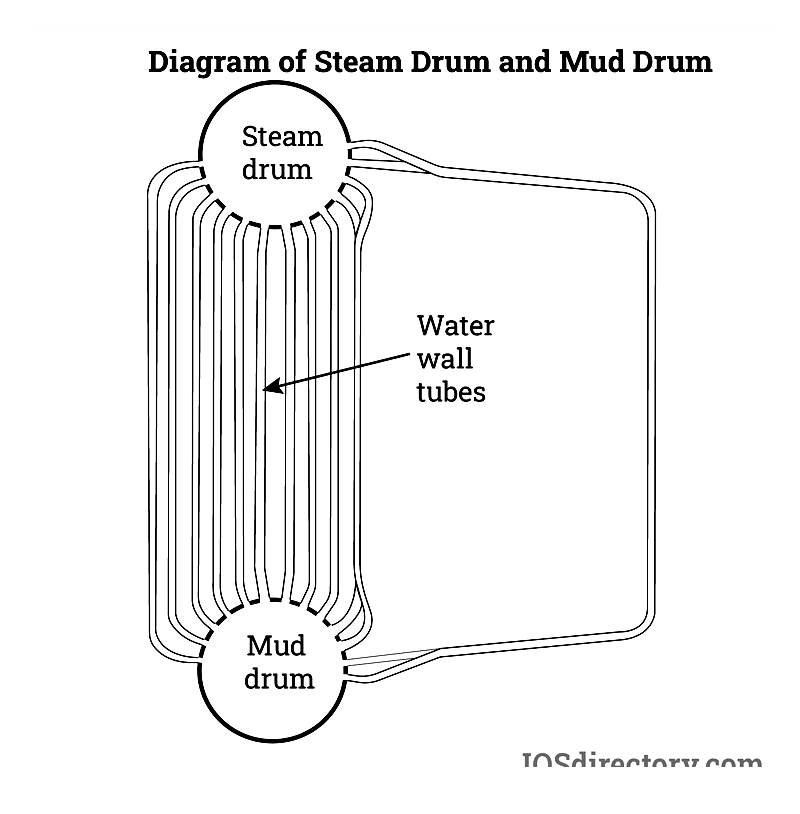
Steam Drum
Separates steam and water, constructed from durable high-carbon steel for pressure resistance.
Mud Drum
Collects sediment for removal during maintenance, preserving efficiency and extending boiler life.
Selecting rental boilers involves considering process needs, fuel type, capacity, and regulations. Boilers are classified by pressure, capacity, efficiency, and emissions for tailored solutions.
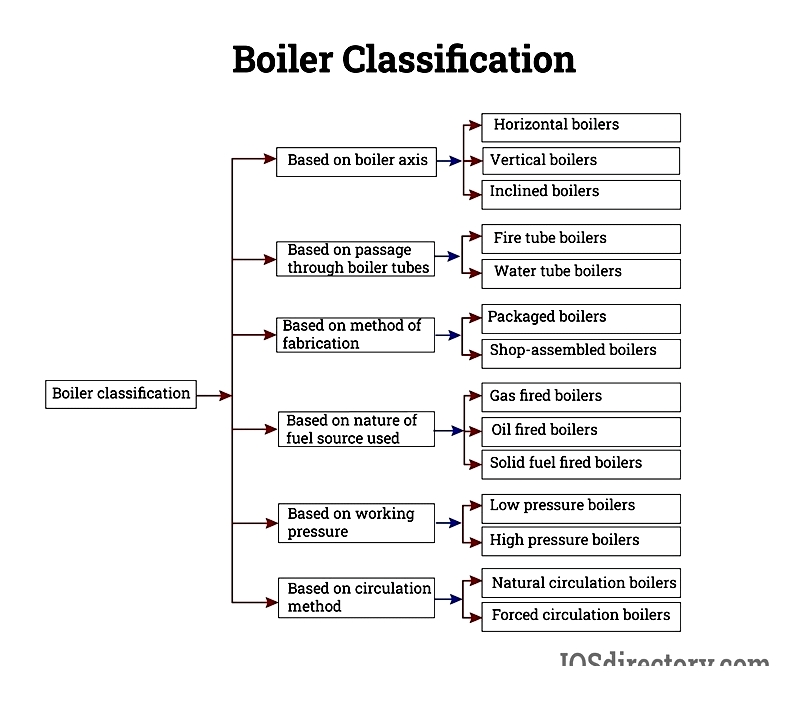
Boiler Classifications
Understanding boiler types ensures proper selection for specific requirements regarding steam, pressure, budget, and space.
- Fire Tube Boilers – Cost-effective for small/medium operations with low-medium pressure needs.
- Water Tube Boilers – High-pressure solutions for large-scale applications with superior efficiency.
- Electric Boilers – Emission-free operation ideal for regulated environments.
- Condensing Boilers – Ultra-efficient (98%) gas-powered models reducing emissions and costs.
- Oil-Fired Boilers – Backup solutions where gas is unavailable.
- Natural Gas Boilers – Clean, efficient combustion with precise steam control.
Choosing the right boiler—whether for rental or purchase—impacts productivity, efficiency, and sustainability. Consult manufacturers for sizing, compliance, and best practice guidance.
Chapter Four: Types of Rental Boilers
Industrial boiler rental agreements define responsibilities for both parties, including boiler management. Maintenance may be handled onsite or by the rental company, with close attention to specifications like horsepower, pressure, and fuel type. Manufacturers provide experts to guide selection and ensure proper boiler matches.
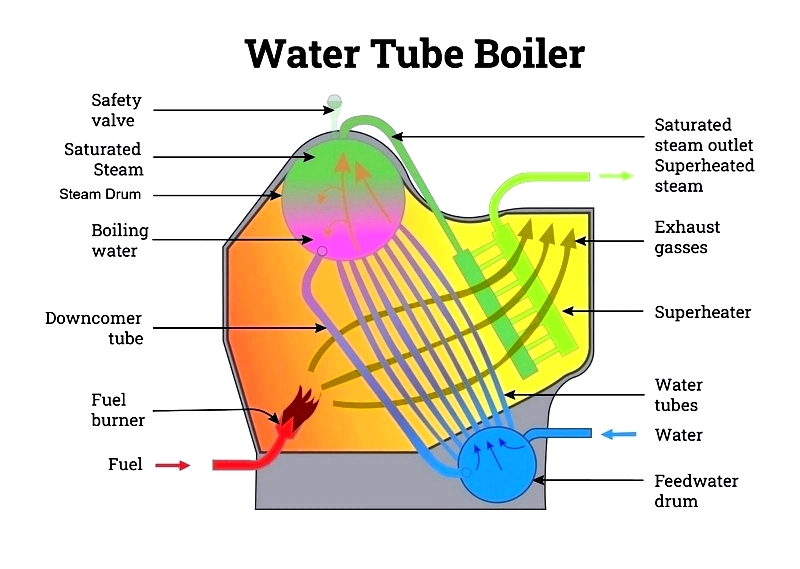
Watertube Boilers
Water circulates through tubes heated by surrounding gases, offering efficient, rapid steam production for large-scale needs.
Skid Mounted Boilers
Compact, movable units ideal for space-limited locations, requiring user-supplied water treatment systems.





